Install a 4-node service chain
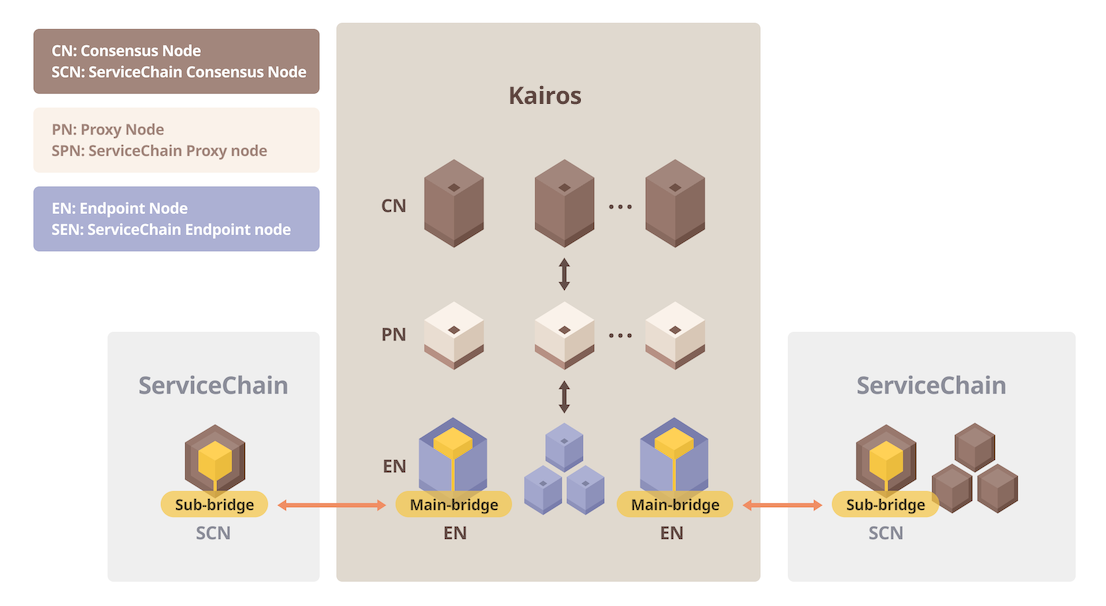
This section covers how to set up a multi-node ServiceChain. We will set up a 4-consensus-node ServiceChain with chainID 1002, as you can see in the blue border box in the figure below.
Prerequisites
- Download packages for
kscn,homibinary from Download. - 4 Linux or MacOS servers
- Minimum hardware requirements
- CPU: 4-core (Intel Xeon or equivalent), RAM: 16GB, HDD: 50GB
- Please refer to System Requirements for more explanation.
Step 0: Install SCN on all nodes
The installation is the uncompression of the downloaded package. Extract the SCN archive on each server.
$ tar xvf kscn-vX.X.X-XXXXX-amd64.tar.gzx kscn-XXXXX-amd64/x kscn-XXXXX-amd64/conf/x kscn-XXXXX-amd64/conf/kscnd.confx kscn-XXXXX-amd64/bin/x kscn-XXXXX-amd64/bin/kscndx kscn-XXXXX-amd64/bin/kscn
For the convenience, we will add the binary path to $PATH. Use the actual path on your node.
$ export PATH=$PATH:~/path/to/kscn-XXXXX-amd64/bin
SCN also provides various RPM distributions like RHEL, CentOS, and Fedora. For more information, please refer to Installation.
$ curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/kaia.repo https://packages.kaia.io/config/rhel/7/prod.repo % Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed 100 118 100 118 0 0 1113 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 1102 $ yum list | grep kaia packages-klaytn-prod 31 kB/s | 2.9 kB 00:00 homi.x86_64 v1.8.0-0.el7 packages-klaytn-prod kbnd.x86_64 v1.8.0-0.el7 packages-klaytn-prod kcnd.x86_64 v1.8.0-0.el7 packages-klaytn-prod kcnd-baobab.x86_64 v1.8.0-0.el7 packages-klaytn-prod kend.x86_64 v1.8.0-0.el7 packages-klaytn-prod kend-baobab.x86_64 v1.8.0-0.el7 packages-klaytn-prod kgen.x86_64 v1.8.0-0.el7 packages-klaytn-prod kpnd.x86_64 v1.8.0-0.el7 packages-klaytn-prod kpnd-baobab.x86_64 v1.8.0-0.el7 packages-klaytn-prod kscnd.x86_64 v1.8.0-0.el7 packages-klaytn-prod ksend.x86_64 v1.8.0-0.el7 packages-klaytn-prod kspnd.x86_64 v1.8.0-0.el7 packages-klaytn-prod $ yum install kscnd
Step 1: Create genesis.json and nodekeys
We will use homi utility to generate the needful files.
homi is a utility that automatically generates scripts, configuration files, and private keys necessary to configure the Kaia blockchain.
You can execute homi from any Linux/Mac PC.
First, extract the homi archive you downloaded.
$ tar xvf homi-vX.X.X-XXXXX-amd64.tar.gzx homi-XXXXX-amd64/x homi-XXXXX-amd64/bin/x homi-XXXXX-amd64/bin/homi
Go to the bin folder and execute homi with following options to generate the files.
homi setup --gen-type local --cn-num 4 --test-num 1 --servicechain --chainID 1002 --p2p-port 22323 -o homi-output
Since Kairos's chainID is 1001, for convenience, the chainID of the ServiceChain constructed in this example is set to 1002. When operating a blockchain by launching an actual service, it is recommended to use it after registering a new chainID value at https://chainlist.defillama.com/ so that chainID does not overlap with other ServiceChains. The ServiceChain port is set to 22323, which is the default port.
$ ./homi setup --gen-type local --cn-num 4 --test-num 1 --servicechain --chainID 1002 --p2p-port 22323 -o homi-outputCreated : homi-output/keys/passwd1Created : homi-output/keys/passwd2Created : homi-output/keys/passwd3Created : homi-output/keys/passwd4Created : homi-output/scripts/genesis.jsonCreated : homi-output/keys/nodekey1Created : homi-output/keys/validator1Created : homi-output/keys/nodekey2Created : homi-output/keys/validator2Created : homi-output/keys/nodekey3Created : homi-output/keys/validator3Created : homi-output/keys/nodekey4Created : homi-output/keys/validator4Created : homi-output/scripts/static-nodes.jsonCreated : homi-output/keys_test/testkey1Created : homi-output/keys_test/keystore1/0xdC7218621513f71d609653d22C39d79d558d9CDCCreated : homi-output/Kaia.jsonCreated : homi-output/Kaia_txpool.json
Among the outputs, we will use nodekey*, genesis.json and static-nodes.json in the subsequent steps.
Step 2: Customize static-nodes.json
Open homi-output/scripts/static-nodes.json in a text editor then update the IP addresses and ports with the actual values of your nodes.
In this example, it is assumed that the IP of each SCN node in the ServiceChain is as shown in the figure below. Remember the port you assigned here, as it will be used later in step 4.
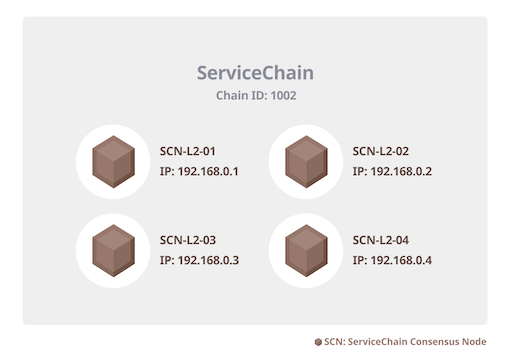
[ "kni://38693ad4b17ff77...23153@192.168.0.1:22323?discport=0\u0026ntype=cn", "kni://f36d969b16f7337...1329b@192.168.0.2:22323?discport=0\u0026ntype=cn", "kni://16e55d8921ab034...b2bec@192.168.0.3:22323?discport=0\u0026ntype=cn", "kni://0973e792a421c1d...bbd71@192.168.0.4:22323?discport=0\u0026ntype=cn"]
After you update static-nodes.json, upload the output folders(homi-output) to all SCNs, i.e. SCN-L2-01, SCN-L2-02, SCN-L2-03, SCN-L2-04 nodes in this example.
$ scp -r path/to/homi-output/ user@192.168.0.1:~/$ scp -r path/to/homi-output/ user@192.168.0.2:~/$ scp -r path/to/homi-output/ user@192.168.0.3:~/$ scp -r path/to/homi-output/ user@192.168.0.4:~/
Step 3: Node initialization
Now, we will initialize each node using the genesis file. On each node, execute the following command.
It will create the data folder storing the chain data and logs on your home directory.
You can change the data folder using the --datadir directive.
In this example, we set the data folder to \~/data.
$ kscn --datadir ~/data init ~/homi-output/scripts/genesis.json$ ls ~/datakeystore klay kscn
Step 4: Install nodekey and static-nodes.json
On every SCNs, copy static-nodes.json to the data folder.
$ cp ~/homi-output/scripts/static-nodes.json ~/data/
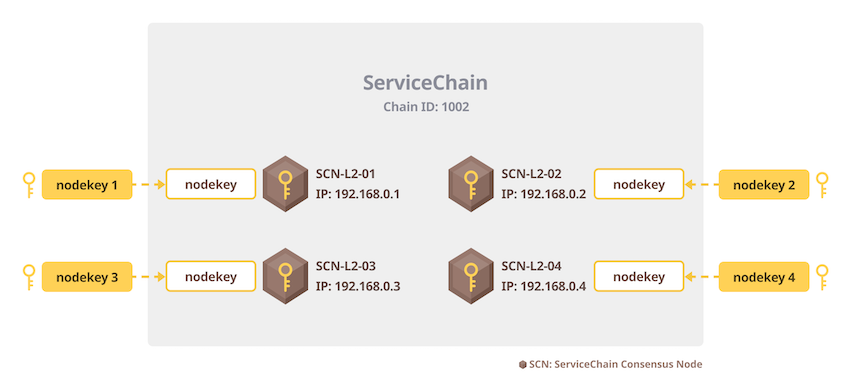
In step 1, we generated 4 nodekeys.
Assign each node key to the SCN and copy the matching nodekey to each SCN's data folder.
For example, use nodekey1 for SCN-L2-01(192.168.0.1) node and use nodekey2, nodekey3 and nodekey4 for SCN-L2-02(192.168.0.2), SCN-L2-03(192.168.0.3) and SCN-L2-04(192.168.0.4) respectively.
$ cp ~/homi-output/keys/nodekey{1..4} ~/data/klay/nodekey
Step 5: Configure nodes
On every SCNs, go to the kscn installation folder and edit conf/kscnd.conf as follows. PORT is the port used to set up homi, and SC_SUB_BRIDGE is required for connecting bridges in the next section. For now, just set it to 0. In DATA_DIR, enter the data folder used in step 3.
...PORT=22323...SC_SUB_BRIDGE=0...DATA_DIR=~/data...
Step 6: Start nodes
Execute the following command on all SCN nodes.
$ kscnd startStarting kscnd: OK
You can check block generation status by watching kaia.blockNumber. If this number is not 0, the node is working fine.
$ kscn attach --datadir ~/data> kaia.blockNumber10
If you want to stop a node, you can use the command kscnd stop
(Example) Creation and confirmation of a value transfer transaction
Now the 4-node ServiceChain is up and running. We will execute a value transfer transaction in the ServiceChain to confirm the installation.
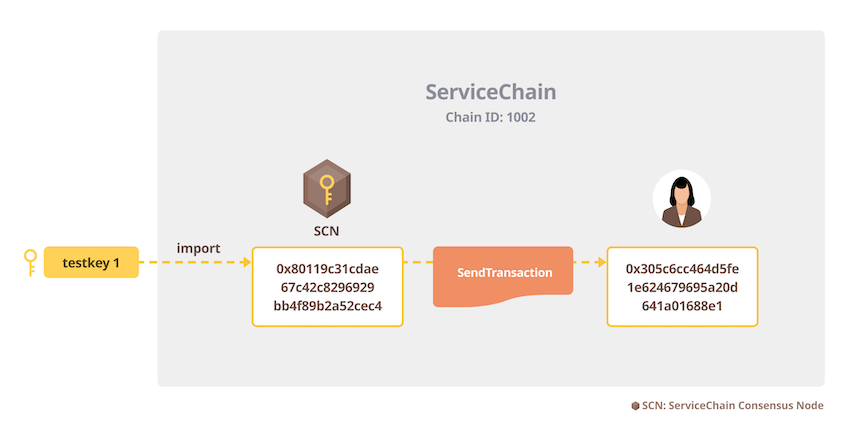
Step 1: Import the test account
testkey1 was automatically generated by homi in step 1. KAIA is allocated to the test account as described in the genesis.json which was also generated by homi.
$ kscn account import --datadir ~/data ~/homi-output/keys_test/testkey1Your new account is locked with a password. Please give a password. Do not forget this password.Passphrase:Repeat passphrase:Address: {80119c31cdae67c42c8296929bb4f89b2a52cec4}
Step 2: Unlock the account
Unlocking the account is possible only through the console of the SCN node that imported testkey1.
$ kscn attach --datadir ~/data> personal.unlockAccount("80119c31cdae67c42c8296929bb4f89b2a52cec4")Unlock account 80119c31cdae67c42c8296929bb4f89b2a52cec4Passphrase:true
Step 3: Send a transaction and check the balance
> kaia.sendTransaction({from: "80119c31cdae67c42c8296929bb4f89b2a52cec4", to: "305c6cc464d5fe1e624679695a20d641a01688e1", value: 10})"0xa0e7102e8f14200cec8d964aacc1c9ed7c22271078b2b213170c64333cbca8a3"> kaia.getBalance("305c6cc464d5fe1e624679695a20d641a01688e1")10
The simplest form of ServiceChain is having one SCN.
The ServiceChain illustrated in this tutorial is a 4-node ServiceChain. You can, however, set up a single-node ServiceChain if you wish.
Simply pass --cn-num 1 instead of --cn-num 4 to homi in 'Step 1:Create genesis.json and nodekeys'.
At least 4 nodes are required to tolerate byzantine faults. Therefore, the minimum number of SCNs to achieve high availability under the BFT algorithm is 4. Having 2 SCN nodes is not enough, because if one SCN fails, the other one cannot reach a consensus on its own.