체인링크 CCIP로 카이아에서 크로스체인 NFT 구축하기: 실무 가이드
소개
대체 불가능한 토큰은 블록체인 기술의 가장 잘 알려진 사용 사례 중 하나가 되었으며, 고유하고 검증 가능한 디지털 자산을 생성할 수 있게 해줍니다. 그러나 기존의 NFT 구현은 단일 블록체인에 묶여 있습니다. 이러한 제한은 유연성을 떨어뜨리고 커뮤니티, 유동성, 유틸리티가 다를 수 있는 생태계에서 자산을 자유롭게 이동하지 못하게 합니다.
크로스체인 NFT는 NFT가 고유성과 출처를 유지하면서 블록체인 간에 원활하게 이동할 수 있게 함으로써 이러한 문제를 해결합니다. 개발자는 체인링크의 체인 간 상호운용성 프로토콜(CCIP)을 통해 표준화된 보안 메시징 프레임워크를 사용하여 체인 간에 신뢰할 수 있는 연결고리를 구축할 수 있습니다.
이 가이드에서는 번 앤 민트 모델을 사용해 크로스체인 NFT를 빌드하고 배포하는 방법을 설명합니다. NFT는 소스 체인에서 소각되고 동일한 토큰아이디와 메타데이터로 대상 체인에서 다시 발행되어, 주어진 시간에 유효한 사본이 하나만 존재하도록 보장합니다.
전제 조건
시작하기 전에 다음 설정이 완료되었는지 확인하세요:
- Node.js 및 npm
- 안전모
- 설치합니다:
npm 설치 --save-dev 하드햇 - 프로젝트 초기화:
npx hardhat --init
- 설치합니다:
- 메타마스크 지갑
- 개발 지갑을 만들거나 설정합니다.
- 카이아 카이로스 테스트넷과 이더리움 세폴리아 네트워크를 모두 메타마스크에 추가하세요.
- 수도꼭지에서 토큰 테스트
- 파일베이스 계정
- NFT 메타데이터(IPFS 스토리지)를 업로드하고 검색하는 데 필요합니다.
크로스 체인 NFT는 어떻게 작동하나요?
대체 불가능한 토큰은 단일 블록체인에 기록된 고유한 디지털 토큰입니다. 발행, 전송, 소유권 등 핵심 동작은 해당 체인에 �연결된 스마트 컨트랙트에 의해 정의됩니다. 이 때문에 NFT는 추가 메커니즘 없이는 자연스럽게 블록체인을 이동할 수 없습니다. 상호 운용성을 위해 개발자는 여러 체인에 컴패니언 컨트랙트를 배포하고 크로스체인 메시징을 통해 이를 연결합니다. 그 결과 크로스체인 NFT는 여러 블록체인에 존재하는 동등한 토큰이지만 주어진 시간에 하나의 사본만 활성화되는 토큰입니다.
크로스 체인 NFT는 일반적으로 다음 세 가지 방법 중 하나로 구현됩니다:
-
소각 및 민트: 소스 체인에서 NFT를 소각한 다음, 대상 체인에서 이에 상응하는 NFT를 발행합니다.
-
잠금 및 민트: NFT가 소스 체인에 잠기고 대상 체인에 복제본이 발행됩니다. 반환하려면 사본을 소각하여 원본의 잠금을 해제해야 합니다.
-
잠금 및 잠금 해제: 동일한 컬렉션이 여러 체인에 배포됩니다. 소유자는 한 체인에서 NFT를 잠그면 다른 체인에서 해당 NFT의 잠금을 해제하여 한 번에 하나의 사본만 사용할 수 있도록 합니다.
이 가이드에서는 크로스체인 NFT에 번 앤 민트 모델을 사용하겠습니다. NFT는 한 체인에서 제거되고 다른 체인에서 다시 생성되며, 전체 프로세스는 체인링크 CCIP에 의해 구동됩니다.
시작하기
이 가이드에서는 체인링크 CCIP를 사용하여 카이아 카이로스 테스트넷과 이더리움 세폴리아 간에 크로스체인 NFT를 발행하고 전송하는 방법을 설명합니다.
결국에는 할 수 있게 될 것입니다:
- 카이로스 테스트넷과 이더리움 세폴리아 모두에 대해 구성된 하드햇 프로젝트를 초기화합니다.
- 종속성으로 체인링크 CCIP 컨트랙트 및 인터페이스 추가하기
- 크로스 체인 전송을 위한 번 앤 민트 메커니즘으로 크로스 체인 NFT 컨트랙트를 구현합니다.
- 두 네트워크에 컨트랙트를 배포하고 체인 간에 NFT를 전송합니다.
하드햇 프로젝트 만들기
이 튜토리얼에서는 하드햇 3을 사용하여 컨트랙트를 배포하고 상호 작용합니다. Hardhat 3는 암호화된 키 저장소에 대한 기본 지원, Solidity에서 테스트 작성 기능, 향상된 프로젝트 툴링과 같은 새로운 기능을 제공합니다.
아래 단계에 따라 프로젝트를 설정하세요:
-
Node.js 및 npm 설치 확인
다음 명령을 실행하여 Node.js 및 npm이 설치되었는지 확인합니다:
node -vnpm -v
-
새 프로젝트 디렉터리 초기화
새 폴더를 만들고, 그 폴더로 이동하여 Node.js 프로젝트를 초기화합니다:
mkdir ccip-nft-kaia-hardhat-example cd ccip-nft-kaia-hardhat-example npm init -y
-
하드햇 프로젝트 만들기
실행:
npx hardhat --init
메시지가 표시되면 Node.js 테스트 러너와 에테르가 포함된 샘플 프로젝트를 선택합니다. 현재 디렉터리에서 초기화하고 필요한 모든 종속성을 설치합니다.
필수 계약 설치
체인링크 CCIP 컨트랙트를 설치합니다:
npm i @chainlink/contracts-ccip --save-dev
표준 체인링크 컨트랙트를 설치합니다:
npm i @chainlink/contracts --save-dev
오픈제플린 컨트랙트를 설치합니다(ERC-721 및 기타 기본 구현 제공):
npm i @openzeppelin/contracts --save-dev
NFT 메타데이터 구성
컨트랙트를 작성하기 전에 발행할 NFT의 사양을 정의해 보겠습니다. 각 NFT에는 이름, 설명, 이미지를 설명하는 메타데이터가 필요하며, 이는 JSON 파일에 저장되고 IPFS에서 호스팅됩니다.
이 가이드에서는 이미지와 메타데이터를 모두 저장하기 위해 Filebase를 사용하겠습니다. 나만의 NFT를 만들려면 Filebase를 통해 이미지와 메타데이터 JSON 파일을 IPFS에 업로드하세요. 업로드 후 파일 탭에서 파일 이름을 클릭하고 IPFS URL을 복사합니다. 이와 비슷하게 보일 것입니다:
https://disastrous-turquoise-parakeet.myfilebase.com/ipfs/QmY1LZF8JHo2r3h4X5VzLLXtJujqnBFGTyo2aqR9joXnt8
다음은 사용할 수 있는 샘플 메타데이터 파일입니다:
{ "name": "Kairos NFT", "description": "gkaia frens! gazuaaaaa!!!", "image": "https://disastrous-turquoise-parakeet.myfilebase.com/ipfs/QmRvQc4wZCp6NF7dFL4ywiWTG7FSH3KKGUAkXGgsdYfcKi"}
스마트 컨트랙트 작성
이 섹션에서는 체인링크 CCIP로 구동되는 번 앤 민트 모델을 사용하여 블록체인 간 NFT 전송을 가능하게 하는 콘트랙트를 구현합니다.
프로젝트의 컨트랙트 디렉토리에 'CrosschainNFT.sol'이라는 새 파일을 생성하고 다음 코드를 붙여넣습니다:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MITpragma solidity ^0.8.20;import {ERC721} from "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC721/ERC721.sol";import {ERC721URIStorage} from "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC721/extensions/ERC721URIStorage.sol";import {ERC721Burnable} from "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC721/extensions/ERC721Burnable.sol";import {IERC20} from "@openzeppelin/contracts/interfaces/IERC20.sol";import {SafeERC20} from "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/utils/SafeERC20.sol";import {ReentrancyGuard} from "@openzeppelin/contracts/utils/ReentrancyGuard.sol";import {Client} from "@chainlink/contracts-ccip/contracts/libraries/Client.sol";import {IRouterClient} from "@chainlink/contracts-ccip/contracts/interfaces/IRouterClient.sol";import {IAny2EVMMessageReceiver} from "@chainlink/contracts-ccip/contracts/interfaces/IAny2EVMMessageReceiver.sol";import {OwnerIsCreator} from "@chainlink/contracts/src/v0.8/shared/access/OwnerIsCreator.sol";import {LinkTokenInterface} from "@chainlink/contracts/src/v0.8/shared/interfaces/LinkTokenInterface.sol";/** * THIS IS AN EXAMPLE CONTRACT THAT USES HARDCODED VALUES FOR CLARITY. * THIS IS AN EXAMPLE CONTRACT THAT USES UN-AUDITED CODE. * DO NOT USE THIS CODE IN PRODUCTION. */ // Source chain is Ethereum Sepolia // Destination chain is Kairos Testnetcontract CrosschainNFT is ERC721, ERC721URIStorage, ERC721Burnable, IAny2EVMMessageReceiver, ReentrancyGuard, OwnerIsCreator { using SafeERC20 for IERC20; enum PayFeesIn { Native, LINK } error InvalidRouter(address router); error OnlyOnEthereumSepolia(); error NotEnoughBalanceForFees(uint256 currentBalance, uint256 calculatedFees); error NothingToWithdraw(); error FailedToWithdrawEth(address owner, address target, uint256 value); error ChainNotEnabled(uint64 chainSelector); error SenderNotEnabled(address sender); error OperationNotAllowedOnCurrentChain(uint64 chainSelector); struct crosschainNFTDetails { address crosschainNFTAddress; bytes ccipExtraArgsBytes; } uint256 constant ETHEREUM_SEPOLIA_CHAIN_ID = 11155111; string tokenNFTURI = "https://disastrous-turquoise-parakeet.myfilebase.com/ipfs/QmY1LZF8JHo2r3h4X5VzLLXtJujqnBFGTyo2aqR9joXnt8"; IRouterClient internal immutable i_ccipRouter; LinkTokenInterface internal immutable i_linkToken; uint64 private immutable i_currentChainSelector; uint256 private _nextTokenId; mapping(uint64 destChainSelector => crosschainNFTDetails crosschainNFTPerChain) public s_chains; event ChainEnabled(uint64 chainSelector, address xNftAddress, bytes ccipExtraArgs); event ChainDisabled(uint64 chainSelector); event CrossChainSent( address from, address to, uint256 tokenId, uint64 sourceChainSelector, uint64 destinationChainSelector ); event CrossChainReceived( address from, address to, uint256 tokenId, uint64 sourceChainSelector, uint64 destinationChainSelector ); modifier onlyRouter() { if (msg.sender != address(i_ccipRouter)) { revert InvalidRouter(msg.sender); } _; } modifier onlyOnEthereumSepolia() { if (block.chainid != ETHEREUM_SEPOLIA_CHAIN_ID) { revert OnlyOnEthereumSepolia(); } _; } modifier onlyEnabledChain(uint64 _chainSelector) { if (s_chains[_chainSelector].crosschainNFTAddress == address(0)) { revert ChainNotEnabled(_chainSelector); } _; } modifier onlyEnabledSender(uint64 _chainSelector, address _sender) { if (s_chains[_chainSelector].crosschainNFTAddress != _sender) { revert SenderNotEnabled(_sender); } _; } modifier onlyOtherChains(uint64 _chainSelector) { if (_chainSelector == i_currentChainSelector) { revert OperationNotAllowedOnCurrentChain(_chainSelector); } _; } constructor(address ccipRouterAddress, address linkTokenAddress, uint64 currentChainSelector) ERC721("Cross Chain NFT", "XNFT") { if (ccipRouterAddress == address(0)) revert InvalidRouter(address(0)); i_ccipRouter = IRouterClient(ccipRouterAddress); i_linkToken = LinkTokenInterface(linkTokenAddress); i_currentChainSelector = currentChainSelector; } function mint() external onlyOnEthereumSepolia { uint256 tokenId = _nextTokenId++; _safeMint(msg.sender, tokenId); _setTokenURI(tokenId, tokenNFTURI); } function enableChain(uint64 chainSelector, address crosschainNFTAddress, bytes memory ccipExtraArgs) external onlyOwner onlyOtherChains(chainSelector) { s_chains[chainSelector] = crosschainNFTDetails({crosschainNFTAddress: crosschainNFTAddress, ccipExtraArgsBytes: ccipExtraArgs}); emit ChainEnabled(chainSelector, crosschainNFTAddress, ccipExtraArgs); } function disableChain(uint64 chainSelector) external onlyOwner onlyOtherChains(chainSelector) { delete s_chains[chainSelector]; emit ChainDisabled(chainSelector); } function crossChainTransferFrom( address from, address to, uint256 tokenId, uint64 destinationChainSelector, PayFeesIn payFeesIn ) external nonReentrant onlyEnabledChain(destinationChainSelector) returns (bytes32 messageId) { string memory tokenUri = tokenURI(tokenId); _burn(tokenId); Client.EVM2AnyMessage memory message = Client.EVM2AnyMessage({ receiver: abi.encode(s_chains[destinationChainSelector].crosschainNFTAddress), data: abi.encode(from, to, tokenId, tokenUri), tokenAmounts: new Client.EVMTokenAmount[](0), extraArgs: s_chains[destinationChainSelector].ccipExtraArgsBytes, feeToken: payFeesIn == PayFeesIn.LINK ? address(i_linkToken) : address(0) }); // Get the fee required to send the CCIP message uint256 fees = i_ccipRouter.getFee(destinationChainSelector, message); if (payFeesIn == PayFeesIn.LINK) { if (fees > i_linkToken.balanceOf(address(this))) { revert NotEnoughBalanceForFees(i_linkToken.balanceOf(address(this)), fees); } // Approve the Router to transfer LINK tokens on contract's behalf. It will spend the fees in LINK i_linkToken.approve(address(i_ccipRouter), fees); // Send the message through the router and store the returned message ID messageId = i_ccipRouter.ccipSend(destinationChainSelector, message); } else { if (fees > address(this).balance) { revert NotEnoughBalanceForFees(address(this).balance, fees); } // Send the message through the router and store the returned message ID messageId = i_ccipRouter.ccipSend{value: fees}(destinationChainSelector, message); } emit CrossChainSent(from, to, tokenId, i_currentChainSelector, destinationChainSelector); } /// @inheritdoc IAny2EVMMessageReceiver function ccipReceive(Client.Any2EVMMessage calldata message) external virtual override onlyRouter nonReentrant onlyEnabledChain(message.sourceChainSelector) onlyEnabledSender(message.sourceChainSelector, abi.decode(message.sender, (address))) { uint64 sourceChainSelector = message.sourceChainSelector; (address from, address to, uint256 tokenId, string memory tokenUri) = abi.decode(message.data, (address, address, uint256, string)); _safeMint(to, tokenId); _setTokenURI(tokenId, tokenUri); emit CrossChainReceived(from, to, tokenId, sourceChainSelector, i_currentChainSelector); } function withdraw(address _beneficiary) public onlyOwner { uint256 amount = address(this).balance; if (amount == 0) revert NothingToWithdraw(); (bool sent,) = _beneficiary.call{value: amount}(""); if (!sent) revert FailedToWithdrawEth(msg.sender, _beneficiary, amount); } function withdrawToken(address _beneficiary, address _token) public onlyOwner { uint256 amount = IERC20(_token).balanceOf(address(this)); if (amount == 0) revert NothingToWithdraw(); IERC20(_token).safeTransfer(_beneficiary, amount); } function tokenURI(uint256 tokenId) public view override(ERC721, ERC721URIStorage) returns (string memory) { return super.tokenURI(tokenId); } function getCCIPRouter() public view returns (address) { return address(i_ccipRouter); } function supportsInterface(bytes4 interfaceId) public view override(ERC721, ERC721URIStorage) returns (bool) { return interfaceId == type(IAny2EVMMessageReceiver).interfaceId || super.supportsInterface(interfaceId); }}
코드 연습
크로스체인NFT는 블록체인 간에 NFT를 전송하기 위해 체인링크 CCIP를 통합하는 ERC-721 콘트랙트입니다. 소스 체인에서 NFT를 소각하고 동일한 토큰아이디와 토큰URI를 사용하여 대상에서 다시 채굴합니다. 이 콘트랙트는 enableChain을 통해 승인된 대상 체인 레지스트리를 유지하고, 크로스체인 메시징을 위해 체인링크 라우터(IRouterClient)에 의존하며, 네이티브 가스 토큰 또는 LINK로 수수료 지불을 지원합니다.
주요 기능
- enableChain
컨트랙트 소유자가 대상 블록체인을 등록할 수 있습니다. 대응하는 NFT 컨트랙트 주소와 CCIP 인수를 s_chains 매핑에 저장하여 해당 체인을 유효한 전송 대상으로 화이트리스트에 올립니다. 설정이 완료되면 체인 활성화 이벤트가 발생합니다.
- 교차 체인 전송
체인 간 NFT 전송을 실행합니다. 먼저 대상 체인이 활성화되어 있는지 확인한 다음 NFT 메타데이터(tokenURI)를 검색하고 소스 체인에서 토큰을 소각합니다. 그런 다음 송금 세부 정보가 포함된 CCIP 메시지를 작성하고 필요한 수수료를 계산한 후 LINK 또는 네이티브 가스로 결제합니다. 라우터를 통해 메시지가 전송되면 전송을 기록하기 위해 CrossChainSent 이벤트가 발생합니다.
이제 '크로스체인NFT.sol'의 핵심 흐름이 명확해졌으니, 다음 단계로 넘어가 보겠습니다.
스마트 컨트랙트 컴파일하기
스마트 컨트랙트를 컴파일하려면 실행하세요:
npx hardhat build
스마트 컨트랙트 배포
이 섹션에서는 필요한 변수를 설정한 다음 이더리움 세폴리아(소스 체인)와 카이로스 테스트넷(대상 체인) 모두에 CrosschainNFT.sol 컨트랙트를 배포하겠습니다.
암호화된 키 저장소 사용
Hardhat 3의 장점 중 하나는 일반 텍스트 파일 대신 암호화된 키 저장소에 개인 키 및 RPC URL과 같은 민감한 값을 저장할 수 있다는 점입니다. 이 가이드에서는 세폴리아 및 카이로스의 _PRIVATE_KEY_와 _RPC URL_을 암호화합니다.
개인 키 추가
npx hardhat keystore set PRIVATE_KEY
이 명령을 처음 실행하면 Hardhat에서 키 저장소에 대한 비밀번호를 만들라는 메시지가 표시됩니다. 값을 추가하거나 업데이트할 때마다 이 비밀번호가 필요합니다.
각 네트워크에 대한 RPC URL 추가
npx hardhat keystore set KAIROS_RPC_URLnpx hardhat keystore set SEPOLIA_RPC_URL
마지막으로 hardhat.config.ts 파일을 편집하여 이러한 암호화된 값을 로드하고 두 네트워크를 구성합니다.
import type { HardhatUserConfig } from "hardhat/config";import hardhatToolboxMochaEthersPlugin from "@nomicfoundation/hardhat-toolbox-mocha-ethers";import { configVariable } from "hardhat/config";const config: HardhatUserConfig = { plugins: [hardhatToolboxMochaEthersPlugin], solidity: { profiles: { default: { version: "0.8.28", }, production: { version: "0.8.28", settings: { optimizer: { enabled: true, runs: 200, }, }, }, }, }, networks: { hardhatMainnet: { type: "edr-simulated", chainType: "l1", }, hardhatOp: { type: "edr-simulated", chainType: "op", }, kairosTestnet: { type: "http", chainType: "l1", url: configVariable("KAIROS_RPC_URL"), accounts: [configVariable("PRIVATE_KEY")], }, ethereumSepolia: { type: "http", chainType: "l1", url: configVariable("SEPOLIA_RPC_URL"), accounts: [configVariable("PRIVATE_KEY")], }, },};export default config;
다음 단계는 이더리움 세폴리아 및 카이로스 테스트넷에 각각 크로스체인NFT 스마트 컨트랙트를 배포하는 것입니다.
이더리움 세폴리아에 크로스체인NFT.sol 배포하기
배포하기 전에 체인링크 CCIP 디렉토리에서 이더리움 세폴리아에 대한 다음 값을 가져옵니다:
- 체인 선택기
- CCIP 라우터 주소
- 링크 토큰 주소
이러한 값은 배포 스크립트에 필요합니다. 다음으로, 프로젝트의 ignition/modules 폴더로 이동하여 'deployEthereumSepolia.ts'라는 새 파일을 생성하고 다음 코드를 붙여넣습니다:
// This setup uses Hardhat Ignition to manage smart contract deployments.// Learn more about it at https://hardhat.org/ignitionimport { buildModule } from "@nomicfoundation/hardhat-ignition/modules";const ETHEREUM_SEPOLIA_ROUTER_ADDRESS = `0x0BF3dE8c5D3e8A2B34D2BEeB17ABfCeBaf363A59`;const ETHEREUM_SEPOLIA_LINK_TOKEN_ADDRESS = `0x779877A7B0D9E8603169DdbD7836e478b4624789`;const ETHEREUM_SEPOLIA_CHAIN_SELECTOR = `16015286601757825753`;const CrosschainNFTSepoliaModule = buildModule("CrosschainNFTSepoliaModule", (m) => { const crosschainNFTSepolia = m.contract("CrosschainNFT", [ETHEREUM_SEPOLIA_ROUTER_ADDRESS, ETHEREUM_SEPOLIA_LINK_TOKEN_ADDRESS, ETHEREUM_SEPOLIA_CHAIN_SELECTOR], { }); return { crosschainNFTSepolia };});export default CrosschainNFTSepoliaModule;
배포 스크립트를 실행합니다:
npx hardhat ignition deploy ignition/modules/deployEthereumSepolia.ts --network ethereumSepolia
카이로스 테스트넷에 크로스체인NFT.sol 배포하기
배포하기 전에 체인링크 CCIP 디렉토리에서 카이로스 테스트넷의 다음 값을 가져옵니다:
- 체인 선택기
- CCIP 라우터 주소
- 링크 토큰 주소
이러한 값은 배포 스크립트에 필요합니다. 그런 다음 프로젝트의 ignition/modules 폴더로 이동하여 '배포카이로스테스트넷.ts'라는 새 파일을 생성하고 다음 코드를 붙여넣습니다:
// This setup uses Hardhat Ignition to manage smart contract deployments.// Learn more about it at https://hardhat.org/ignitionimport { buildModule } from "@nomicfoundation/hardhat-ignition/modules";const KAIROS_TESTNET_ROUTER_ADDRESS = `0x41477416677843fCE577748D2e762B6638492755`;const KAIROS_TESTNET_LINK_TOKEN_ADDRESS = `0xAF3243f975afe2269Da8Ffa835CA3A8F8B6A5A36`;const KAIROS_TESTNET_CHAIN_SELECTOR = `2624132734533621656`;const CrosschainNFTKairosModule = buildModule("CrosschainNFTKairosModule", (m) => { const crosschainNFTKairos = m.contract("CrosschainNFT", [KAIROS_TESTNET_ROUTER_ADDRESS, KAIROS_TESTNET_LINK_TOKEN_ADDRESS, KAIROS_TESTNET_CHAIN_SELECTOR], { }); return { crosschainNFTKairos };});export default CrosschainNFTKairosModule;
배포 스크립트를 실행합니다:
npx hardhat ignition deploy ignition/modules/deployKairosTestnet.ts --network kairosTestnet
스마트 컨트랙트와 상호작용하기
이 섹션에서는 배포된 크로스체인NFT 스마트 컨트랙트와 상호작용하기 위해 각각 enableChain, mint, crosschainTransfer 함수를 실행해 보겠습니다.
1단계: 이더리움 세폴리아에서 enableChain을 호출합니다.
enableChain을 호출하기 전에 다음 값을 준비합니다:
- 세폴리아 컨트랙트 주소: 이더리움 세폴리아에 배포된 크로스체인NFT.sol 컨트랙트의 주소입니다.
- 카이로스 컨트랙트 주소: 카이로스 테스트넷에 배포된 크로스체인NFT.sol 컨트랙트의 주소입니다.
- 체인 선택기: 2624132734533621656 (카이로스 테스트넷의 CCIP 체인 선택기).
- CCIP extraArgs: 0x97a657c9000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007A120(가스 제한이 500,000으로 설정된 extraArgs의 기본 인코딩 값입니다).
그런 다음 스크립트 폴더에 새 타입스크립트 파일을 생성하고 이름을 'enableChainSepolia.ts'로 지정한 다음 다음 코드를 붙여넣습니다:
// scripts/enableChainSepolia.tsimport { network } from "hardhat";async function main() { const connection = await network.connect({ network: "ethereumSepolia" }); const { ethers } = connection; const [signer] = await ethers.getSigners(); console.log(`Using account: ${signer.address}`); // Get the contract factory by name const CrosschainNFT = await ethers.getContractFactory("CrosschainNFT", signer); // Contract addresses and parameters const crosschainNFTAddressEthereumSepolia = `0xb1fe42BBd7842703820C7480c22409b872319B22`; const crosschainNFTAddressKairosTestnet = `0x8c464Bb9Bf364F68b898ed0708b8f5F66EF6Cfb1`; const chainSelectorKairosTestnet = `2624132734533621656`; const ccipExtraArgs = `0x97a657c9000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007A120`; // Attach to the deployed contract const crosschainNFTSepolia = CrosschainNFT.attach(crosschainNFTAddressEthereumSepolia); console.log(`Enabling chain for Kairos Testnet...`); const tx = await crosschainNFTSepolia.enableChain( chainSelectorKairosTestnet, crosschainNFTAddressKairosTestnet, ccipExtraArgs ); console.log(`Transaction hash: ${tx.hash}`); console.log(`Waiting for confirmation...`); const receipt = await tx.wait(); console.log(`Transaction confirmed in block: ${receipt?.blockNumber}`); console.log(`Chain enabled successfully!`);}main().catch((error) => { console.error(error); process.exitCode = 1;});
다음 명령을 실행하여 함수를 호출합니다:
npx hardhat run scripts/enableChainSepolia.ts --network ethereumSepolia
2단계: 카이로스 테스트넷에서 enableChain을 호출합니다.
enableChain을 호출하기 전에 다음 값을 준비합니다:
- 카이로스 컨트랙트 주소: 카이로스 테스트넷에 배포된 크로스체인NFT.sol 컨트랙트의 주소입니다.
- 세폴리아 컨트랙트 주소: 이더리움 세폴리아에 배포된 크로스체인NFT.sol 컨트랙트의 주소입니다.
- 체인 선택기: 16015286601757825753 (카이로스 테스트넷의 CCIP 체인 선택기)
- CCIP extraArgs: 0x97a657c9000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007A120(가스 제한이 500,000으로 설정된 extraArgs의 기본 인코딩 값입니다.)
그런 다음 스크립트 폴더에 새 TypeScript 파일을 만들고 이름을 enableChainKairos.ts로 지정한 다음 다음 코드를 붙여넣습니다:
// scripts/enableChainKairos.tsimport { network } from "hardhat";async function main() { const connection = await network.connect({ network: "kairosTestnet" }); const { ethers } = connection; const [signer] = await ethers.getSigners(); console.log(`Using account: ${signer.address}`); // Get the contract factory by name const CrosschainNFT = await ethers.getContractFactory("CrosschainNFT", signer); // Contract addresses and parameters const crosschainNFTAddressKairosTestnet = `0x8c464Bb9Bf364F68b898ed0708b8f5F66EF6Cfb1`; const crosschainNFTAddressEthereumSepolia = `0xb1fe42BBd7842703820C7480c22409b872319B22`; const chainSelectorEthereumSepolia = `16015286601757825753`; const ccipExtraArgs = `0x97a657c9000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007A120`; // Attach to the deployed contract on Kairos const crosschainNFTKairos = CrosschainNFT.attach(crosschainNFTAddressKairosTestnet); console.log(`Enabling chain for Ethereum Sepolia...`); const tx = await crosschainNFTKairos.enableChain( chainSelectorEthereumSepolia, crosschainNFTAddressEthereumSepolia, ccipExtraArgs ); console.log(`Transaction hash: ${tx.hash}`); console.log(`Waiting for confirmation...`); const receipt = await tx.wait(); console.log(`Transaction confirmed in block: ${receipt?.blockNumber}`); console.log(`Chain enabled successfully!`);}main().catch((error) => { console.error(error); process.exitCode = 1;});
다음 명령을 실행하여 함수를 호출합니다:
npx hardhat run scripts/enableChainKairos.ts --network KairosTestnet
3단계: 이더리움 세폴리아에서 LINK로 계약 자금 조달하기
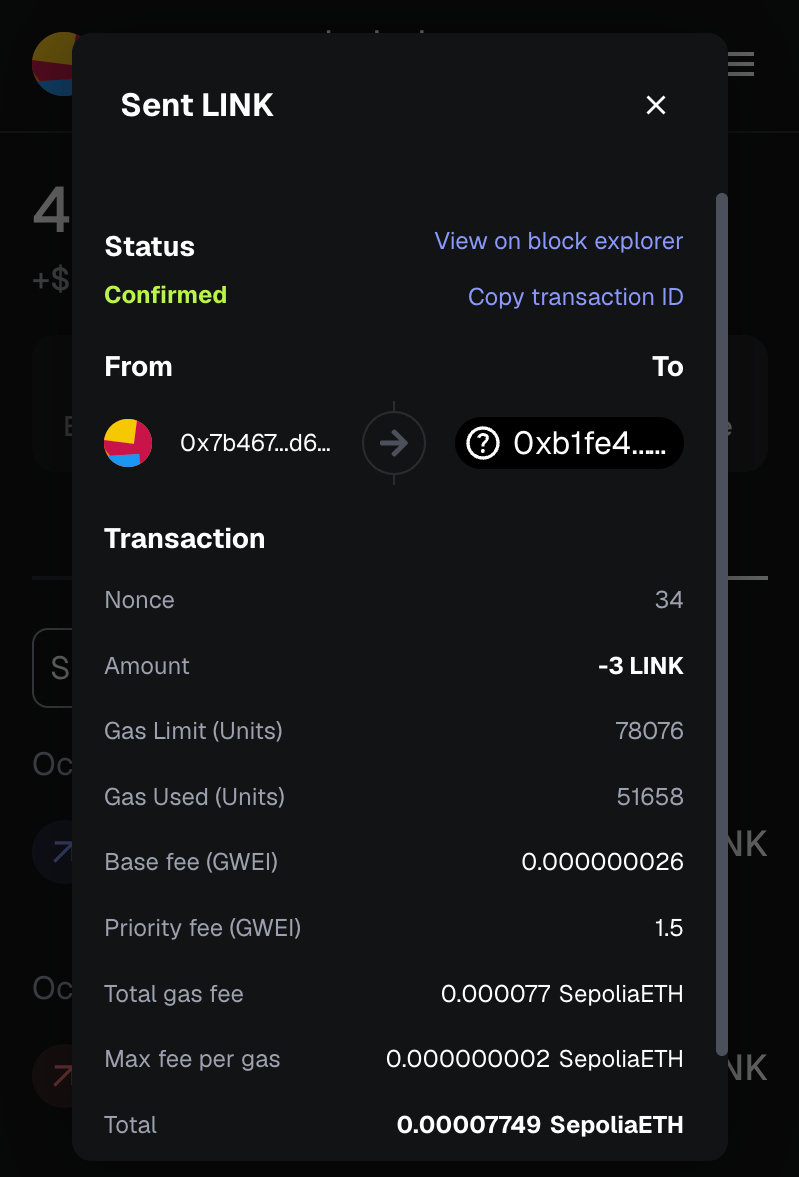
CCIP 수수료를 충당하려면 이더리움 세폴리아에 배포된 크로스체인NFT 컨트랙트(crosschainNFTAddressEthereumSepolia)에 LINK로 자금을 조달하세요. 제공된 수도꼭지에서 테스트 링크를 받을 수 있습니다. 이 가이드에서는 LINK 3개를 보내면 충분합니다.
4단계: 이더리움 세폴리아에서 새로운 크로스체인NFT를 발행하기
다음으로, 이더리움 세폴리아에 배포된 크로스체인NFT 콘트랙트에서 새로운 NFT를 발행합니다.
스크립트 폴더에 새 TypeScript 파일을 만들고 이름을 mint.ts로 지정한 ��다음 다음 코드를 붙여넣습니다:
// scripts/mint.tsimport { network } from "hardhat";async function main() { // Connect to the network const connection = await network.connect({ network: "ethereumSepolia" });if (connection.networkName !== "ethereumSepolia") { console.error(`Must be called from Ethereum Sepolia`); process.exitCode = 1; return; } const { ethers } = connection; const [signer] = await ethers.getSigners(); console.log(`Using account: ${signer.address}`); // Get the contract factory const CrosschainNFT = await ethers.getContractFactory("CrosschainNFT", signer); const crosschainNFTAddressEthereumSepolia = `0xb1fe42BBd7842703820C7480c22409b872319B22` // Attach to the deployed contract const crosschainNFT = CrosschainNFT.attach(crosschainNFTAddressEthereumSepolia); console.log(`Minting NFT...`); const tx = await crosschainNFT.mint(); console.log(`Transaction hash: ${tx.hash}`); console.log(`Waiting for confirmation...`); const receipt = await tx.wait(); console.log(`Transaction confirmed in block: ${receipt?.blockNumber}`); console.log(`NFT minted successfully!`);}main().catch((error) => { console.error(error); process.exitCode = 1;});
이 스크립트는 채굴 과정을 처리하고 교차 체인 전송을 위해 NFT를 준비합니다.
다음 명령을 실행하여 함수를 호출합니다:
npx hardhat run scripts/mint.ts --network ethereumSepolia
5단계: 체인 간 NFT 전송하기
이더리움 세폴리아에서는 크로스체인 트랜스퍼 프롬 함수를 호출하여 NFT를 카이로스 테스트넷으로 전송합니다.
다음 값을 입력합니다:
- 보낸 사람: 이더리움 세폴리아의 EOA 주소
- 받는 사람: 카이로스 테스트넷에서 수신자의 EOA 주소(본인의 주소일 수도 있음)
- 토큰아이디: 전송하려는 NFT의 ID입니다.
- 대상체인선택자: 2624132734533621656 (카이로스 테스트넷의 CCIP 체인 선택기)
- payFeesIn: 1 (CCIP 수수료가 LINK로 결제됨을 나타냄)
전송 스크립트 실행
스크립트 폴더에 새 타입스크립트 파일을 만들고 이름을 crossChainTransferNFT.ts로 지정한 다음 다음 코드를 붙여넣습니다:
// scripts/crossChainTransferNFT.tsimport { network } from "hardhat";async function main() { // Connect to the network const connection = await network.connect({ network: "ethereumSepolia" }); // Check if we're on the correct network if (connection.networkName !== "ethereumSepolia") { console.error(`Must be called from Ethereum Sepolia`); process.exitCode = 1; return; } const { ethers } = connection; const [signer] = await ethers.getSigners(); console.log(`Using account: ${signer.address}`); // Get the contract factory const CrosschainNFT = await ethers.getContractFactory("CrosschainNFT", signer); const crosschainNFTAddressEthereumSepolia = `0xb1fe42BBd7842703820C7480c22409b872319B22`; // Transfer parameters const from = `0x7b467A6962bE0ac80784F131049A25CDE27d62Fb`; const to = `0x7b467A6962bE0ac80784F131049A25CDE27d62Fb`; const tokenId = 0; // Put NFT token id here const destinationChainSelector = "2624132734533621656"; // Kairos Testnet const payFeesIn = 1; // 0 - Native, 1 - LINK // Attach to the deployed contract const crosschainNFT = CrosschainNFT.attach(crosschainNFTAddressEthereumSepolia); const tx = await crosschainNFT.crossChainTransferFrom( from, to, tokenId, destinationChainSelector, payFeesIn ); console.log(`Transaction hash: ${tx.hash}`); console.log(`Waiting for confirmation...`); const receipt = await tx.wait(); console.log(`Transaction confirmed in block: ${receipt?.blockNumber}`); console.log(`Cross-chain transfer initiated successfully!`); console.log(`Note: The NFT will arrive on Kairos Testnet after CCIP processes the message.`);}main().catch((error) => { console.error(error); process.exitCode = 1;});
그런 다음 스크립트를 실행합니다:
npx hardhat run scripts/crossChainTransferNFT.ts --network ethereumSepolia
전송 확인
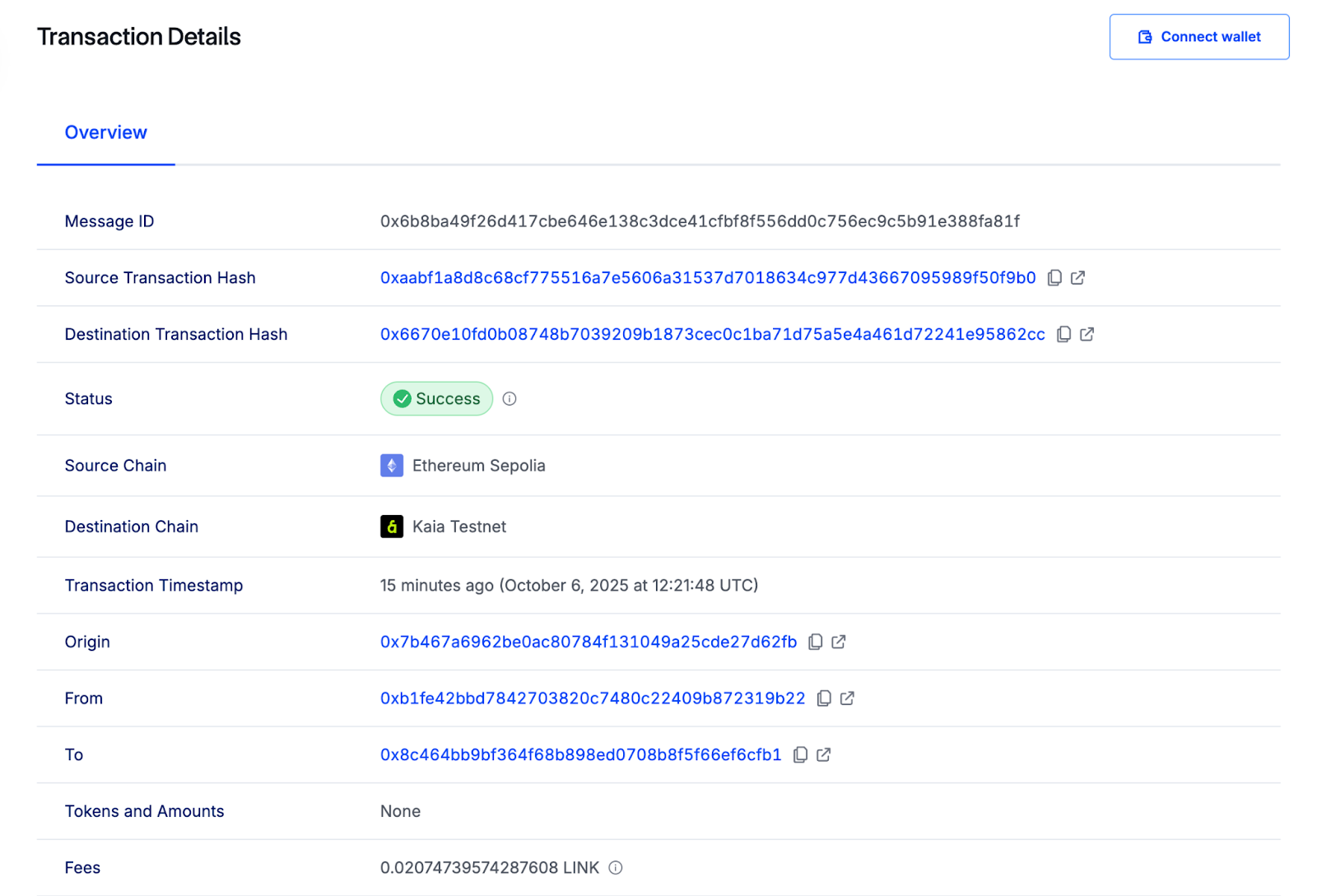
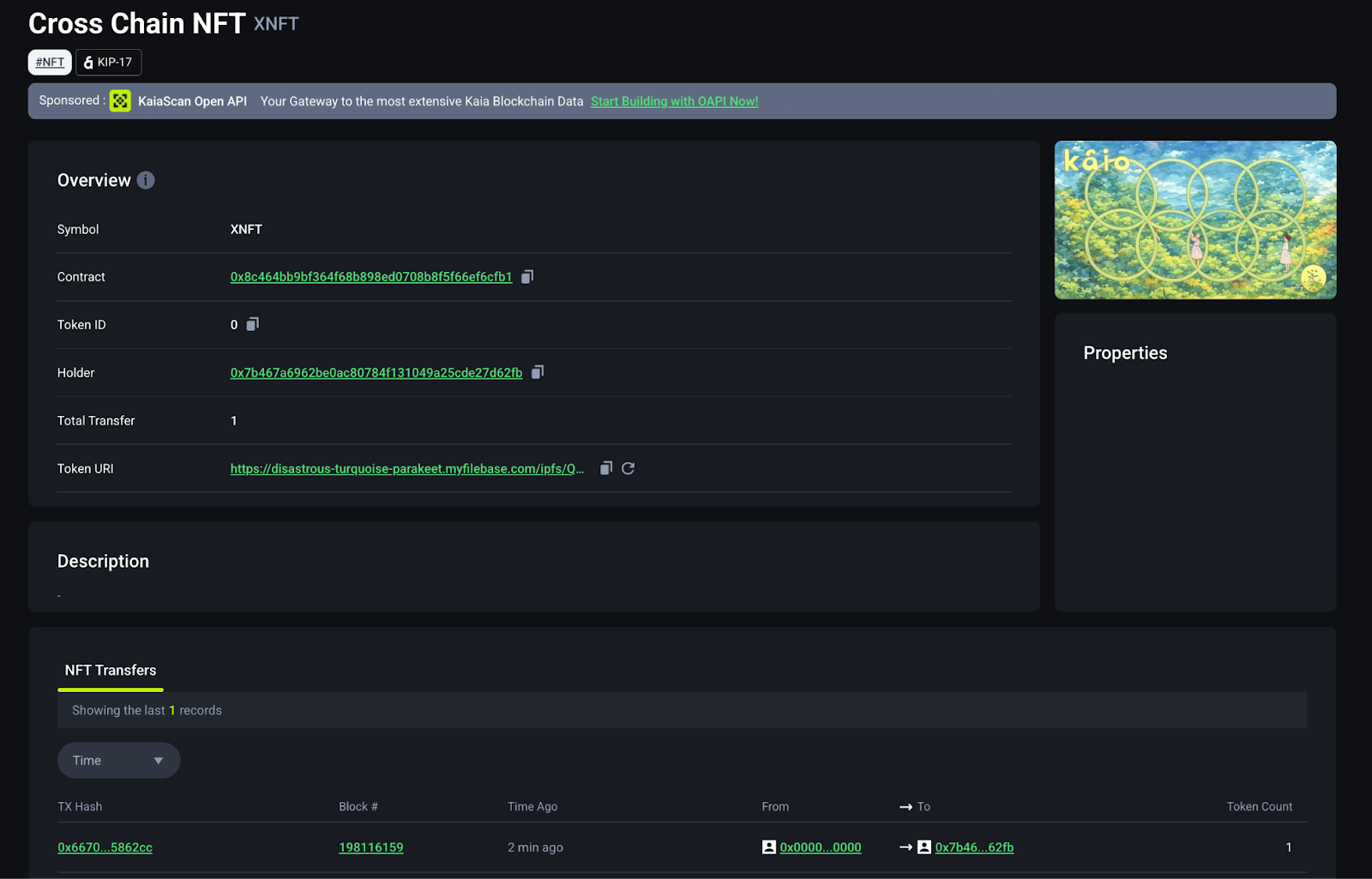
CCIP Explorer](https://ccip.chain.link/#/side-drawer/msg/0x2a43cf8076ed6290dd0bf8bdbbc87abe2d238da43b6bf514e70909dd0f35c9db)에서 크로스체인 전송을 모니터링하고, Kaiascan에서 트랜잭션을 확인할 수 있습니다.
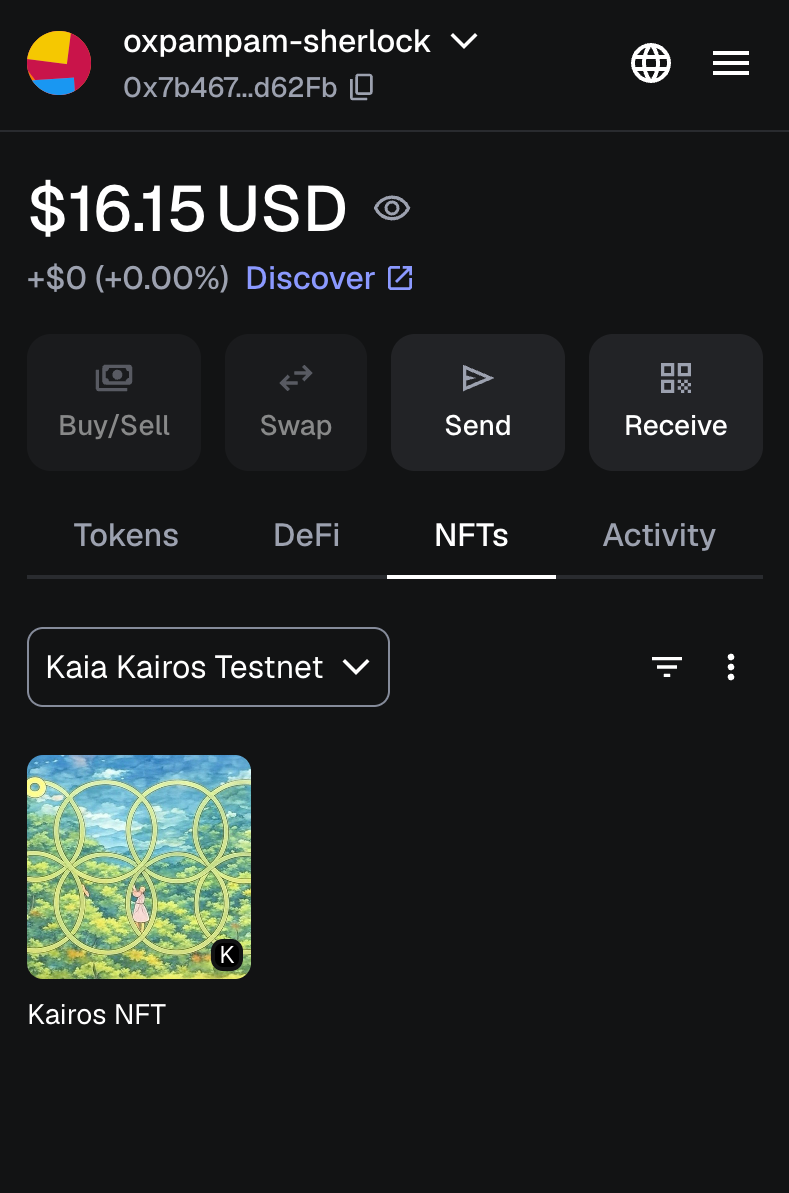
NFT가 카이로스 테스트넷에 도착하면 메타마스크 지갑에 추가합니다:
- 메타마스크에서 NFT 탭을 엽니다.
- NFT 가져오기를 클릭합니다.
- 카이로스 테스트넷의 크로스체인NFT 컨트랙트 주소와 받은 토큰아이디를 입력합니다(예: 0).
이제 NFT가 메타마스크 지갑에 표시됩니다.
결론
이 튜토리얼에서는 체인링크 CCIP를 사용해 번 앤 민트 모델을 사용해 카이아 카이로스 테스트넷과 이더리움 세폴리아 간에 NFT를 전송하는 방법을 배웠습니다.
CCIP에 대해 자세히 알아보고 추가 사용 사례를 살펴보려면 공식 체인링크 CCIP 문서를 참조하시기 바랍니다.