擴展解決方案
Kaia offers robust scaling solutions to ensure high throughput and responsiveness even under heavy network load. These solutions include Service Chains and a novel Multi-Channel communication architecture
服務鏈
Kaia 中的服務鏈是獨立於 Kaia 主鏈的輔助區塊鏈, ,為需要特殊節點配置、定製安全級別、 或超高吞吐量的單個 dApp 量身定製,這使得在主鏈上部署 dApp 變得不方便或經濟上不可行。
雖然有完全去中心化的擴展解決方案,但由於其難以接近的界面(如挑戰或退出)和非即時終結性, ,我們在 Kaia 的服務鏈中採取了不同的方法,犧牲了完全去中心化以獲得更好的可用性、 即時終結性、高性能和高可用性。
Kaia 服務鏈可用於實現各種特定服務目標, ,並可因多種原因連接到主鏈,包括數據錨定(定期將區塊哈希值 從服務鏈存儲到主鏈,以彌補因節點數量較少而降低的服務鏈安全性)或 價值轉移(KAIA(Kaia 的原生價��值單位)和 dApp 發行的代幣 的鏈間轉移)。
網絡
與 Kaia 主鏈相連的服務鏈統稱為服務鏈網絡。 請注意,在 Kaia 未來的迭代中,服務鏈和主鏈之間的連接方法可能會發生變化。
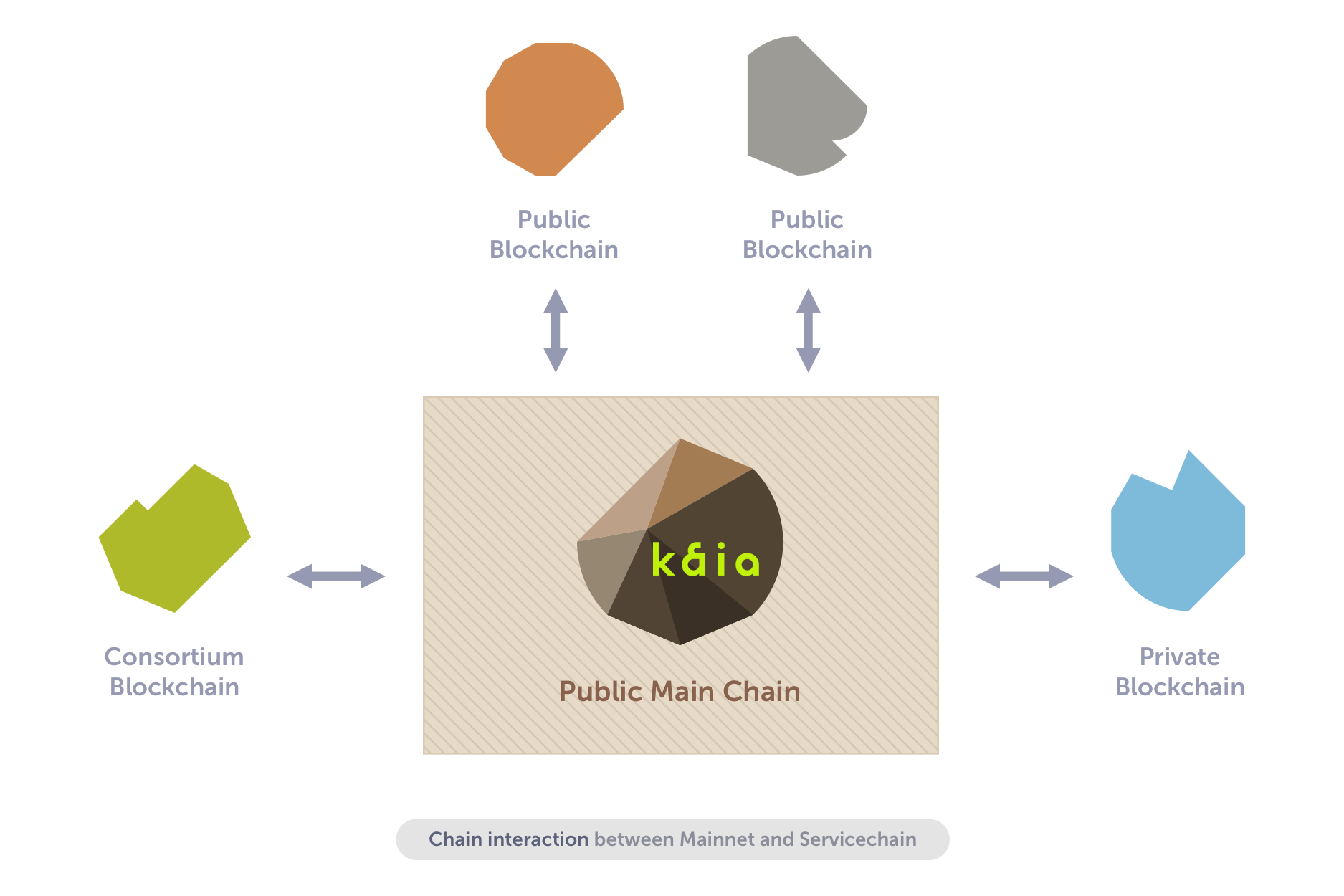
圖 1 顯示了用於滿足各種業務需求的服務鏈的網絡拓撲結構,這些服務鏈與 Kaia 主鏈連接 ,以擴展 Kaia 網絡。
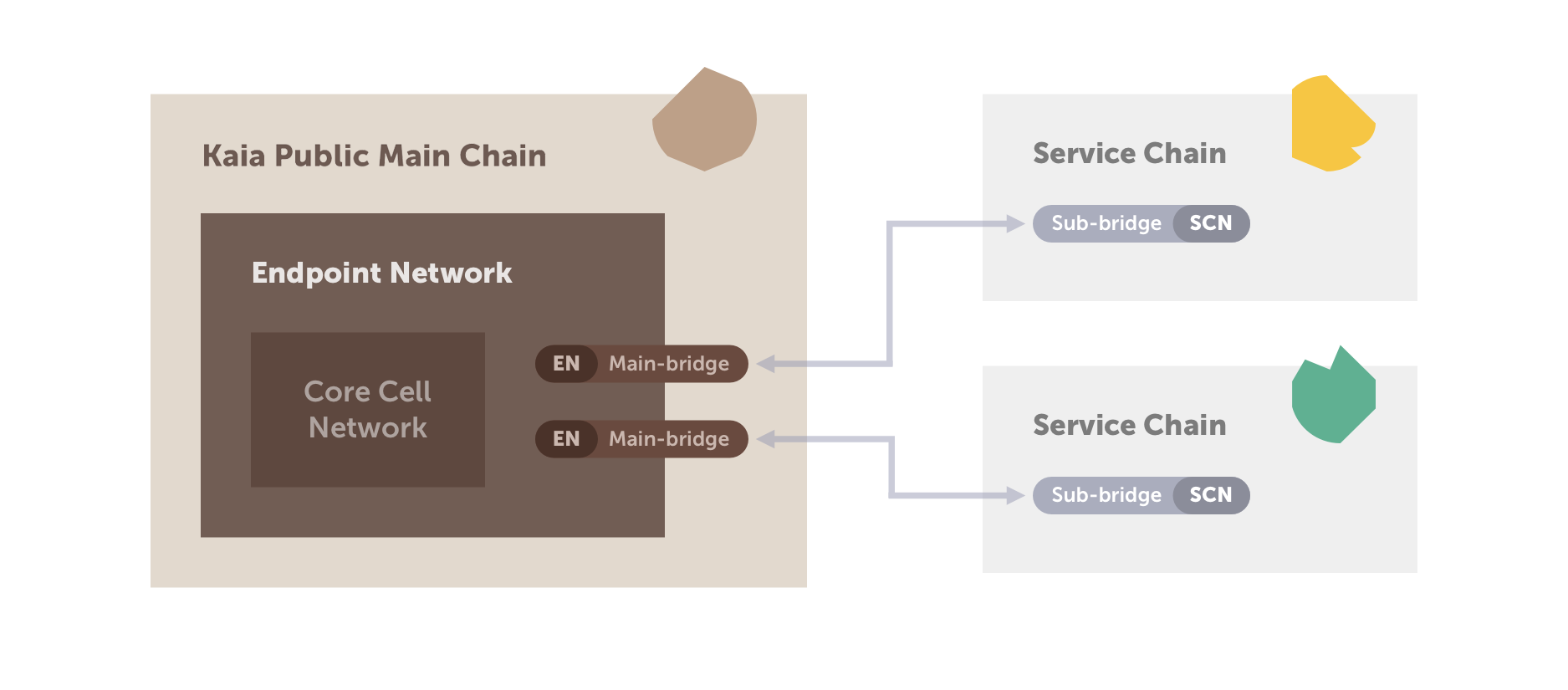
圖 2 顯示了 SCN(服務鏈共識節點)與 Kaia 主鏈的 EN(端點節點)直接連接的示例 ,該示例在使用服務鏈功能時採用了主/分橋模式。
特點
服務鏈通過提供數據完整性機制和支持不同鏈之間的令牌傳輸,對 Kaia 進行了擴展和增強。
數據錨定
為了保證數據的完整性,服務鏈可以自動將每個服務鏈塊的哈希值作為特殊事務錨定到主鏈上。 這種數據錨定可以向服務用戶確保,服務鏈中的數據一旦創建就不能更改。
價值轉移
為了幫助服務提供商(SP)在不同鏈之間輕鬆遷移服務用戶和價值,可以啟用 在不同鏈之間傳輸代幣,如 KAIA(Kaia 的原生價值單位)和 dApp 發行的 Kaia 代幣。 用戶可以通過向一個特殊合約(稱為橋合約)發送交易,輕鬆申請將代幣轉移到其他鏈上。
Multi-Channel Communication
Kaia employs a multi-channel communication architecture to enhance network performance and resilience, particularly during periods of high transaction volume. By separating different message types onto dedicated communication channels, Kaia can maintain efficient block propagation and consensus even under heavy network congestion.
Architecture
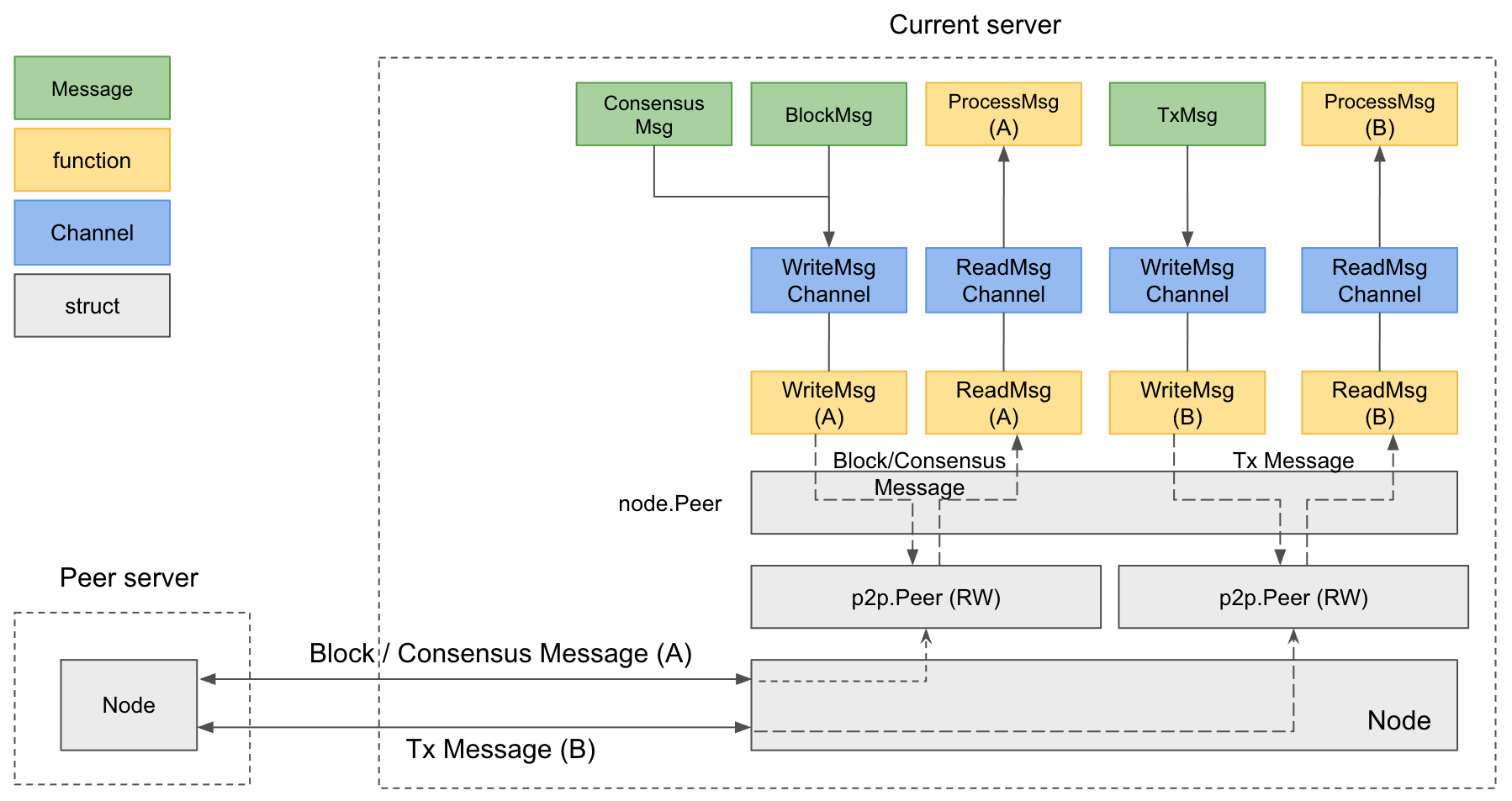
Multi-Channel Connection
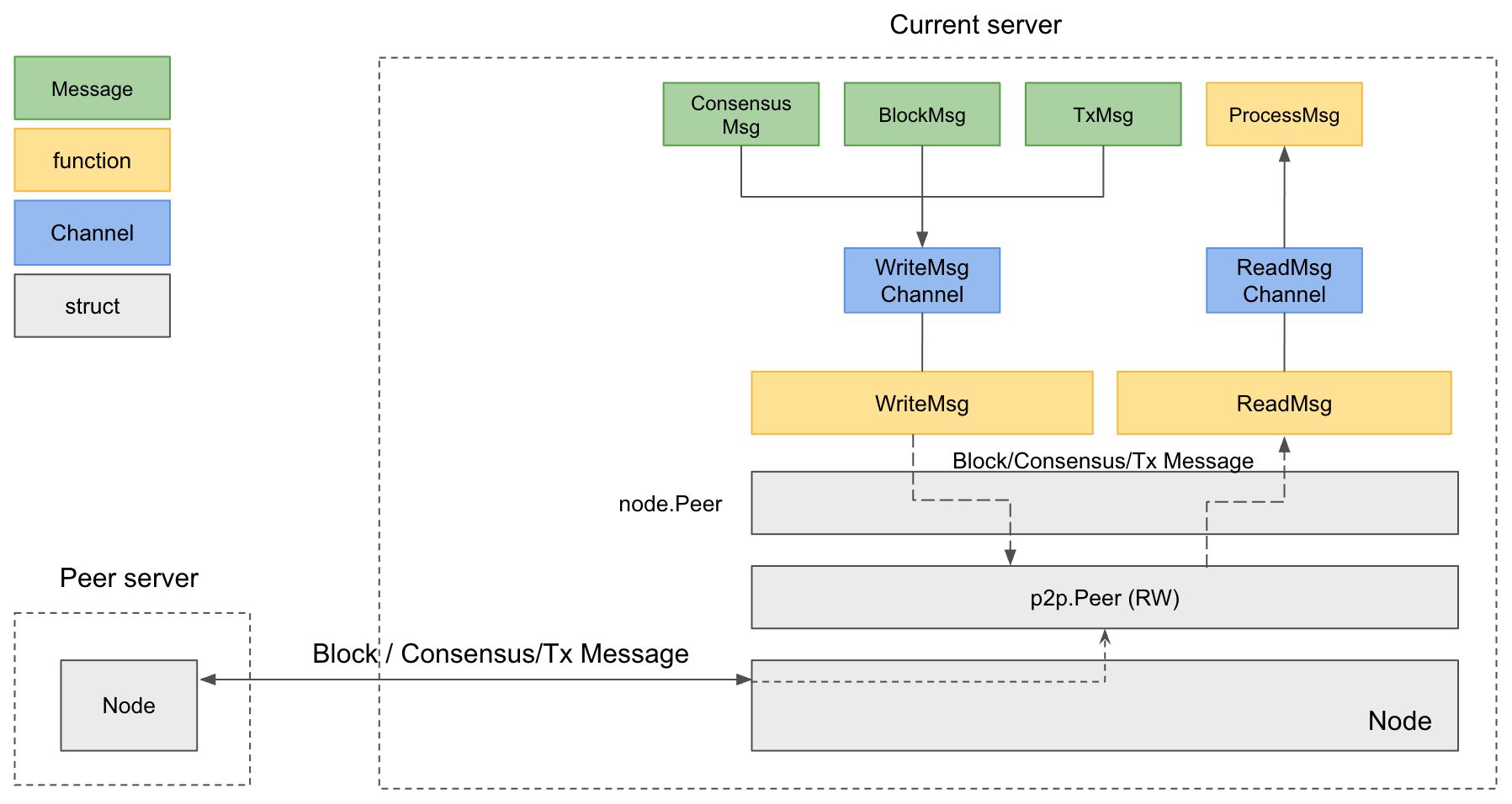
Single-Channel Connection
Configuration Modes
- Multi-Channel: Uses two ports. Enabled by default in
kenddue toMULTICHANNEL=1inkend.conf. Disable by settingMULTICHANNEL=0. Customize ports using--portand--subportflags. - Single-Channel: Uses one port (default 32323). Active when
MULTICHANNELis not set or set to0.
How Multi-Channel Works
Multi-channel separates different message types onto dedicated ports:
- Main Port: Handles block-related messages (requests/responses for hash, header, body, receipt) and consensus messages (Request, Preprepare, Prepare, Commit, RoundChange). The meaning of the messages can be found in PBFT.
- Subport: Handles transaction messages.
This separation enhances network stability: if one port fails, the other continues operating. For example, if the subport (typically congested during high traffic) fails, the main port maintains essential block and consensus operations.
Connection Establishment
- Multi-Channel to Multi-Channel: Both ports are used.
- Other Cases (Multi-Channel to Single-Channel or Single-Channel to Single-Channel): A single port is used.
If a node attempts to connect without specifying a subport, it initially connects using a single port. During the handshake, if the peer is multi-channel, the connection is re-established using both ports.
Port Configuration (KNI)
See the KNI scheme for details. Default ports are 32323 (main) and 32324 (sub).
Integration with KNI
Multi-channel integrates with KNI for node discovery and connection. KNI URLs allow specifying both main and subports.
Implementation Note
Kaia's multi-channel implementation deviates slightly from the original specification. While the details of this deviation are beyond the scope of this document, the core principles of enhanced network communication and robustness remain central to Kaia's operation. This information is primarily relevant for node operators and developers.
In summary, multi-channel enhances Kaia's network by segregating message traffic, improving efficiency and resilience. While providing advanced configuration options for node operators, the system remains transparent to general users.