What's New
Explore our latest updates and additions to the docs.
Searcher's Guide to Kaia v2.1 MEV Auction SDK
Use the Kaia v2.1 MEV Auction SDK to deposit funds, submit sealed bids, and participate in MEV opportunity auctions on the Kaia network.
Node Storage Optimization in Kaia v2.1
Explore data compression and FlatTrie features to effectively optimize node storage introduced in Kaia v2.1.
New AI-Powered Search is Live on Kaia Docs!
Integrate an AI search tool for documentation to provide automatically trained answers and built-in analytics.
SDK Documentation
Build freely with tools tailored for your language.
Seamlessly integrate with Kaia Network using our enhanced SDKs for JavaScript, Java, Python and more. Built on trusted foundations like Ethers, Web3.js, Web3j, and Web3.py, our libraries give you the power to submit transactions, read smart contracts, and develop complex applications with extended functionality - all in your preferred programming language.
View More SDKs →JSON-RPC API Reference
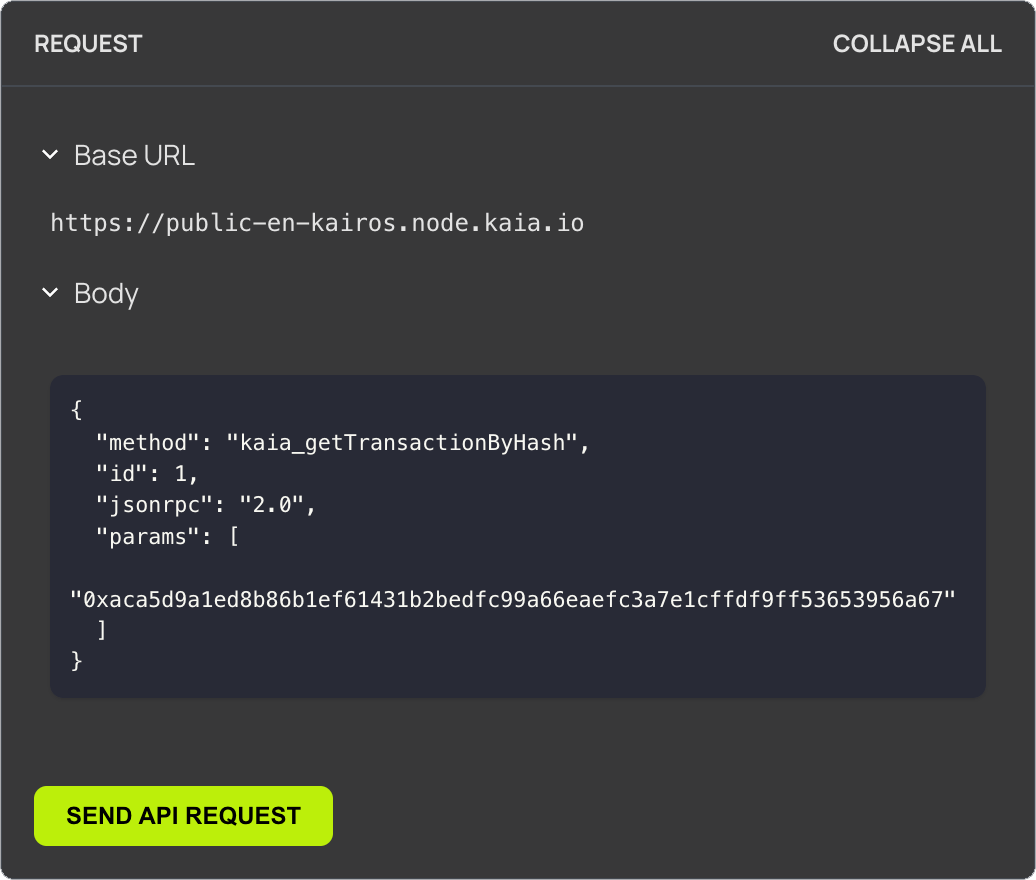
Discover and Engage with Kaia's JSON-RPC APIs
Unlock Kaia's full potential with our interactive API documentation. Test API calls directly in the docs, explore detailed request and response examples, and generate code snippets in curl, Python, Node.js, and Java. Whether developing new applications or integrating with existing systems, our comprehensive API reference provides the tools for efficient development on the Kaia platform.
Get started with Kaia's JSON RPC APIs →