链锁 CCIP

导言
Chainlink Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) 为开发者和去中心化应用程序(dApps)提供了一种安全、高效的跨区块链交互方式。 利用 CCIP,您可以发送代币和任意消息,以触发目标合约上的操作,如铸造 NFT、重新平衡指数或调用自定义函数。
在本教程中,您将学习如何使用 Chainlink CCIP 从 Kaia 智能合约向另一条链上的合约发送信息和代币,以及如何接收这些信息和代币。
先决条件
- 代工厂安装
- 使用
curl -L https://foundry.paradigm.xyz | bash安装,然后运行foundryup。 - 使用
forge --version,cast --version和anvil --version进行验证。
- 使用
- MetaMask 钱包
- 设置开发钱包
- 在 MetaMask 中添加 Kaia Kairos 测试网络和以太坊 Sepolia 网络。
- 从水龙头测试代币
- KAIA:用于从 Kaia 部署和发送的气体。
- LINK (testnet):用 LINK 支付 CCIP 费用。
- 目标链上的本地代币(例如,Sepolia ETH:用于部署,如果选择,用于支付本地 CCIP 费用)。
入门
在本指南中,您将使用 Chainlink CCIP 在 Kaia(Kairos Testnet)和以太坊 Sepolia 之间收发跨链消息。
到最后,你会
- 初始化为 Kairos 和 Sepolia 配置的 Foundry 项目
- 将 Chainlink CCIP 合同和接口添加为依赖项
- 执行信使合约,跨链收发信息
- 部署到两个网络并验证往返信息
创建项目
在本节中,您将使用 Foundry 设置开发环境。 要创建一个新的 Foundry 项目,首先要创建一个新目录:
mkdir kaia-foundry-ccip-example
那就跑吧
cd kaia-foundry-ccip-exampleforge init
这将创建一个具有以下基本布局的 Foundry 项目:
├── foundry.toml├── script├── src└── test
安装 Chainlink 智能合约
要在 Foundry 项目中使用 Chainlink CCIP,需要使用 forge install 将 Chainlink CCIP 智能合约安装为项目依赖项。
要安装 Chainlink CCIP 智能合约,请运行
forge install smartcontractkit/chainlink-ccip@2114b90f39c82c052e05af7c33d42c1ae98f4180forge install smartcontractkit/chainlink-evm@ff814eb0a01f89d9a215f825d243bf421e6434a9
安装完成后,创建一个 remapping.txt 文件:
forge remappings > remappings.txt
然后将以下内容粘贴到新创建的文件中:
@chainlink/contracts/=lib/chainlink-evm/contracts/@chainlink/contracts-ccip/=lib/chainlink-ccip/chains/evm/contracts/
编写智能合约
在本节中,您将使用下面的代码跨链发送和接收信息。
在项目的 src 目录下创建一个名为 Messenger.sol 的新文件,并将下面的代码复制到该文件中:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MITpragma solidity ^0.8.0;import { IRouterClient } from "@chainlink/contracts-ccip/interfaces/IRouterClient.sol";import {OwnerIsCreator} from "@chainlink/contracts/src/v0.8/shared/access/OwnerIsCreator.sol";import { Client } from "@chainlink/contracts-ccip/libraries/Client.sol";import { CCIPReceiver } from "@chainlink/contracts-ccip/applications/CCIPReceiver.sol";import {IERC20} from "@chainlink/contracts/src/v0.8/vendor/openzeppelin-solidity/v4.8.3/contracts/token/ERC20/IERC20.sol";import {SafeERC20} from "@chainlink/contracts/src/v0.8/vendor/openzeppelin-solidity/v4.8.3/contracts/token/ERC20/utils/SafeERC20.sol";/** * THIS IS AN EXAMPLE CONTRACT THAT USES HARDCODED VALUES FOR CLARITY. * THIS IS AN EXAMPLE CONTRACT THAT USES UN-AUDITED CODE. * DO NOT USE THIS CODE IN PRODUCTION. *//// @title - A simple messenger contract for sending/receiving string data across chains.contract Messenger is CCIPReceiver, OwnerIsCreator { using SafeERC20 for IERC20; // Custom errors to provide more descriptive revert messages. error NotEnoughBalance(uint256 currentBalance, uint256 calculatedFees); // Used to make sure contract has enough balance. error NothingToWithdraw(); // Used when trying to withdraw Ether but there's nothing to withdraw. error FailedToWithdrawEth(address owner, address target, uint256 value); // Used when the withdrawal of Ether fails. error DestinationChainNotAllowlisted(uint64 destinationChainSelector); // Used when the destination chain has not been allowlisted by the contract owner. error SourceChainNotAllowlisted(uint64 sourceChainSelector); // Used when the source chain has not been allowlisted by the contract owner. error SenderNotAllowlisted(address sender); // Used when the sender has not been allowlisted by the contract owner. error InvalidReceiverAddress(); // Used when the receiver address is 0. // Event emitted when a message is sent to another chain. event MessageSent( bytes32 indexed messageId, // The unique ID of the CCIP message. uint64 indexed destinationChainSelector, // The chain selector of the destination chain. address receiver, // The address of the receiver on the destination chain. string text, // The text being sent. address feeToken, // the token address used to pay CCIP fees. uint256 fees // The fees paid for sending the CCIP message. ); // Event emitted when a message is received from another chain. event MessageReceived( bytes32 indexed messageId, // The unique ID of the CCIP message. uint64 indexed sourceChainSelector, // The chain selector of the source chain. address sender, // The address of the sender from the source chain. string text // The text that was received. ); bytes32 private s_lastReceivedMessageId; // Store the last received messageId. string private s_lastReceivedText; // Store the last received text. // Mapping to keep track of allowlisted destination chains. mapping(uint64 => bool) public allowlistedDestinationChains; // Mapping to keep track of allowlisted source chains. mapping(uint64 => bool) public allowlistedSourceChains; // Mapping to keep track of allowlisted senders. mapping(address => bool) public allowlistedSenders; IERC20 private s_linkToken; /// @notice Constructor initializes the contract with the router address. /// @param _router The address of the router contract. /// @param _link The address of the link contract. constructor(address _router, address _link) CCIPReceiver(_router) { s_linkToken = IERC20(_link); } /// @dev Modifier that checks if the chain with the given destinationChainSelector is allowlisted. /// @param _destinationChainSelector The selector of the destination chain. modifier onlyAllowlistedDestinationChain(uint64 _destinationChainSelector) { if (!allowlistedDestinationChains[_destinationChainSelector]) revert DestinationChainNotAllowlisted(_destinationChainSelector); _; } /// @dev Modifier that checks if the chain with the given sourceChainSelector is allowlisted and if the sender is allowlisted. /// @param _sourceChainSelector The selector of the destination chain. /// @param _sender The address of the sender. modifier onlyAllowlisted(uint64 _sourceChainSelector, address _sender) { if (!allowlistedSourceChains[_sourceChainSelector]) revert SourceChainNotAllowlisted(_sourceChainSelector); if (!allowlistedSenders[_sender]) revert SenderNotAllowlisted(_sender); _; } /// @dev Modifier that checks the receiver address is not 0. /// @param _receiver The receiver address. modifier validateReceiver(address _receiver) { if (_receiver == address(0)) revert InvalidReceiverAddress(); _; } /// @dev Updates the allowlist status of a destination chain for transactions. function allowlistDestinationChain( uint64 _destinationChainSelector, bool allowed ) external onlyOwner { allowlistedDestinationChains[_destinationChainSelector] = allowed; } /// @dev Updates the allowlist status of a source chain for transactions. function allowlistSourceChain( uint64 _sourceChainSelector, bool allowed ) external onlyOwner { allowlistedSourceChains[_sourceChainSelector] = allowed; } /// @dev Updates the allowlist status of a sender for transactions. function allowlistSender(address _sender, bool allowed) external onlyOwner { allowlistedSenders[_sender] = allowed; } /// @notice Sends data to receiver on the destination chain. /// @notice Pay for fees in LINK. /// @dev Assumes your contract has sufficient LINK. /// @param _destinationChainSelector The identifier (aka selector) for the destination blockchain. /// @param _receiver The address of the recipient on the destination blockchain. /// @param _text The text to be sent. /// @return messageId The ID of the CCIP message that was sent. function sendMessagePayLINK( uint64 _destinationChainSelector, address _receiver, string calldata _text ) external onlyOwner onlyAllowlistedDestinationChain(_destinationChainSelector) validateReceiver(_receiver) returns (bytes32 messageId) { // Create an EVM2AnyMessage struct in memory with necessary information for sending a cross-chain message Client.EVM2AnyMessage memory evm2AnyMessage = _buildCCIPMessage( _receiver, _text, address(s_linkToken) ); // Initialize a router client instance to interact with cross-chain router IRouterClient router = IRouterClient(this.getRouter()); // Get the fee required to send the CCIP message uint256 fees = router.getFee(_destinationChainSelector, evm2AnyMessage); if (fees > s_linkToken.balanceOf(address(this))) revert NotEnoughBalance(s_linkToken.balanceOf(address(this)), fees); // Approve the Router to transfer LINK tokens on contract's behalf. It will spend the fees in LINK s_linkToken.approve(address(router), fees); // Send the CCIP message through the router and store the returned CCIP message ID messageId = router.ccipSend(_destinationChainSelector, evm2AnyMessage); // Emit an event with message details emit MessageSent( messageId, _destinationChainSelector, _receiver, _text, address(s_linkToken), fees ); // Return the CCIP message ID return messageId; } /// @notice Sends data to receiver on the destination chain. /// @notice Pay for fees in native gas. /// @dev Assumes your contract has sufficient native gas tokens. /// @param _destinationChainSelector The identifier (aka selector) for the destination blockchain. /// @param _receiver The address of the recipient on the destination blockchain. /// @param _text The text to be sent. /// @return messageId The ID of the CCIP message that was sent. function sendMessagePayNative( uint64 _destinationChainSelector, address _receiver, string calldata _text ) external onlyOwner onlyAllowlistedDestinationChain(_destinationChainSelector) validateReceiver(_receiver) returns (bytes32 messageId) { // Create an EVM2AnyMessage struct in memory with necessary information for sending a cross-chain message Client.EVM2AnyMessage memory evm2AnyMessage = _buildCCIPMessage( _receiver, _text, address(0) ); // Initialize a router client instance to interact with cross-chain router IRouterClient router = IRouterClient(this.getRouter()); // Get the fee required to send the CCIP message uint256 fees = router.getFee(_destinationChainSelector, evm2AnyMessage); if (fees > address(this).balance) revert NotEnoughBalance(address(this).balance, fees); // Send the CCIP message through the router and store the returned CCIP message ID messageId = router.ccipSend{value: fees}( _destinationChainSelector, evm2AnyMessage ); // Emit an event with message details emit MessageSent( messageId, _destinationChainSelector, _receiver, _text, address(0), fees ); // Return the CCIP message ID return messageId; } /// handle a received message function _ccipReceive( Client.Any2EVMMessage memory any2EvmMessage ) internal override onlyAllowlisted( any2EvmMessage.sourceChainSelector, abi.decode(any2EvmMessage.sender, (address)) ) // Make sure source chain and sender are allowlisted { s_lastReceivedMessageId = any2EvmMessage.messageId; // fetch the messageId s_lastReceivedText = abi.decode(any2EvmMessage.data, (string)); // abi-decoding of the sent text emit MessageReceived( any2EvmMessage.messageId, any2EvmMessage.sourceChainSelector, // fetch the source chain identifier (aka selector) abi.decode(any2EvmMessage.sender, (address)), // abi-decoding of the sender address, abi.decode(any2EvmMessage.data, (string)) ); } /// @notice Construct a CCIP message. /// @dev This function will create an EVM2AnyMessage struct with all the necessary information for sending a text. /// @param _receiver The address of the receiver. /// @param _text The string data to be sent. /// @param _feeTokenAddress The address of the token used for fees. Set address(0) for native gas. /// @return Client.EVM2AnyMessage Returns an EVM2AnyMessage struct which contains information for sending a CCIP message. function _buildCCIPMessage( address _receiver, string calldata _text, address _feeTokenAddress ) private pure returns (Client.EVM2AnyMessage memory) { // Create an EVM2AnyMessage struct in memory with necessary information for sending a cross-chain message return Client.EVM2AnyMessage({ receiver: abi.encode(_receiver), // ABI-encoded receiver address data: abi.encode(_text), // ABI-encoded string tokenAmounts: new Client.EVMTokenAmount[](0), // Empty array as no tokens are transferred extraArgs: Client._argsToBytes( // Additional arguments, setting gas limit and allowing out-of-order execution. // Best Practice: For simplicity, the values are hardcoded. It is advisable to use a more dynamic approach // where you set the extra arguments off-chain. This allows adaptation depending on the lanes, messages, // and ensures compatibility with future CCIP upgrades. Read more about it here: https://docs.chain.link/ccip/concepts/best-practices/evm#using-extraargs Client.GenericExtraArgsV2({ gasLimit: 200_000, // Gas limit for the callback on the destination chain allowOutOfOrderExecution: true // Allows the message to be executed out of order relative to other messages from the same sender }) ), // Set the feeToken to a feeTokenAddress, indicating specific asset will be used for fees feeToken: _feeTokenAddress }); } /// @notice Fetches the details of the last received message. /// @return messageId The ID of the last received message. /// @return text The last received text. function getLastReceivedMessageDetails() external view returns (bytes32 messageId, string memory text) { return (s_lastReceivedMessageId, s_lastReceivedText); } /// @notice Fallback function to allow the contract to receive Ether. /// @dev This function has no function body, making it a default function for receiving Ether. /// It is automatically called when Ether is sent to the contract without any data. receive() external payable {} /// @notice Allows the contract owner to withdraw the entire balance of Ether from the contract. /// @dev This function reverts if there are no funds to withdraw or if the transfer fails. /// It should only be callable by the owner of the contract. /// @param _beneficiary The address to which the Ether should be sent. function withdraw(address _beneficiary) public onlyOwner { // Retrieve the balance of this contract uint256 amount = address(this).balance; // Revert if there is nothing to withdraw if (amount == 0) revert NothingToWithdraw(); // Attempt to send the funds, capturing the success status and discarding any return data (bool sent, ) = _beneficiary.call{value: amount}(""); // Revert if the send failed, with information about the attempted transfer if (!sent) revert FailedToWithdrawEth(msg.sender, _beneficiary, amount); } /// @notice Allows the owner of the contract to withdraw all tokens of a specific ERC20 token. /// @dev This function reverts with a 'NothingToWithdraw' error if there are no tokens to withdraw. /// @param _beneficiary The address to which the tokens will be sent. /// @param _token The contract address of the ERC20 token to be withdrawn. function withdrawToken( address _beneficiary, address _token ) public onlyOwner { // Retrieve the balance of this contract uint256 amount = IERC20(_token).balanceOf(address(this)); // Revert if there is nothing to withdraw if (amount == 0) revert NothingToWithdraw(); IERC20(_token).safeTransfer(_beneficiary, amount); }}
上面的代码是一个双向 CCIP 合约,可在允许列表的链上发送和接收字符串信息,并带有所有者控制、LINK 或本地费用支付功能。 让我们来看看本合同中要用到的主要功能:
1. 所有列表
- allowlistSourceChain(selector, allowed):控制允许哪些源链向此合约传递消息。
- allowlistDestinationChain(selector, allowed):控制允许向哪些目标链发送此合约。
- allowlistedSenders[address](通过 allowlistSender(addr, allowed)):当信息到达时,限制信任源链上的哪些发件人地址。
测试前在两端都设置好。 信息源必须信任发送方和链。 目的地也必须列入允许发送列表。
2. 发送信息
sendMessagePayLINK(selector, receiver, text):发送信息并在 LINK 中支付 CCIP 费用。 这将生成一条信息,报出费用,检查 LINK 余额,批准路由器,然后执行 ccipSend。 �完成后,它会返回一个与发送信息相关的唯一 ID。
发送消息支付本地(选择器、接收器、文本):发送信息并以本地令牌支付 CCIP 费用。 这将生成一条信息,报出费用,检查本地余额,然后执行 ccipSend(值:费用)。 完成后,它会返回一个与发送信息相关的唯一 ID。
3. 建立信息
_buildCCIPMessage(receiver, text, feeTokenAddress) -> EVM2AnyMessage
- 对接收器和文本进行编码
- 不发送令牌(令牌数量为空)
- 使用带有可配置 gasLimit 的 GenericExtraArgsV2 封装 extraArgs
- 将 feeToken 设置为 LINK 或本地 address(0)。
4. 接收信息
CCIP 调用 _ccipReceive(...) 在目标链上。 合同:
- 根据允许列表验证源链和发件人
- 解码字符串
- 将其存储为最后收到的有效载荷
- 发射 MessageReceived
- 通过以下方式读回最后一次接收的有效载荷: getLastReceivedMessageDetails() -> (messageId, text)
编译智能合约
要编译智能合约,请运行
forge build
部署智能合约
将钱包设置为部署器
在将智能合约部署到网络之前,您需要设置一个钱包作为部署器。 为此,您可以使用 cast wallet import 命令将钱包的私钥导入 Foundry 的安全加密密钥库:
cast wallet import deployer --interactive
运行上述命令后,系统会提示你输入私钥和用于签署交易的密码。
要确认钱包已作为部署者账户导入到 Foundry 项目中,请运行
cast wallet list
设置环境变量
要设置环境,请在项目主目录下创建 .env 文件,并为 Kairos Testnet 和 Ethereum Sepolia 添加 RPC URL、CCIP 链选择器、CCIP 路由器地址和LINK 令牌地址:
KAIROS_RPC_URL="https://public-en-kairos.node.kaia.io"ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL="https://ethereum-sepolia-rpc.publicnode.com"KAIROS_CHAIN_SELECTOR=2624132734533621656ETH_SEPOLIA_CHAIN_SELECTOR=16015286601757825753KAIROS_ROUTER_ADDRESS="0x41477416677843fCE577748D2e762B6638492755"ETH_SEPOLIA_ROUTER_ADDRESS="0x0BF3dE8c5D3e8A2B34D2BEeB17ABfCeBaf363A59"KAIROS_LINK_ADDRESS="0xAF3243f975afe2269Da8Ffa835CA3A8F8B6A5A36"ETH_SEPOLIA_LINK_ADDRESS="0x779877A7B0D9E8603169DdbD7836e478b4624789"
创建.env文件后,运行以下命令在当前命令行会话中加载环境变量:
source .env
完成合约编译和环境设置后,就可以部署智能合约了。
要使用 Foundry 部署智能合约,可以使用 forge create 命令。 该命令要求您指定要部署的智能合约、要部署到的网络的 RPC URL 和要��部署的账户。
将发送方合同部署到 Kairos Testnet
要将 Sender 智能合约部署到 Kaia Kairos Testnet,请运行以下命令:
forge create --rpc-url $KAIROS_RPC_URL --account deployer --broadcast src/Messenger.sol:Messenger --constructor-args $KAIROS_ROUTER_ADDRESS $KAIROS_LINK_ADDRESS
出现提示时,输入之前导入钱包私钥时设置的密码。
运行上述命令后,合同将部署到 Kairos 测试网络上。 您可以使用 Kaiascan block explorer 查看部署状态和合同。
使您的合约能够向以太坊 Sepolia 上的接收方合约发送 CCIP 消息
首先,我们需要更新目标链的交易允许列表状态。 为此,请运行以下命令:
cast send `SENDER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $KAIROS_RPC_URL "allowlistDestinationChain(uint64, bool)" $ETH_SEPOLIA_CHAIN_SELECTOR true --account deployer
上面的代码调用 allowlistDestinationChain() 来设置发送方合约允许的目标链选择器。 每个链选择器都可以在 [CCIP 目录] (https://docs.chain.link/ccip/directory) 中找到。
在以太坊 Sepolia 上部署接收器合约
要将 Receiver 智能合约部署到以太坊 Sepolia,请运行以下命令:
forge create --rpc-url $ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL --account deployer --broadcast src/Messenger.sol:Messenger --constructor-args $ETH_SEPOLIA_ROUTER_ADDRESS $ETH_SEPOLIA_LINK_ADDRESS
出现提示时,输入之前导入钱包私钥时设置的密码。
运行上述命令后,合约将部署到以太坊 Sepolia 上。 您可以使用 ETH Sepolia 区块浏览器 查看部署状态和合约。
启用您的合同,以便从 Kairos Testnet 上的发件人合同接收 CCIP 信息
首先,我们需要更新交易源链的允许列表状态。 为此,请运行以下命令:
cast send `RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL "allowlistSourceChain(uint64, bool)" $KAIROS_CHAIN_SELECTOR true --account deployer
上面的代码调用 allowlistSourceChain() 来设置接收器合约允许使用的源代码链选择器。 每个链选择器都可以在 [CCIP 目录] (https://docs.chain.link/ccip/directory) 中找到。
启用您的合同,以便从 Kairos Testnet 上的发件人合同接收 CCIP 信息
要更新发件人的交易允许列表状态,请运行以下命令:
cast send `RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL "allowlistSender(address, bool)" 0x12798F1E2013A110E3C8B23aC1f36c00B8DFD4d9 true --account deployer
此时,您在 Kairos Testnet 上有一个发送方合约,在 Ethereum Sepolia 上有一个接收方合约。 作为安全措施,您启用了发送方合约,以便向 Ethereum Sepolia 发送 CCIP 消息,并启用了接收方合约,以便从发送方和 Kairos Testnet 接收 CCIP 消息。
为智能合约提供资金
为了支付发送信息的相关费用,发送方合约需要持有 LINK 代币余额,如果发送数据并使用原生代币支付,则需要持有 ETH 和 KAIA。
链接
直接从您的钱包或通过运行以下指令为您的合约注资:
cast send $KAIROS_LINK_ADDRESS --rpc-url $KAIROS_RPC_URL "transfer(address,uint256)" `SENDER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` 5000000000000000000 --account deployer
上述命令将在 Kairos Testnet 上向发送方合约发送 5 个 LINK 令牌。
在运行所提供的施放命令之前,请将 SENDER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS 替换为已部署的发送方合同的合同地址。
与智能合约互动
在本节中,您将使用 Foundry cast 命令行工具与已部署的智能合约进行交互,并调用它们的功能。
发送数据并通过 LINK 支付
在此步骤中,您将使用 CCIP 发送短信,使用 CCIP 的费用将在 LINK 中支付。
为此,您需要使用 cast 命令调用部署到 Kairos Testnet 的发送方合约上的 sendMessagePayLINK(uint64, address, string) 函数,以便向以太坊 Sepolia 上的接收方合约发送消息数据。
要调用发送方智能合约的_sendMessagePayLINK(uint64, address, string)_ 函数,请运行
cast send `SENDER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $KAIROS_RPC_URL "sendMessagePayLINK(uint64, address, string)" $ETH_SEPOLIA_CHAIN_SELECTOR `RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` "gKaia builders" --account deployer
上述命令调用 sendMessagePayLINK(uint64, address, string) 发送信息。 传递给该方法的参数包括目标链(Ethereum Sepolia)的链选择器、接收方合约地址以及要包含在消息中的文本数据(Hello Builders)。
运行该命令后,将返回一个唯一的 messageId。
交易完成后,CCIP 会花几分钟时间将数据传送到 Ethereum Sepolia,并调用 Receiver 合约上的 ccipReceive 函数。 要验证跨链交易,请打开 CCIP explorer 并使用交易哈希值进行搜索。

接下来要做的是检查目的地链上的接收器合同。 为此,您需要运行下面的命令调用 getLastReceivedMessageDetails() :
cast call `RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL "getLastReceivedMessageDetails()"
在运行所提供的 cast 命令之前,请将 RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS 替换为已部署的 Receiver 合同的合同地址。
收到的文本和信息 ID 会以十六进制数据的形式返回,就像这样:
0x6fe4577cdbf2ebf73a9023b3dd9818f990879fec890ac92cf6b8d6f8bc5e59640000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000040000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000e48656c6c6f206275696c64657273000000000000000000000000000000000000
要将十六进制数据转换为字符串,特别是接收到的文本,请运行下面的命令:
cast to-utf8 e48656c6c6f206275696c64657273000000000000000000000000000000000000
现在你应该看到 Hello builders 意味着我们的跨链操作成功了。
这些示例合同旨在双向运行。 您可以使用它们将数据从 Kairos Testnet 发送到 Ethereum Sepolia,再从 Ethereum Sepolia 发送回 Kairos Testnet。
发送数据并以本地方式支付
在此部分,您将用 CCIP 发送短信,并用本地令牌支付费用。 您将从 Ethereum Sepolia 向 Kaia(Kairos Testnet)发送数据。 这就颠倒了先前的方向,因此 Sepolia 合约充当发送方,而 Kairos 合约充当接收方。
首先,我们需要用以太坊 Sepolia 上的 ETH 为发送方合约提��供资金。 为此,请运行以下 cast 命令:
cast send --rpc-url $ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL `SENDER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --value 300000000000000000 --account deployer
这将在以太坊 Sepolia 上向您的发送者合约发送 0.3 ETH。
将 SENDER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS 替换为发件人合同地址。
下一步是在以太坊 Sepolia 上允许发送者合约的目的链。 为此,请运行以下命令:
cast send `SENDER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL "allowlistDestinationChain(uint64, bool)" $KAIROS_CHAIN_SELECTOR true --account deployer
下一步是允许从 Kairos Testnet 上的接收器合��同中获取源链。 为此,请运行以下命令:
cast send `RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $KAIROS_RPC_URL "allowlistSourceChain(uint64, bool)" $ETH_SEPOLIA_CHAIN_SELECTOR true --account deployer
然后运行以下命令,在 Kairos Testnet 的接收器合约上执行 allowlistSender:
cast send `RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $KAIROS_RPC_URL "allowlistSender(address, bool)" 0x09a0CF7628c64c683B9d61a8B9EBc14BB984c65c true --account deployer
将合约连接起来后,就可以运行这条命令向接收合约发送数据了:
cast send `SENDER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL "sendMessagePayNative(uint64, address, string)" $KAIROS_CHAIN_SELECTOR 0x12798F1E2013A110E3C8B23aC1f36c00B8DFD4d9 "gKaia Builders" --account deployer
上述命令调用 sendMessagePayNative(uint64, address, string) 发送信息。 传递给该方法的参数包括目标链(Kairos Testnet)的链选择器、接收器合同地址以及要包含在信息中的文本数据(gKaia Builders)。
运行该命令后,将返回一个唯一的 messageId。
交易完成后,CCIP 会花几分钟时间将数据传送到 Kairos Testnet��,并调用接收器合同上的 ccipReceive 函数。 要验证跨链交易,请打开 CCIP explorer 并使用交易哈希值进行搜索。
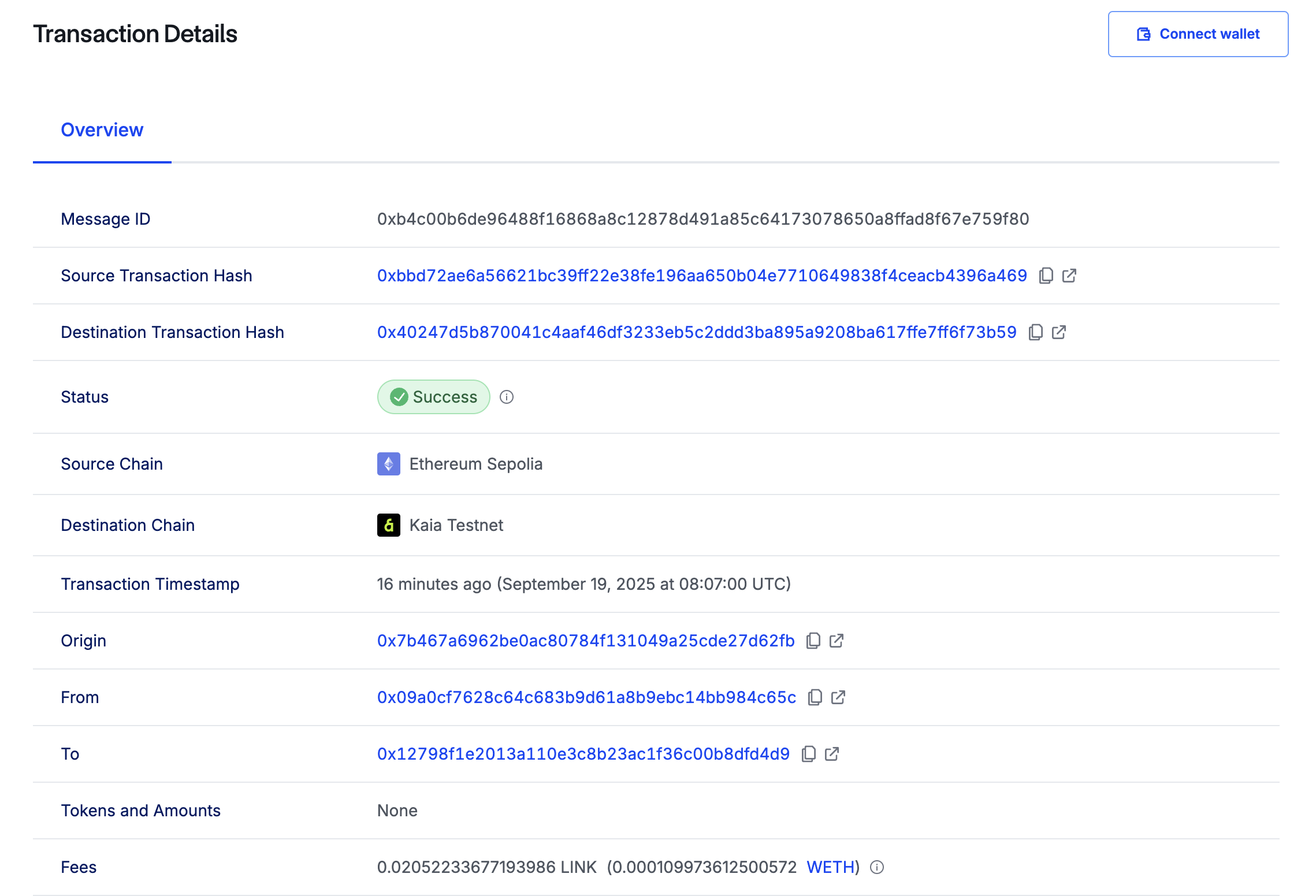
接下来要做的是检查目的地链上的接收器合同。 为此,您需要运行下面的命令调用 getLastReceivedMessageDetails() :
cast call `RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $KAIROS_RPC_URL "getLastReceivedMessageDetails()"
将 RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS 替换为接收方合同的合同地址。
收到的文本和信息 ID 会以十六进制数据形式返回,就像这样:
0xb4c00b6de96488f16868a8c12878d491a85c64173078650a8ffad8f67e759f800000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000040000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000e674b616961206275696c64657273000000000000000000000000000000000000
要将十六进制数据转换为字符串,特别是接收到的文本,请运行下面的命令:
cast to-utf8 674b616961206275696c64657273000000000000000000000000000000000000
现在你应该看到 gKaia builders,这意味着我们的跨链操作成功了。
结论
在本教程中,您将学习如何使用 Chainlink CCIP 从 Kaia Kairos Testnet 向另一条链 Ethereum Sepolia 发送消息,反之亦然。 有关 Chainlink CCIP 及其工作原理的更多深入指南,请参阅 Chainlink CCIP Documentation。