チェーンリンクCCIPを用いたKaia上でのクロスチェーンNFTの構築:実践ガイド
はじめに
NFTはブロックチェーン技術の最も認知度の高いユースケースの1つとなっており、ユニークで検証可能なデジタル資産の創造を可能にしている。 しかし、従来のNFTの実装は単一のブロックチェーンに縛られていた。 この制限は柔軟性を低下させ、コミュニティ、流動性、有用性が異なる生態系を自由に行き来することを妨げる。
クロスチェーンNFTは、NFTの一意性と出所を保持したままブロックチェーン間をシームレスに移動できるようにすることで、この課題を解決します。 チェーンリンクのCCIP(Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol)により、開発者は標準化された安全なメッセージングフレームワークを使用して、チェーン間の信頼性の高いブリッジを構築することができます。
このガイドでは、バーン&ミントモデルを使用してCrosschain NFTを構築し、デプロイします。 NFTはソースチェインで焼かれ、デスティネーションチェインで同じtokenIdとメタデータで再鋳造される。
前提条件
始める前に、以下のセットアップが完了していることを確認してください:
- Node.js および npm
- ハードハット
- インストールする:npm install --save-dev hardhat`
- プロジェクトを初期化する:
npx hardhat --init
- メタマスク ウォレット
- 開発用ウォレットを作成または設定する。
- MetaMaskにKaia Kairos TestnetとEthereum Sepoliaネットワークの両方を追加する。
- 蛇口からのテスト・トークン
- ファイルベース アカウント
- NFTメタデータのアップロードと取得に必要(IPFSストレージ)。
クロスチェーンNFTはどのように機能するのか?
NFTは単一のブロックチェーン上に記録された固有のデジタルトークンです。 鋳造、送金、所有権などの中核的な動作は、そのチェーンに結びついたスマートコントラクトによって定義される。 このため、NFTは追加的な仕組みなしにブロックチェーン間を自然に移動することはできない。 相互運用性を実現するために、開発者はコンパニオンコントラクトを複数のチェーンに展開し、クロスチェーン・メッセージングを通じてそれらをリンクさせる。 その結果、クロスチェーンNFT:ブロックチェーンをまたがって存在する同等のトークンだが、いつでもアクティブなのは1つのコピーだけである。
クロスチェーンNFTは通常、3つの方法のいずれかで実装される:
-
Burn and mint:NFTはソースチェーンで焼かれ、デスティネーションチェーンで同等のものが鋳造される。
-
ロックとミント:NFTはソースチェーン上でロックされ、デスティネーション上で複製が鋳造される。 返却するには、複製を焼いてオリジナルのロックを解除する必要がある。
-
ロックとアンロック:同一のコレクションが複数のチェーンに展開される。 オーナーはあるチェーンのNFTをロックし、別のチェーンのNFTのロックを解除する。
このガイドでは、Crosschain NFTにburn and mintモデルを使用する。 NFTは、チェーンリンクCCIPによって、あるチェーンから取り除かれ、別のチェーンに再作成される。
はじめに
このガイドでは、Chainlink CCIPを使用して、Kaia Kairos TestnetとEthereum Sepoliaの間でクロスチェーンNFTを作成し、転送します。
最後には、次のことができるようになるだろう:
- Kairos TestnetとEthereum Sepoliaの両方に設定されたHardhatプロジェクトの初期化
- Chainlink CCIPコントラクトとインタフェースを依存関係として追加する
- クロスチェーン送金のためのバーンアンドミントメカニズムを備えたクロスチェーンNFT契約の導入
- 両方のネットワークに契約を展開し、チェーンをまたいでNFTを送信する。
ハードハット・プロジェクトの作成
このチュートリアルでは、Hardhat 3を使用して、コントラクトをデプロイし、対話します。 Hardhat 3は、暗号化されたキーストアのネイティブサポート、Solidityでテストを記述する機能、プロジェクトツールの改善などの新機能を提供します。
以下の手順に従ってプロジェクトをセットアップしてください:
-
Node.jsとnpmのインストールを確認する
以下のコマンドを実行して、Node.jsとnpmがインストールされていることを確認する:
node -vnpm -v
-
新しいプロジェクト・ディレクトリを初期化する
新しいフォルダを作成し、その中に移動して、Node.jsプロジェクトを初期化する:
mkdir ccip-nft-kaia-hardhat-example cd ccip-nft-kaia-hardhat-example npm init -y
-
ハードハット・プロジェクトの作成
走れ:
npx hardhat --init
プロンプトが表示されたら、Node.js テストランナーと ethers を含むサンプルプロジェクトを選択します。 カレント・ディレクトリで初期化し、必要な依存関係をすべてインストールする。
必要な契約の取り付け
チェーンリンクCCIP契約を取り付ける:
npm i @chainlink/contracts-ccip --save-dev
標準的なチェーンリンク契約を取り付ける:
npm i @chainlink/contracts --save-dev
OpenZeppelinコントラクトをインストールする(ERC-721とその他の基本実装を提供する):
npm i @openzeppelin/contracts --save-dev
NFTメタデータの設定
契約書を書く前に、NFTの仕様を定義しておこう。 各NFTは、その名前、説明、画像を記述するメタデータを必要とし、JSONファイルに格納され、IPFS上でホストされる。
このガイドでは、画像とメタデータの両方を保存するためにFilebaseを使用します。 独自のNFTを作成したい場合は、画像とメタデータのJSONファイルをFilebaseを通じてIPFSにアップロードしてください。 アップロード後、Filesタブでファイル名をクリックし、IPFSのURLをコピーします。 こんな感じだ:
https://disastrous-turquoise-parakeet.myfilebase.com/ipfs/QmY1LZF8JHo2r3h4X5VzLLXtJujqnBFGTyo2aqR9joXnt8
以下は、使用可能なメタデータ・ファイルのサンプルです:
{ "name": "Kairos NFT", "description": "gkaia frens! gazuaaaaa!!!", "image": "https://disastrous-turquoise-parakeet.myfilebase.com/ipfs/QmRvQc4wZCp6NF7dFL4ywiWTG7FSH3KKGUAkXGgsdYfcKi"}
スマートコントラクトの記述
このセクションでは、チェーンリンクCCIPのバーン&ミントモデルを使用して、ブロックチェーン間のNFT転送を可能にするコントラクトを実装します。
プロジェクトのコントラクトディレクトリにCrosschainNFT.solという名前で新規ファイルを作成し、以下のコードを貼り付けます:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MITpragma solidity ^0.8.20;import {ERC721} from "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC721/ERC721.sol";import {ERC721URIStorage} from "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC721/extensions/ERC721URIStorage.sol";import {ERC721Burnable} from "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC721/extensions/ERC721Burnable.sol";import {IERC20} from "@openzeppelin/contracts/interfaces/IERC20.sol";import {SafeERC20} from "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/utils/SafeERC20.sol";import {ReentrancyGuard} from "@openzeppelin/contracts/utils/ReentrancyGuard.sol";import {Client} from "@chainlink/contracts-ccip/contracts/libraries/Client.sol";import {IRouterClient} from "@chainlink/contracts-ccip/contracts/interfaces/IRouterClient.sol";import {IAny2EVMMessageReceiver} from "@chainlink/contracts-ccip/contracts/interfaces/IAny2EVMMessageReceiver.sol";import {OwnerIsCreator} from "@chainlink/contracts/src/v0.8/shared/access/OwnerIsCreator.sol";import {LinkTokenInterface} from "@chainlink/contracts/src/v0.8/shared/interfaces/LinkTokenInterface.sol";/** * THIS IS AN EXAMPLE CONTRACT THAT USES HARDCODED VALUES FOR CLARITY. * THIS IS AN EXAMPLE CONTRACT THAT USES UN-AUDITED CODE. * DO NOT USE THIS CODE IN PRODUCTION. */ // Source chain is Ethereum Sepolia // Destination chain is Kairos Testnetcontract CrosschainNFT is ERC721, ERC721URIStorage, ERC721Burnable, IAny2EVMMessageReceiver, ReentrancyGuard, OwnerIsCreator { using SafeERC20 for IERC20; enum PayFeesIn { Native, LINK } error InvalidRouter(address router); error OnlyOnEthereumSepolia(); error NotEnoughBalanceForFees(uint256 currentBalance, uint256 calculatedFees); error NothingToWithdraw(); error FailedToWithdrawEth(address owner, address target, uint256 value); error ChainNotEnabled(uint64 chainSelector); error SenderNotEnabled(address sender); error OperationNotAllowedOnCurrentChain(uint64 chainSelector); struct crosschainNFTDetails { address crosschainNFTAddress; bytes ccipExtraArgsBytes; } uint256 constant ETHEREUM_SEPOLIA_CHAIN_ID = 11155111; string tokenNFTURI = "https://disastrous-turquoise-parakeet.myfilebase.com/ipfs/QmY1LZF8JHo2r3h4X5VzLLXtJujqnBFGTyo2aqR9joXnt8"; IRouterClient internal immutable i_ccipRouter; LinkTokenInterface internal immutable i_linkToken; uint64 private immutable i_currentChainSelector; uint256 private _nextTokenId; mapping(uint64 destChainSelector => crosschainNFTDetails crosschainNFTPerChain) public s_chains; event ChainEnabled(uint64 chainSelector, address xNftAddress, bytes ccipExtraArgs); event ChainDisabled(uint64 chainSelector); event CrossChainSent( address from, address to, uint256 tokenId, uint64 sourceChainSelector, uint64 destinationChainSelector ); event CrossChainReceived( address from, address to, uint256 tokenId, uint64 sourceChainSelector, uint64 destinationChainSelector ); modifier onlyRouter() { if (msg.sender != address(i_ccipRouter)) { revert InvalidRouter(msg.sender); } _; } modifier onlyOnEthereumSepolia() { if (block.chainid != ETHEREUM_SEPOLIA_CHAIN_ID) { revert OnlyOnEthereumSepolia(); } _; } modifier onlyEnabledChain(uint64 _chainSelector) { if (s_chains[_chainSelector].crosschainNFTAddress == address(0)) { revert ChainNotEnabled(_chainSelector); } _; } modifier onlyEnabledSender(uint64 _chainSelector, address _sender) { if (s_chains[_chainSelector].crosschainNFTAddress != _sender) { revert SenderNotEnabled(_sender); } _; } modifier onlyOtherChains(uint64 _chainSelector) { if (_chainSelector == i_currentChainSelector) { revert OperationNotAllowedOnCurrentChain(_chainSelector); } _; } constructor(address ccipRouterAddress, address linkTokenAddress, uint64 currentChainSelector) ERC721("Cross Chain NFT", "XNFT") { if (ccipRouterAddress == address(0)) revert InvalidRouter(address(0)); i_ccipRouter = IRouterClient(ccipRouterAddress); i_linkToken = LinkTokenInterface(linkTokenAddress); i_currentChainSelector = currentChainSelector; } function mint() external onlyOnEthereumSepolia { uint256 tokenId = _nextTokenId++; _safeMint(msg.sender, tokenId); _setTokenURI(tokenId, tokenNFTURI); } function enableChain(uint64 chainSelector, address crosschainNFTAddress, bytes memory ccipExtraArgs) external onlyOwner onlyOtherChains(chainSelector) { s_chains[chainSelector] = crosschainNFTDetails({crosschainNFTAddress: crosschainNFTAddress, ccipExtraArgsBytes: ccipExtraArgs}); emit ChainEnabled(chainSelector, crosschainNFTAddress, ccipExtraArgs); } function disableChain(uint64 chainSelector) external onlyOwner onlyOtherChains(chainSelector) { delete s_chains[chainSelector]; emit ChainDisabled(chainSelector); } function crossChainTransferFrom( address from, address to, uint256 tokenId, uint64 destinationChainSelector, PayFeesIn payFeesIn ) external nonReentrant onlyEnabledChain(destinationChainSelector) returns (bytes32 messageId) { string memory tokenUri = tokenURI(tokenId); _burn(tokenId); Client.EVM2AnyMessage memory message = Client.EVM2AnyMessage({ receiver: abi.encode(s_chains[destinationChainSelector].crosschainNFTAddress), data: abi.encode(from, to, tokenId, tokenUri), tokenAmounts: new Client.EVMTokenAmount[](0), extraArgs: s_chains[destinationChainSelector].ccipExtraArgsBytes, feeToken: payFeesIn == PayFeesIn.LINK ? address(i_linkToken) : address(0) }); // Get the fee required to send the CCIP message uint256 fees = i_ccipRouter.getFee(destinationChainSelector, message); if (payFeesIn == PayFeesIn.LINK) { if (fees > i_linkToken.balanceOf(address(this))) { revert NotEnoughBalanceForFees(i_linkToken.balanceOf(address(this)), fees); } // Approve the Router to transfer LINK tokens on contract's behalf. It will spend the fees in LINK i_linkToken.approve(address(i_ccipRouter), fees); // Send the message through the router and store the returned message ID messageId = i_ccipRouter.ccipSend(destinationChainSelector, message); } else { if (fees > address(this).balance) { revert NotEnoughBalanceForFees(address(this).balance, fees); } // Send the message through the router and store the returned message ID messageId = i_ccipRouter.ccipSend{value: fees}(destinationChainSelector, message); } emit CrossChainSent(from, to, tokenId, i_currentChainSelector, destinationChainSelector); } /// @inheritdoc IAny2EVMMessageReceiver function ccipReceive(Client.Any2EVMMessage calldata message) external virtual override onlyRouter nonReentrant onlyEnabledChain(message.sourceChainSelector) onlyEnabledSender(message.sourceChainSelector, abi.decode(message.sender, (address))) { uint64 sourceChainSelector = message.sourceChainSelector; (address from, address to, uint256 tokenId, string memory tokenUri) = abi.decode(message.data, (address, address, uint256, string)); _safeMint(to, tokenId); _setTokenURI(tokenId, tokenUri); emit CrossChainReceived(from, to, tokenId, sourceChainSelector, i_currentChainSelector); } function withdraw(address _beneficiary) public onlyOwner { uint256 amount = address(this).balance; if (amount == 0) revert NothingToWithdraw(); (bool sent,) = _beneficiary.call{value: amount}(""); if (!sent) revert FailedToWithdrawEth(msg.sender, _beneficiary, amount); } function withdrawToken(address _beneficiary, address _token) public onlyOwner { uint256 amount = IERC20(_token).balanceOf(address(this)); if (amount == 0) revert NothingToWithdraw(); IERC20(_token).safeTransfer(_beneficiary, amount); } function tokenURI(uint256 tokenId) public view override(ERC721, ERC721URIStorage) returns (string memory) { return super.tokenURI(tokenId); } function getCCIPRouter() public view returns (address) { return address(i_ccipRouter); } function supportsInterface(bytes4 interfaceId) public view override(ERC721, ERC721URIStorage) returns (bool) { return interfaceId == type(IAny2EVMMessageReceiver).interfaceId || super.supportsInterface(interfaceId); }}
コード・チュートリアル
CrosschainNFTはチェーンリンクCCIPを統合し、ブロックチェーン間でNFTを移転するERC-721コントラクトです。 ソースチェーン上のNFTを焼き、同じtokenIdとtokenURIでデスティネーションに再mintする。 この契約は、enableChainを通じて承認されたデスティネーションチェーンのレジストリを維持し、クロスチェーンメッセージングをチェーンリンクルーター(IRouterClient)に依存し、ネイティブガストークンまたはLINKでの手数料支払いをサポートする。
主な機能
- イネーブルチェーン
コントラクトの所有者が宛先ブロックチェーンを登録できるようにする。 s_chainsのマッピングに相手のNFTコントラクトアドレスとCCIP引数を格納し、チェーンを有効な転送先としてホワイトリスト化する。 セットアップが完了すると、ChainEnabledイベントが発生する。
- クロスチェーン転送元
チェインをまたいだNFTの転送を実行する。 まず、デスティネーションチェーンが有効であることを確認し、次にNFTメタデータ(tokenURI)を取得し、ソースチェーン上でトークンをバーンします。 次に、CCIPメッセージに移籍の詳細を記載し、必要な手数料を計算し、LINKかネイティブ・ガスで支払う。 メッセージがルーターを経由して送信されると、CrossChainSent イベントが発生し、転送のログが記録される。
CrosschainNFT.sol`のコアフローが明らかになったところで、次のステップに進もう。
スマート・コントラクトのコンパイル
スマート・コントラクトをコンパイルするには、以下を実行する:
npx hardhat build
スマートコントラクトの導入
このセクションでは、必要な変数を設定し、「CrosschainNFT.sol」コントラクトをEthereum Sepolia(ソースチェーン)とKairos Testnet(デスティネーションチェーン)の両方にデプロイします。
暗号化キーストアの使用
Hardhat 3の利点の一つは、秘密鍵やRPC URLのような機密性の高い値を、プレーンテキストファイルではなく、暗号化されたキーストアに保存できることです。 このガイドでは、セポリアとカイロスの_PRIVATE_KEY_と_RPC URL_を暗号化します。
**秘密鍵を追加する
npx hardhat keystore set PRIVATE_KEY
このコマンドを初めて実行すると、Hardhatはキーストアのパスワードを作成するよう促します。 このパスワードは、値を追加したり更新したりするときに必要になります。
各ネットワークのRPC URLを追加する。
npx hardhat keystore set KAIROS_RPC_URLnpx hardhat keystore set SEPOLIA_RPC_URL
最後に、hardhat.config.tsファイルを編集して、これらの暗号化された値をロードし、2つのネットワークを設定する。
import type { HardhatUserConfig } from "hardhat/config";import hardhatToolboxMochaEthersPlugin from "@nomicfoundation/hardhat-toolbox-mocha-ethers";import { configVariable } from "hardhat/config";const config: HardhatUserConfig = { plugins: [hardhatToolboxMochaEthersPlugin], solidity: { profiles: { default: { version: "0.8.28", }, production: { version: "0.8.28", settings: { optimizer: { enabled: true, runs: 200, }, }, }, }, }, networks: { hardhatMainnet: { type: "edr-simulated", chainType: "l1", }, hardhatOp: { type: "edr-simulated", chainType: "op", }, kairosTestnet: { type: "http", chainType: "l1", url: configVariable("KAIROS_RPC_URL"), accounts: [configVariable("PRIVATE_KEY")], }, ethereumSepolia: { type: "http", chainType: "l1", url: configVariable("SEPOLIA_RPC_URL"), accounts: [configVariable("PRIVATE_KEY")], }, },};export default config;
次のステップは、CrosschainNFTスマートコントラクトをそれぞれEthereum SepoliaとKairos Testnetにデプロイすることである。
CrosschainNFT.solをEthereum Sepoliaにデプロイする。
デプロイする前に、Chainlink CCIP DirectoryからEthereum Sepoliaの以下の値を取得してください:
- チェーンセレクター
- CCIPルーターアドレス
- LINKトークンのアドレス
これらの値は、デプロイ スクリプトで必要になります。 次に、プロジェクトの ignition/modules フォルダに移動し、deployEthereumSepolia.ts という名前の新規ファイルを作成し、以下のコードを貼り付ける:
// This setup uses Hardhat Ignition to manage smart contract deployments.// Learn more about it at https://hardhat.org/ignitionimport { buildModule } from "@nomicfoundation/hardhat-ignition/modules";const ETHEREUM_SEPOLIA_ROUTER_ADDRESS = `0x0BF3dE8c5D3e8A2B34D2BEeB17ABfCeBaf363A59`;const ETHEREUM_SEPOLIA_LINK_TOKEN_ADDRESS = `0x779877A7B0D9E8603169DdbD7836e478b4624789`;const ETHEREUM_SEPOLIA_CHAIN_SELECTOR = `16015286601757825753`;const CrosschainNFTSepoliaModule = buildModule("CrosschainNFTSepoliaModule", (m) => { const crosschainNFTSepolia = m.contract("CrosschainNFT", [ETHEREUM_SEPOLIA_ROUTER_ADDRESS, ETHEREUM_SEPOLIA_LINK_TOKEN_ADDRESS, ETHEREUM_SEPOLIA_CHAIN_SELECTOR], { }); return { crosschainNFTSepolia };});export default CrosschainNFTSepoliaModule;
デプロイスクリプトを実行します:
npx hardhat ignition deploy ignition/modules/deployEthereumSepolia.ts --network ethereumSepolia
KairosテストネットにCrosschainNFT.solをデプロイする
デプロイ前に、Chainlink CCIP DirectoryからKairos Testnetの以下の値を取得してください:
- チェーンセレクター
- CCIPルーターアドレス
- LINKトークンのアドレス
これらの値は、デプロイ スクリプトで必要になります。 次に、プロジェクトの ignition/modules フォルダに移動し、deployKairosTestnet.ts という名前のファイルを新規作成し、以下のコードを貼り付けます:
// This setup uses Hardhat Ignition to manage smart contract deployments.// Learn more about it at https://hardhat.org/ignitionimport { buildModule } from "@nomicfoundation/hardhat-ignition/modules";const KAIROS_TESTNET_ROUTER_ADDRESS = `0x41477416677843fCE577748D2e762B6638492755`;const KAIROS_TESTNET_LINK_TOKEN_ADDRESS = `0xAF3243f975afe2269Da8Ffa835CA3A8F8B6A5A36`;const KAIROS_TESTNET_CHAIN_SELECTOR = `2624132734533621656`;const CrosschainNFTKairosModule = buildModule("CrosschainNFTKairosModule", (m) => { const crosschainNFTKairos = m.contract("CrosschainNFT", [KAIROS_TESTNET_ROUTER_ADDRESS, KAIROS_TESTNET_LINK_TOKEN_ADDRESS, KAIROS_TESTNET_CHAIN_SELECTOR], { }); return { crosschainNFTKairos };});export default CrosschainNFTKairosModule;
デプロイスクリプトを実行します:
npx hardhat ignition deploy ignition/modules/deployKairosTestnet.ts --network kairosTestnet
スマート・コントラクトとの対話
このセクションでは、enableChain、mint、crosschainTransferの各関数を実行することで、デプロイされたCrosschainNFTスマートコントラクトと対話する。
ステップ 1: イーサリアム・セポリアで enableChain を呼び出す
enableChainを呼び出す前に、以下の値を用意する:
- Sepoliaコントラクトアドレス:Ethereum Sepolia上にデプロイされたCrosschainNFT.solコントラクトのアドレス。
- Kairos contract address: Kairos TestnetにデプロイされたCrosschainNFT.solコントラクトのアドレス。
- **チェーンセレクタ2624132734533621656 (Kairos TestnetのCCIPチェーンセレクタ)。
- CCIP extraArgs:0x97a657c90000000000000000000000000007A120 (これは、gasLimitが500,000に設定されたextraArgsのデフォルトのエンコード値です)。
次に、scriptsフォルダに新しいTypeScriptファイルを作成し、名前をenableChainSepolia.tsとし、以下のコードを貼り付ける:
// scripts/enableChainSepolia.tsimport { network } from "hardhat";async function main() { const connection = await network.connect({ network: "ethereumSepolia" }); const { ethers } = connection; const [signer] = await ethers.getSigners(); console.log(`Using account: ${signer.address}`); // Get the contract factory by name const CrosschainNFT = await ethers.getContractFactory("CrosschainNFT", signer); // Contract addresses and parameters const crosschainNFTAddressEthereumSepolia = `0xb1fe42BBd7842703820C7480c22409b872319B22`; const crosschainNFTAddressKairosTestnet = `0x8c464Bb9Bf364F68b898ed0708b8f5F66EF6Cfb1`; const chainSelectorKairosTestnet = `2624132734533621656`; const ccipExtraArgs = `0x97a657c9000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007A120`; // Attach to the deployed contract const crosschainNFTSepolia = CrosschainNFT.attach(crosschainNFTAddressEthereumSepolia); console.log(`Enabling chain for Kairos Testnet...`); const tx = await crosschainNFTSepolia.enableChain( chainSelectorKairosTestnet, crosschainNFTAddressKairosTestnet, ccipExtraArgs ); console.log(`Transaction hash: ${tx.hash}`); console.log(`Waiting for confirmation...`); const receipt = await tx.wait(); console.log(`Transaction confirmed in block: ${receipt?.blockNumber}`); console.log(`Chain enabled successfully!`);}main().catch((error) => { console.error(error); process.exitCode = 1;});
次のコマンドを実行して関数を呼び出す:
npx hardhat run scripts/enableChainSepolia.ts --network ethereumSepolia
ステップ2:Kairos TestnetでenableChainを呼び出す
enableChainを呼び出す前に、以下の値を用意する:
- Kairosコントラクトアドレス:KairosテストネットにデプロイされたCrosschainNFT.solコントラクトのアドレス
- Sepoliaコントラクトアドレス:Ethereum Sepolia上にデプロイされたCrosschainNFT.solコントラクトのアドレス
- **チェーンセレクタ16015286601757825753 (Kairos TestnetのCCIPチェーンセレクタ)
- CCIP extraArgs:0x97a657c9000000000000000000000007A120 (これは、gasLimitが500,000に設定されたextraArgsのデフォルトのエンコード値です)
次に、scriptsフォルダに新しいTypeScriptファイルを作成し、名前をenableChainKairos.tsとし、以下のコードを貼り付けます:
// scripts/enableChainKairos.tsimport { network } from "hardhat";async function main() { const connection = await network.connect({ network: "kairosTestnet" }); const { ethers } = connection; const [signer] = await ethers.getSigners(); console.log(`Using account: ${signer.address}`); // Get the contract factory by name const CrosschainNFT = await ethers.getContractFactory("CrosschainNFT", signer); // Contract addresses and parameters const crosschainNFTAddressKairosTestnet = `0x8c464Bb9Bf364F68b898ed0708b8f5F66EF6Cfb1`; const crosschainNFTAddressEthereumSepolia = `0xb1fe42BBd7842703820C7480c22409b872319B22`; const chainSelectorEthereumSepolia = `16015286601757825753`; const ccipExtraArgs = `0x97a657c9000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000007A120`; // Attach to the deployed contract on Kairos const crosschainNFTKairos = CrosschainNFT.attach(crosschainNFTAddressKairosTestnet); console.log(`Enabling chain for Ethereum Sepolia...`); const tx = await crosschainNFTKairos.enableChain( chainSelectorEthereumSepolia, crosschainNFTAddressEthereumSepolia, ccipExtraArgs ); console.log(`Transaction hash: ${tx.hash}`); console.log(`Waiting for confirmation...`); const receipt = await tx.wait(); console.log(`Transaction confirmed in block: ${receipt?.blockNumber}`); console.log(`Chain enabled successfully!`);}main().catch((error) => { console.error(error); process.exitCode = 1;});
次のコマンドを実行して関数を呼び出す:
npx hardhat run scripts/enableChainKairos.ts --network KairosTestnet
ステップ3:イーサリアム・セポリア上のLINKでコントラクトに資金を提供する
CCIPの手数料を賄うには、イーサリアム・セポリア(crosschainNFTAddressEthereumSepolia)上に展開されたCrosschainNFTコントラクトにLINKで資金を提供します。 付属の蛇口からテストLINKを入手できる。 このガイドでは、3LINKを送信すれば十分である。
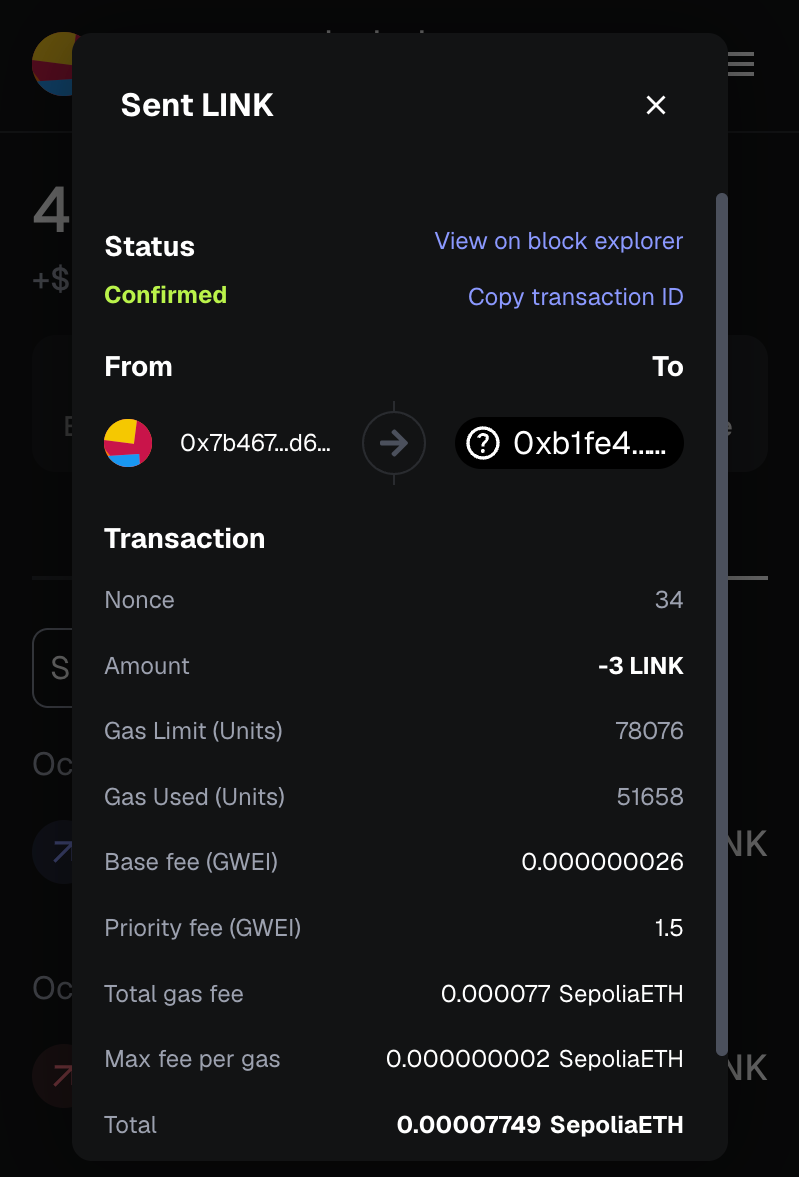
ステップ4:Ethereum Sepolia上で新しいCrosschainNFTをミントする
次に、Ethereum SepoliaにデプロイされたCrosschainNFTコントラクト上で新たなNFTをミントする。
scriptsフォルダに新しいTypeScriptファイルを作成し、名前をmint.tsとし、以下のコードを貼り付けます:
// scripts/mint.tsimport { network } from "hardhat";async function main() { // Connect to the network const connection = await network.connect({ network: "ethereumSepolia" });if (connection.networkName !== "ethereumSepolia") { console.error(`Must be called from Ethereum Sepolia`); process.exitCode = 1; return; } const { ethers } = connection; const [signer] = await ethers.getSigners(); console.log(`Using account: ${signer.address}`); // Get the contract factory const CrosschainNFT = await ethers.getContractFactory("CrosschainNFT", signer); const crosschainNFTAddressEthereumSepolia = `0xb1fe42BBd7842703820C7480c22409b872319B22` // Attach to the deployed contract const crosschainNFT = CrosschainNFT.attach(crosschainNFTAddressEthereumSepolia); console.log(`Minting NFT...`); const tx = await crosschainNFT.mint(); console.log(`Transaction hash: ${tx.hash}`); console.log(`Waiting for confirmation...`); const receipt = await tx.wait(); console.log(`Transaction confirmed in block: ${receipt?.blockNumber}`); console.log(`NFT minted successfully!`);}main().catch((error) => { console.error(error); process.exitCode = 1;});
このスクリプトは鋳造処理を行い、クロスチェーン転送のためにNFTを準備する。
次のコマンドを実行して関数を呼び出す:
npx hardhat run scripts/mint.ts --network ethereumSepolia
ステップ5:チェーン間のNFT�の移動
Ethereum Sepoliaでは、crossChainTransferFrom関数を呼び出してNFTをKairos Testnetに送信します。
以下の値を設定する:
- from:イーサリアム・セポリア上のあなたのEOAアドレス
- **宛先:Kairos TestnetのEOAアドレス(ご自身のアドレスでも可)
- tokenId:譲渡したい NFT の ID
- DestinationChainSelector:2624132734533621656 (Kairos TestnetのCCIPチェーンセレクタ)
- payFeesIn:1 (CCIPの料金がLINKで支払われることを示す)
転送スクリプトの実行
scriptsフォルダに新しいTypeScriptファイルを作成し、名前をcrossChainTransferNFT.tsとし、以下のコードを貼り付けます:
// scripts/crossChainTransferNFT.tsimport { network } from "hardhat";async function main() { // Connect to the network const connection = await network.connect({ network: "ethereumSepolia" }); // Check if we're on the correct network if (connection.networkName !== "ethereumSepolia") { console.error(`Must be called from Ethereum Sepolia`); process.exitCode = 1; return; } const { ethers } = connection; const [signer] = await ethers.getSigners(); console.log(`Using account: ${signer.address}`); // Get the contract factory const CrosschainNFT = await ethers.getContractFactory("CrosschainNFT", signer); const crosschainNFTAddressEthereumSepolia = `0xb1fe42BBd7842703820C7480c22409b872319B22`; // Transfer parameters const from = `0x7b467A6962bE0ac80784F131049A25CDE27d62Fb`; const to = `0x7b467A6962bE0ac80784F131049A25CDE27d62Fb`; const tokenId = 0; // Put NFT token id here const destinationChainSelector = "2624132734533621656"; // Kairos Testnet const payFeesIn = 1; // 0 - Native, 1 - LINK // Attach to the deployed contract const crosschainNFT = CrosschainNFT.attach(crosschainNFTAddressEthereumSepolia); const tx = await crosschainNFT.crossChainTransferFrom( from, to, tokenId, destinationChainSelector, payFeesIn ); console.log(`Transaction hash: ${tx.hash}`); console.log(`Waiting for confirmation...`); const receipt = await tx.wait(); console.log(`Transaction confirmed in block: ${receipt?.blockNumber}`); console.log(`Cross-chain transfer initiated successfully!`); console.log(`Note: The NFT will arrive on Kairos Testnet after CCIP processes the message.`);}main().catch((error) => { console.error(error); process.exitCode = 1;});
でスクリプトを実行する:
npx hardhat run scripts/crossChainTransferNFT.ts --network ethereumSepolia
転送を確認する
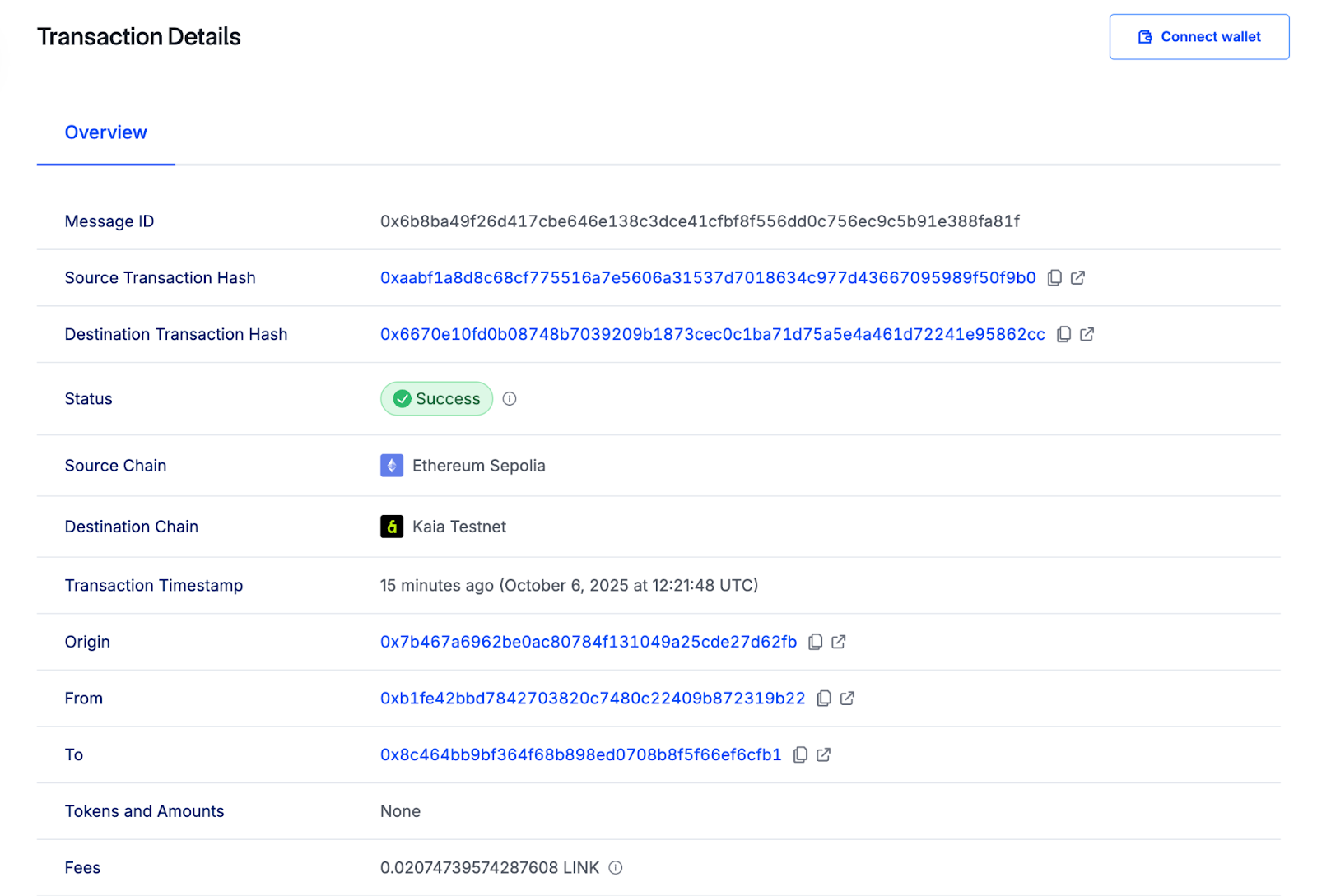
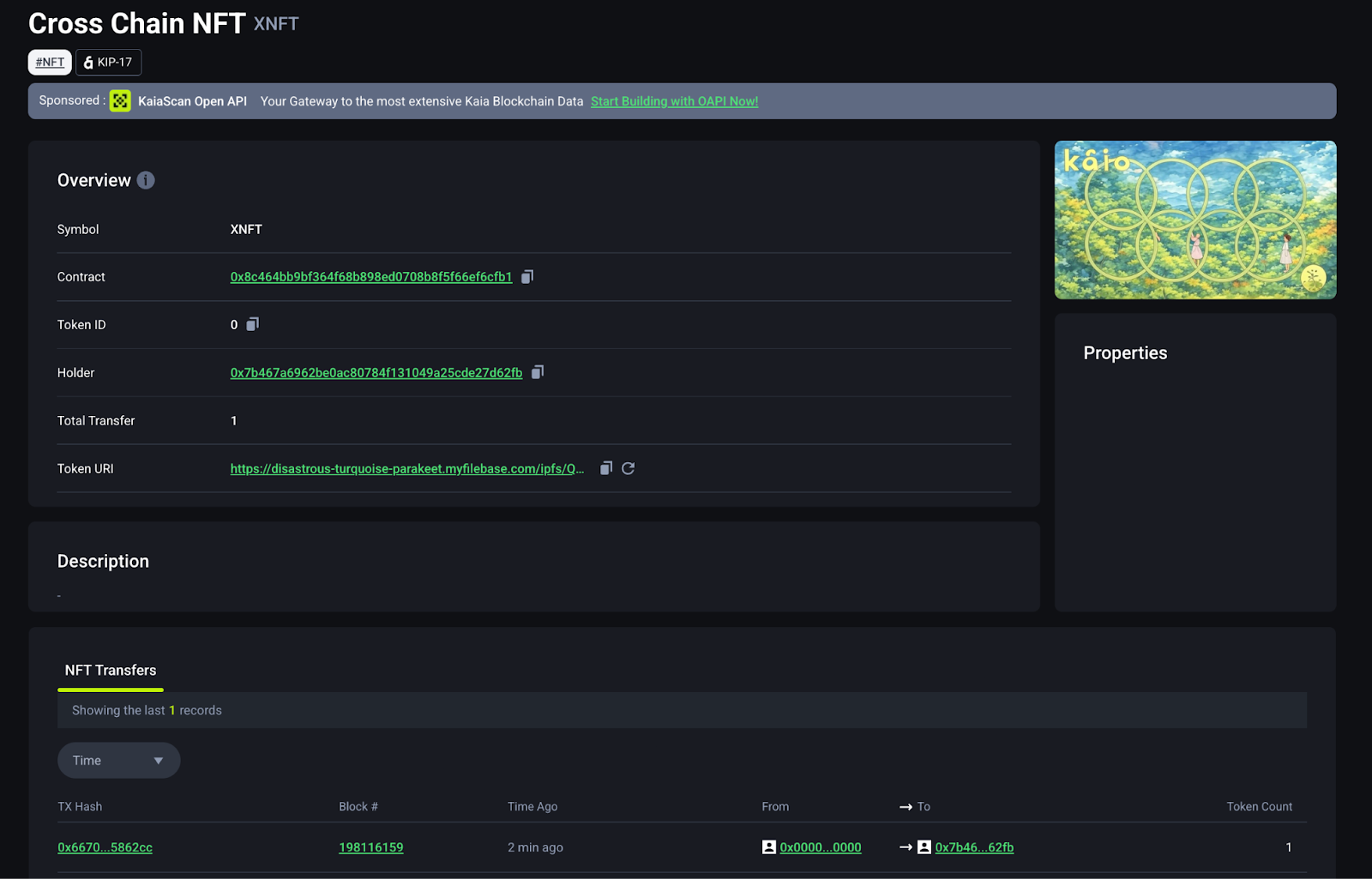
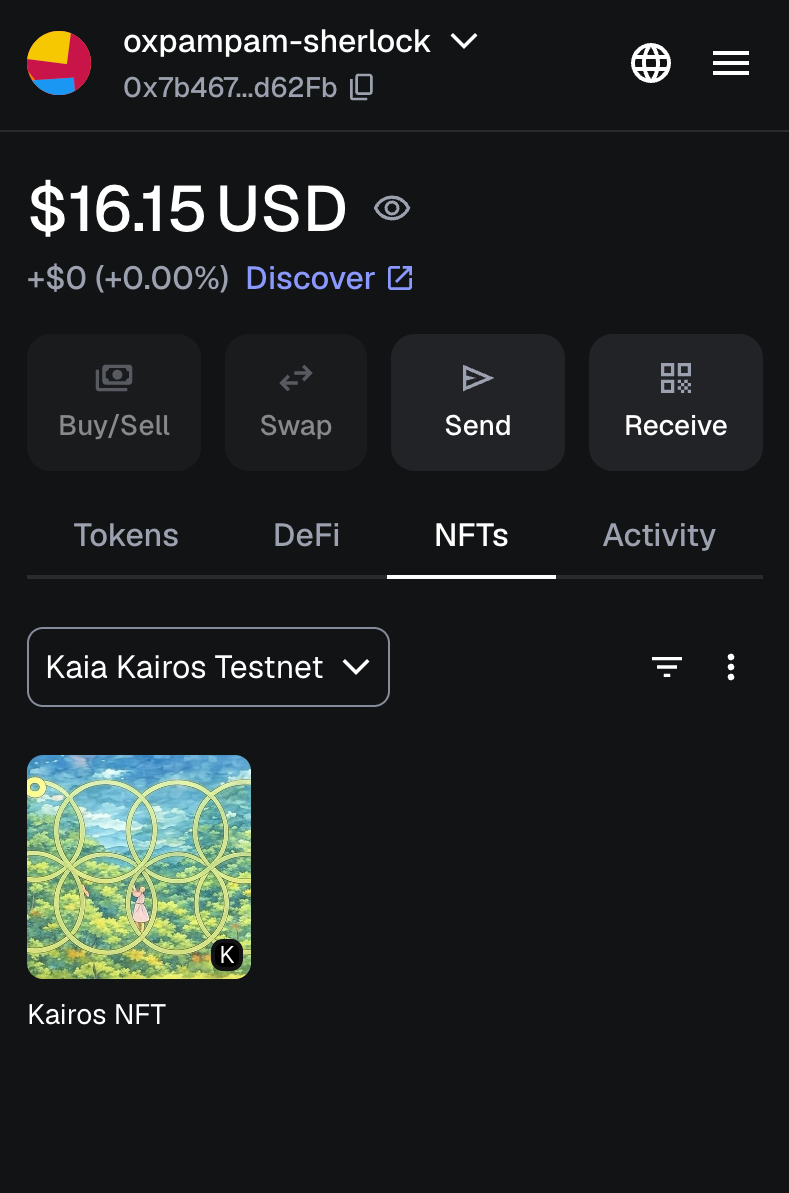
NFT が Kairos Testnet に到着したら、MetaMask ウォレットに追加します:
- MetaMaskのNFTタブを開く。
- NFTのインポートをクリックします。
- Kairos Testnet上のCrosschainNFTコントラクトアドレスと、受け取ったtokenId(例:0)を入力します。
NFTがMetaMaskウォレットに表示されます。
結論
このチュートリアルでは、Chainlink CCIPを使ってKaia Kairos TestnetとEthereum Sepoliaの間でバーン&ミントモデルを使ってNFTを転送する方法を学びました。
CCIPをより深く理解し、その他の使用例を調べるには、公式のChainlink CCIP Documentationをご覧ください。