Scaling Solutions
Kaia offers robust scaling solutions to ensure high throughput and responsiveness even under heavy network load. These solutions include Service Chains and a novel Multi-Channel communication architecture
Service Chain
Service chains in Kaia are auxiliary blockchains independent from the Kaia main chain, tailored for individual dApp requiring special node configurations, customized security levels, or exceptionally high throughput that makes deploying the dApp on the main chain inconvenient or economically infeasible.
While there are fully-decentralized scaling solutions, due to their difficult interfaces such as challenge or exit and non-immediate finality, we take a different approach in Kaia’s Service Chain by sacrificing the full decentralization for better usability, instant finality, high performance, and high availability.
Kaia service chains may be used for various service-specific goals, and can connect to the main chain for multiple reasons including data anchoring (periodic storing of block hashes from the service chain onto the main chain to compensate for the decreased security of the service chain due to the smaller number of nodes) or value transfer (interchain transfer of KAIA, Kaia’s native unit of value, and the tokens issued by dApps).
Network
Service chains connected to Kaia main chain are collectively called Service Chain Network. Note that the method of connection between service chains and the main chain may change in Kaia’s future iterations.
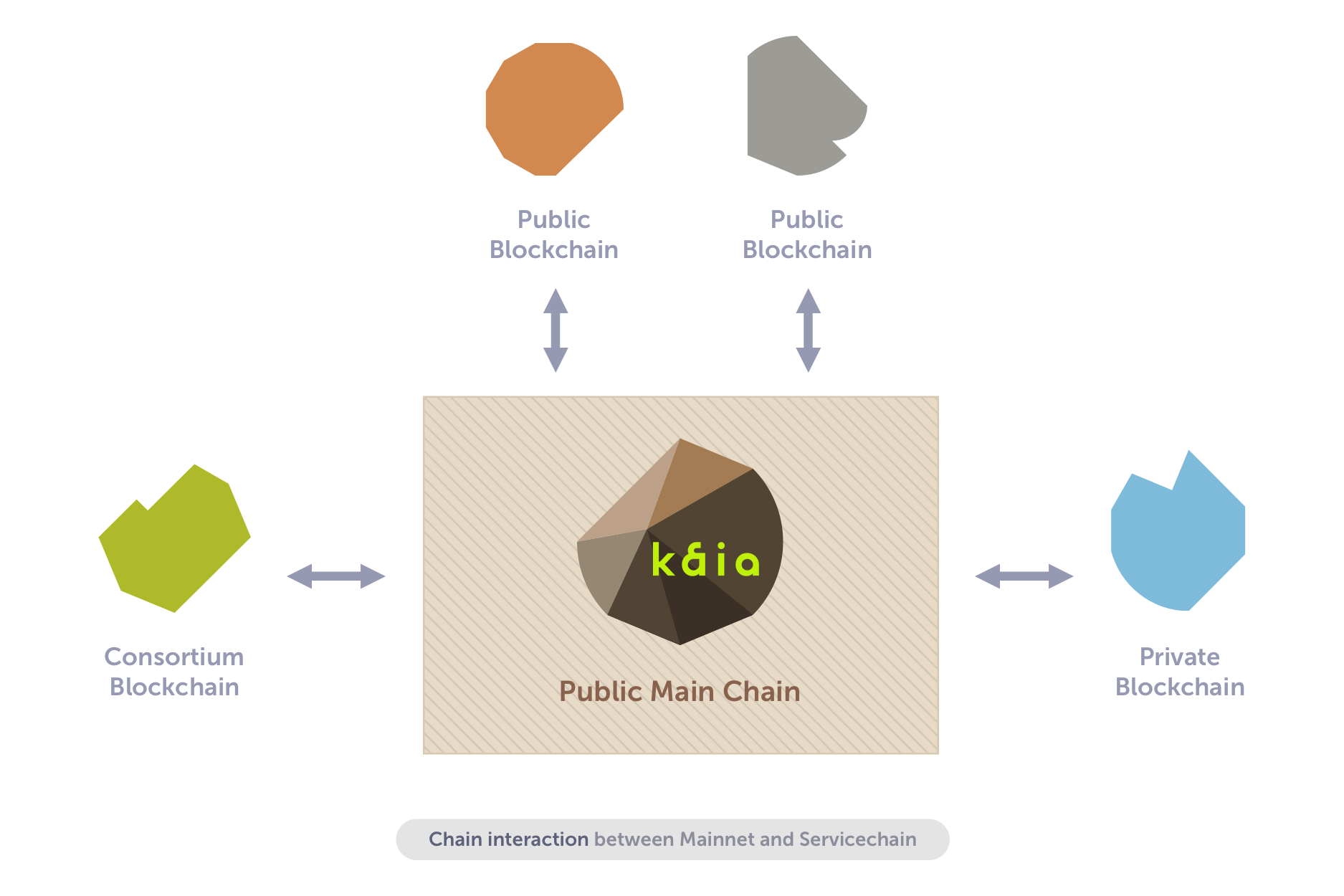
Figure 1 shows the network topology of service chains being used to meet various business needs, connected with Kaia main chain to expand the Kaia network.
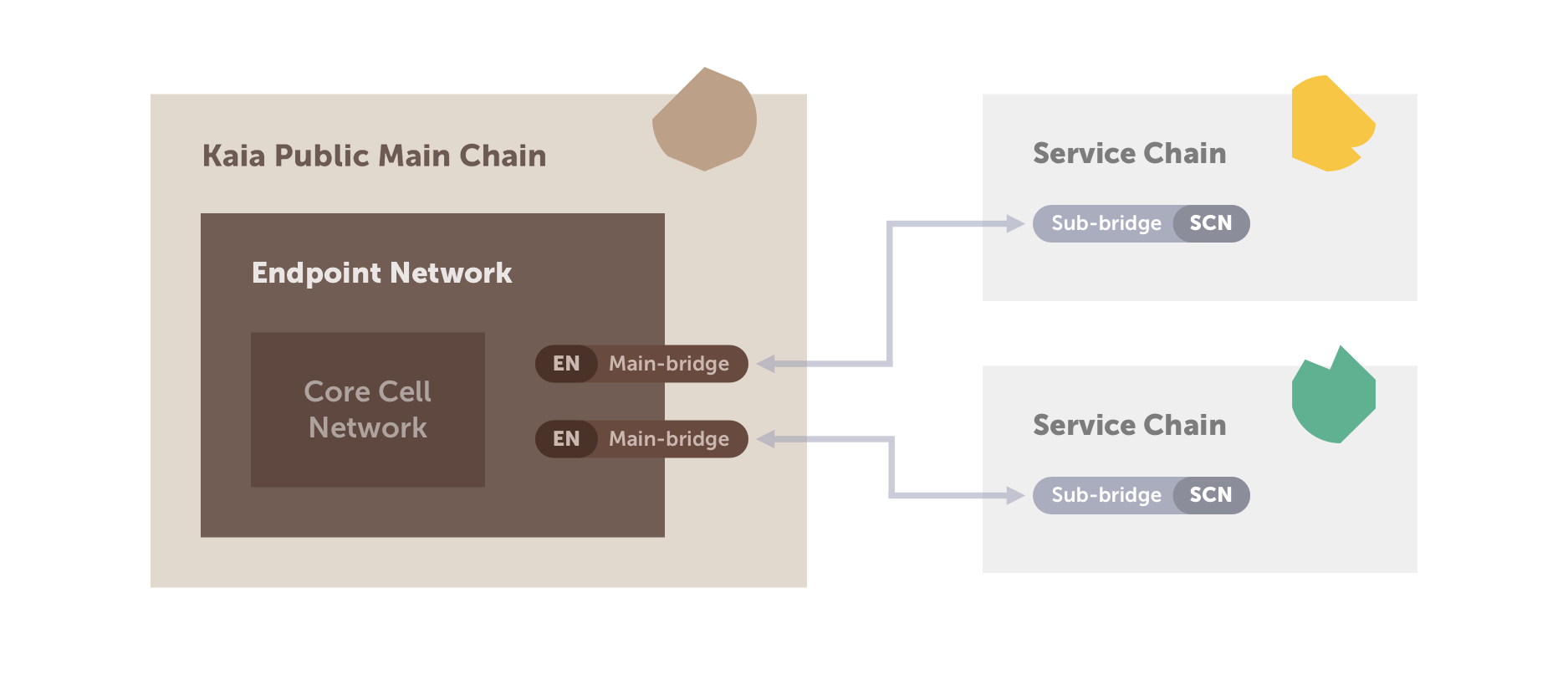
Figure 2 shows an example of SCN (Service Chain Consensus Node) connected directly with Kaia main chain’s EN (Endpoint Node) using a main/sub-bridge model in using the service chain’s features.
Features
Service Chain expands and augments Kaia by providing a data integrity mechanism and supporting token transfers between different chains.
Data Anchoring
For data integrity, Service Chain can automatically anchor every service chain block hash as a special transaction to the main chain. This data anchoring can ensure to the service users that the data in the service chain cannot be altered once it is created.
Value Transfer
To help the service providers (SPs) to easily migrate service users and values across chains, transferring tokens, such as KAIA (Kaia's native unit of value) and Kaia tokens issued by dApps, between different chains can be enabled. Users can easily request to transfer tokens to other chains by sending a transaction to a special contract, called bridge contract.
Multi-Channel Communication
Kaia employs a multi-channel communication architecture to enhance network performance and resilience, particularly during periods of high transaction volume. By separating different message types onto dedicated communication channels, Kaia can maintain efficient block propagation and consensus even under heavy network congestion.
Architecture
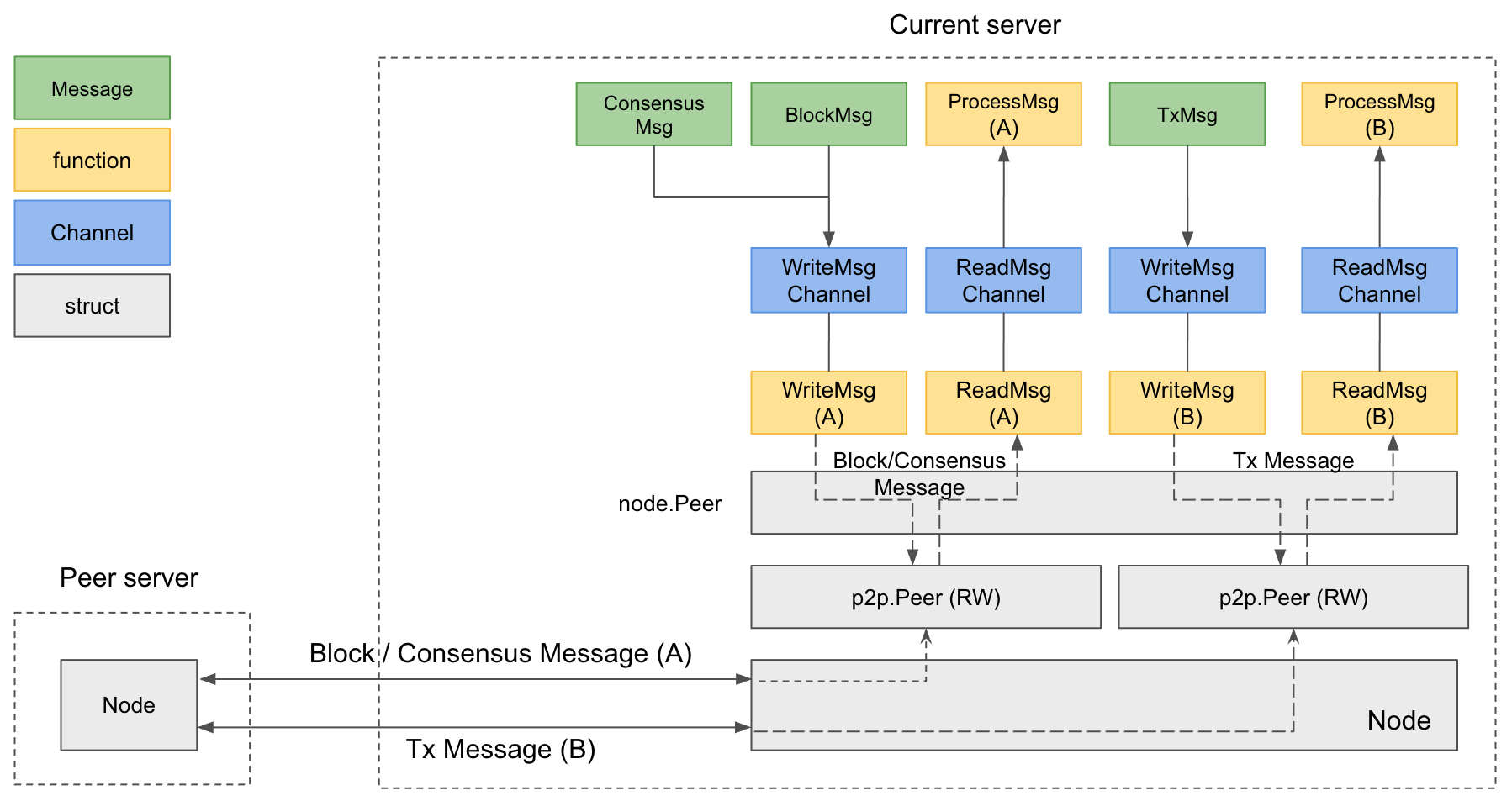
Multi-Channel Connection
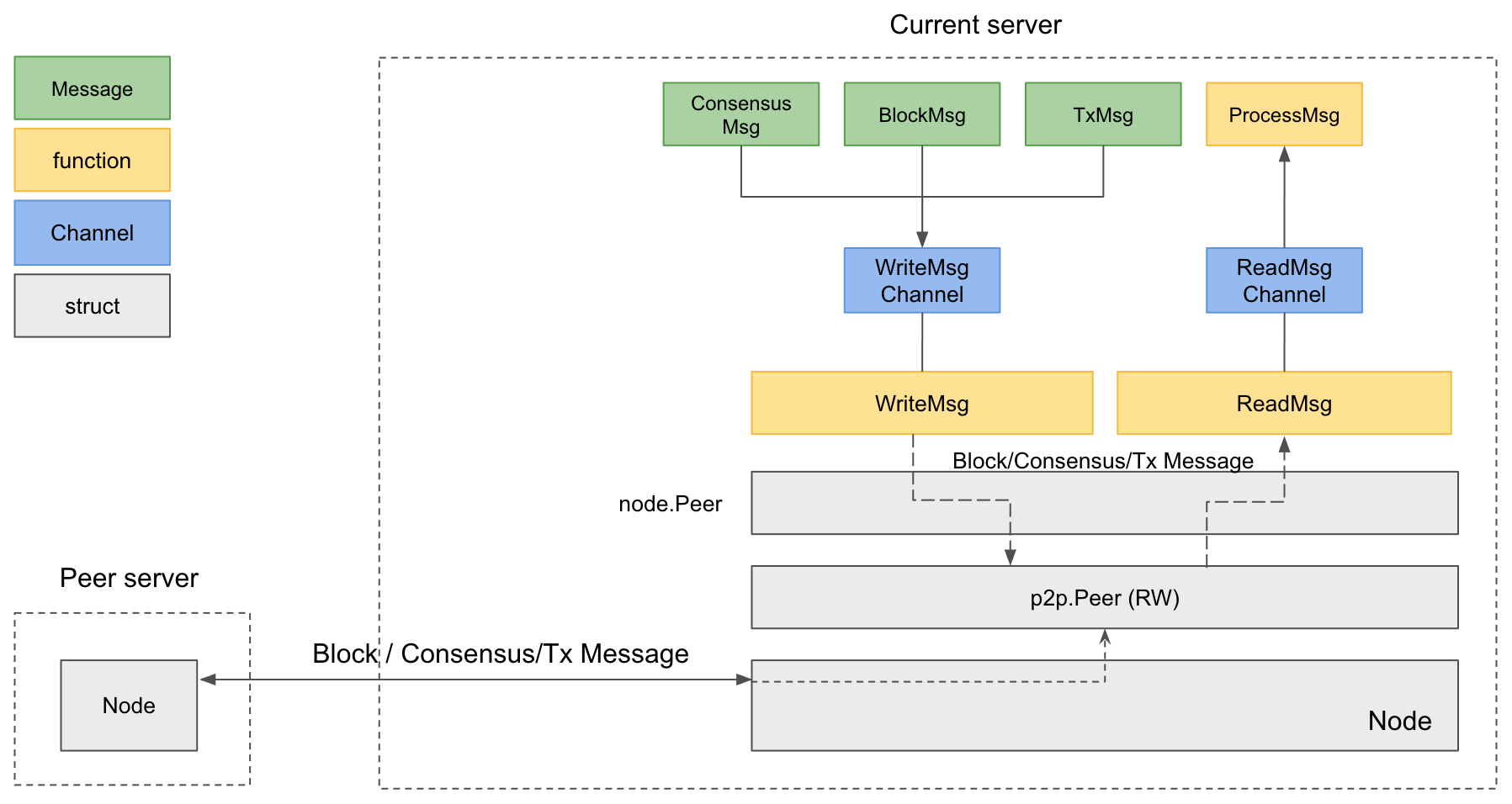
Single-Channel Connection
Configuration Modes
- Multi-Channel: Uses two ports. Enabled by default in
kenddue toMULTICHANNEL=1inkend.conf. Disable by settingMULTICHANNEL=0. Customize ports using--portand--subportflags. - Single-Channel: Uses one port (default 32323). Active when
MULTICHANNELis not set or set to0.
How Multi-Channel Works
Multi-channel separates different message types onto dedicated ports:
- Main Port: Handles block-related messages (requests/responses for hash, header, body, receipt) and consensus messages (Request, Preprepare, Prepare, Commit, RoundChange). The meaning of the messages can be found in PBFT.
- Subport: Handles transaction messages.
This separation enhances network stability: if one port fails, the other continues operating. For example, if the subport (typically congested during high traffic) fails, the main port maintains essential block and consensus operations.
Connection Establishment
- Multi-Channel to Multi-Channel: Both ports are used.
- Other Cases (Multi-Channel to Single-Channel or Single-Channel to Single-Channel): A single port is used.
If a node attempts to connect without specifying a subport, it initially connects using a single port. During the handshake, if the peer is multi-channel, the connection is re-established using both ports.
Port Configuration (KNI)
See the KNI scheme for details. Default ports are 32323 (main) and 32324 (sub).
Integration with KNI
Multi-channel integrates with KNI for node discovery and connection. KNI URLs allow specifying both main and subports.
Implementation Note
Kaia's multi-channel implementation deviates slightly from the original specification. While the details of this deviation are beyond the scope of this document, the core principles of enhanced network communication and robustness remain central to Kaia's operation. This information is primarily relevant for node operators and developers.
In summary, multi-channel enhances Kaia's network by segregating message traffic, improving efficiency and resilience. While providing advanced configuration options for node operators, the system remains transparent to general users.