Build Fee Delegation Example
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. How fee delegation works
- 2.1 Transaction signing by the sender
- 2.2 Transaction signing by the fee payer
- 3. Simple server and client for fee delegation
- 3.1 Thiết lập môi trường
- 3.2 Khách hàng của người gửi
- 3.2 Fee payer's server
- 4. Run example
- 4.1 Run
feepayer_server.js - 4.2 Run
sender_client.js - 4.3 Check
feepayer_server.js - 4.4 Xem trên Kaiascan
- 4.1 Run
1. Introduction
Hướng dẫn này sẽ hướng dẫn bạn cách tạo một ví dụ máy chủ-máy khách đơn giản bằng cách sử dụng Kaia SDK (ethers-ext) để chứng minh cách các giao dịch chuyển giá trị được ủy quyền theo phí hoạt động trên Kaia. Mã hướng dẫn và ví dụ được thử nghiệm trên mạng thử nghiệm Kairos.
2. How fee delegation works
Let's skim through how fee delegation works.
2.1 Transaction signing by the sender
Sender always should sign the transaction before sending a transaction.
Để ký một giao dịch, hãy sử dụng signTransaction để ký một giao dịch bằng khóa riêng được cung cấp.
const senderAddress = "SENDER_ADDRESS";const senderPrivateKey ="SENDER_PRIVATE_KEY";const recieverAddr = "RECEIVER_ADDRESS";// Tạo giao dịch mớilet tx = { type: TxType.FeeDelegatedValueTransfer, to: recieverAddr, value: parseKaia("0.01"), from: senderAddress,}; // Ký giao dịchtx = await senderWallet.populateTransaction(tx);console.log(tx);const senderTxHashRLP = await senderWallet.signTransaction(tx);console.log("senderTxHashRLP", senderTxHashRLP);
Nếu không có lỗi, thì senderTxHashRLP sẽ có giao dịch đã ký được ký bởi senderPrivateKey.
Bây giờ, bạn cần gửi senderTxHashRLP cho người trả phí. Có nhiều cách khác nhau để thực hiện điều này. Trong hướng dẫn này, chúng tôi sẽ cung cấp cho bạn một mã máy chủ-máy khách đơn giản làm ví dụ về việc gửi senderTxHashRLP đến người trả phí.
2.2 Transaction signing by the fee payer
Khi người trả phí nhận được senderTxHashRLP, người trả phí sẽ ký lại senderTxHashRLP bằng khóa riêng của họ và gửi giao dịch đến Kaia. The below code snippet illustrates the process.
Phương thức sendTransactionAsFeePayer sẽ ký giao dịch bằng khóa riêng của người trả phí được cung cấp trước khi gửi giao dịch. Trước khi chạy mã, vui lòng thay thế "FEEPAYER_ADDRESS" và "PRIVATE_KEY" bằng các giá trị thực tế.
Lưu ý rằng khi người trả phí gửi giao dịch đến Kaia thay mặt cho người gửi, thì loại giao dịch senderTxHashRLP phải là loại giao dịch FeeDelegatedValueTransfer.
const feePayerAddress = "FEEPAYER_ADDRESS";const feePayerPrivateKey = "FEEPAYER_PRIVATE_KEY"const sentTx = await feePayerWallet.sendTransactionAsFeePayer(senderTxHashRLP);console.log("tx đã gửi", sentTx);const rc = await sentTx.wait();console.log("biên lai", rc);
3. Máy chủ và máy khách đơn giản cho việc ủy quyền phí
Hãy viết một máy chủ và một client đơn giản sử dụng mã phân quyền phí ở trên.
3.1 Cài đặt môi trường
Chúng ta sẽ sử dụng npm init -y để thiết lập dự án Node.js của mình và cài đặt ethers-ext
mkdir feedelegation_servercd feedelegation_servernpm init -ynpm install - -save @kaiachain/ethers-ext@^1.2.0 ethers@6
@kaiachain/ethers-ext@^1.2.0 khuyến nghị sử dụng phiên bản node 22 hoặc mới hơn.
3.2 Khách hàng của người gửi
First, we are going to write a sender_client.js as below.
Trong ví dụ, vui lòng thay thế "SENDER_ADDRESS", "SENDER_PRIVATEKEY" và "RECEIVER_ADDRESS" bằng các giá trị thực tế.
const { Socket } = require("net");const client = new Socket();const { Wallet, TxType, parseKaia } = require("@kaiachain/ethers-ext").v6;const ethers = require("ethers");const senderAddress = "SENDER_ADDRESS";const senderPrivateKey = "SENDER_PRIVATE_KEY";const recieverAddr = "RECEIVER_ADDRESS";const sendFeeDelegateTx = async () => { try { const provider = new ethers.JsonRpcProvider("https://public-en-kairos.node.kaia.io"); const senderWallet = new Wallet(senderPrivateKey, provider); // Tạo giao dịch mới let tx = { type: TxType.FeeDelegatedValueTransfer, to: recieverAddr, value: parseKaia("0.01"), from: senderAddress, }; // Ký giao dịch tx = await senderWallet.populateTransaction(tx); console.log(tx); const senderTxHashRLP = await senderWallet.signTransaction(tx); console.log("senderTxHashRLP", senderTxHashRLP); if (!senderTxHashRLP) { throw new Error("Không thể tạo giao dịch thô"); } // Gửi giao dịch thô đã ký đến máy chủ của người trả phí client.connect(1337, "127.0.0.1", () => { console.log("Kết nối thành công với dịch vụ ủy quyền phí"); client.write(senderTxHashRLP); }); client.on("data", (data) => { console.log("Nhận dữ liệu từ máy chủ:", data.toString()); }); client.on("error", (error) => { console.error("Lỗi kết nối:", error); s; }); client.on("close", () => { console.log("Kết nối đã đóng"); }); } catch (error) { console.error("Lỗi giao dịch:", error); client.end(); process.exit(1); } } sendFeeDelegateTx();
Mã code trên ký một giao dịch chuyển giá trị được ủy quyền phí bằng senderPrivateKey và gửi senderTxHashRLP đã ký đến máy chủ của người trả phí, đang chạy trên cổng 1337 tại 127.0.0.1, tức là localhost.
3.3 Máy chủ của bên thanh toán phí
Bây giờ chúng ta sẽ viết máy chủ của người trả phí, feepayer_server.js, máy chủ này sẽ ký senderTxHashRLP đã nhận bằng feePayerPrivateKey và gửi nó đến mạng thử nghiệm Kairos.
Trong ví dụ dưới đây, vui lòng thay thế "FEEPAYER_ADDRESS" và "FEEPAYER_PRIVATEKEY" bằng các giá trị thực tế.
const { createServer } = require("net");const { Wallet, JsonRpcProvider } = require("@kaiachain/ethers-ext").v6;const feePayerAddress = "FEEPAYER_ADDRESS";const feePayerPrivateKey = "FEEPAYER_PRIVATE_KEY";const provider = new JsonRpcProvider("https://public-en-kairos.node.kaia.io");const feePayerWallet = new Wallet(feePayerPrivateKey, provider);const feePayerSign = async (senderTxHashRLP, socket) => { try { // Gửi giao dịch const sentTx = await feePayerWallet.sendTransactionAsFeePayer(senderTxHashRLP); console.log("sentTx", sentTx); const rc = await sentTx.wait(); console.log("receipt", rc); if (rc.transactionHash) { socket.write(`Tx hash: ${rc.transactionHash}\n`); socket.write(`Sender Tx hash: ${rc.senderTxHash || ""}\n`); } } catch (error) { console.error("Lỗi trong feePayerSign:", error); socket.write(`Lỗi: ${error.message}\n`); }};const server = createServer(function (socket) { console.log("Client is connected ..."); socket.write("This is fee delegating service"); socket.write("Fee payer is " + feePayerAddress); socket.on("data", function (data) { console.log("Nhận dữ liệu từ client:", data.toString()); feePayerSign(data.toString(), socket); }); socket.on("error", (error) => { console.error("Lỗi socket:", error); }); socket.on("end", () => { console.log("Client disconnected"); });});server.listen(1337, "127.0.0.1");console.log("Dịch vụ đại lý phí đã khởi động ...");
The server listens on port 1337.
When there is incoming data, it signs the data with feePayerPrivateKey and sends it to the Kaia blockchain. Nó giả định rằng data là senderTxHashRLP từ sender_client.js.
4. Run example
Prepare two terminals, one for sender_client.js and another for feepayer_server.js.
4.1 Run feepayer_server.js
Chạy lệnh sau để khởi động máy chủ của người thanh toán phí:
node feepayer_server.js// Kết quả đầu raDịch vụ ủy quyền phí đã khởi động ...
The server starts and is now listening on port 1337.
4.2 Run sender_client.js
Let's run sender_client.js to send a fee delegated transaction.
$ node sender_client.js// output{ type: 9, to: '0x3a388d3fD71A0d9722c525E17007DdCcc41e1C47', value: 10000000000000000n, từ: '0x7D3C7202582299470F2aD3DDCB8EF2F45407F871', nonce: 202, gasLimit: 52500, gasPrice: '27500000000', chainId: '1001'}senderTxHashRLP 0x09f88681ca85066720b30082cd14943a388d3fd71a0d9722c525e17007ddccc41e1c47872386f26fc10000947d3c7202582299470f2ad3ddcb8ef2f45407f871f847f8458207f6a0820d11029771f2fa368ce11da01f1c9e7f4de6d48915074d149e132692f9d63ea0131c62470a6799dfc5d7e3a7ac8d0a4f3b8fb8b59110ca5dabb26a9ee409f274Kết nối với dịch vụ ủy quyền phíNhận dữ liệu từ máy chủ: Đây là ủy quyền phí, người trả phí dịch vụ là 0x88311cD55B656D2502b50f62E83F8279c1641e70
It will sign a transaction with the sender private key and send the signed transaction to the fee delegated service (i.e., fee payer's server). Sau đó, nó sẽ nhận được phản hồi từ dịch vụ ủy quyền phí, bao gồm địa chỉ Fee payer và Tx hash. Tx hash là băm của một giao dịch được gửi đến mạng Kaia.
4.3 Kiểm tra feepayer_server.js
Trên giao diện điều khiển của máy chủ, bạn sẽ thấy các kết quả sau đây. Nó in hóa đơn giao dịch từ Kaia.
$ node feepayer_server.jsDịch vụ ủy quyền phí đã khởi động ...Khách hàng đã kết nối ...Đã nhận dữ liệu từ khách hàng: 0x09f88681ca85066720b30082cd14943a388d3fd71a0d9722c525e17007ddccc41e1c47872386f26fc10000947d3c7202582299470f2ad3ddcb8ef2f45407f871f847f8458207f6a0820d11029771f2fa368ce11da01f1c9e7f4de6d48915074d149e132692f9d63ea0131c62470a6799dfc5d7e3a7ac8d0a4f3b8fb8b59110ca5dabb26a9ee409f274sentTx TransactionResponse {… to: '0x3a388d3fD71A0d9722c525E17007DdCcc41e1C47', from: '0x7D3C7202582299470F2aD3DDCB8EF2F45407F871', contractAddress: null, hash: '0x7cb1e8d20b4db7d9db1abc094781e1af83a9391153aab8cc935510639a548222', index: 0, blockHash: '0x50d3d7e143579e17dbc17b761c8e04331c6d4d950fe7563ac9a79d42a649de0a', blockNumber: 177078710, logsBloom: '0x00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000', gasUsed: 31000n, blobGasUsed: null, cumulativeGasUsed: 31000n, gasPrice: 27500000000n, blobGasPrice: null, type: 0, status: 1, root: undefined}
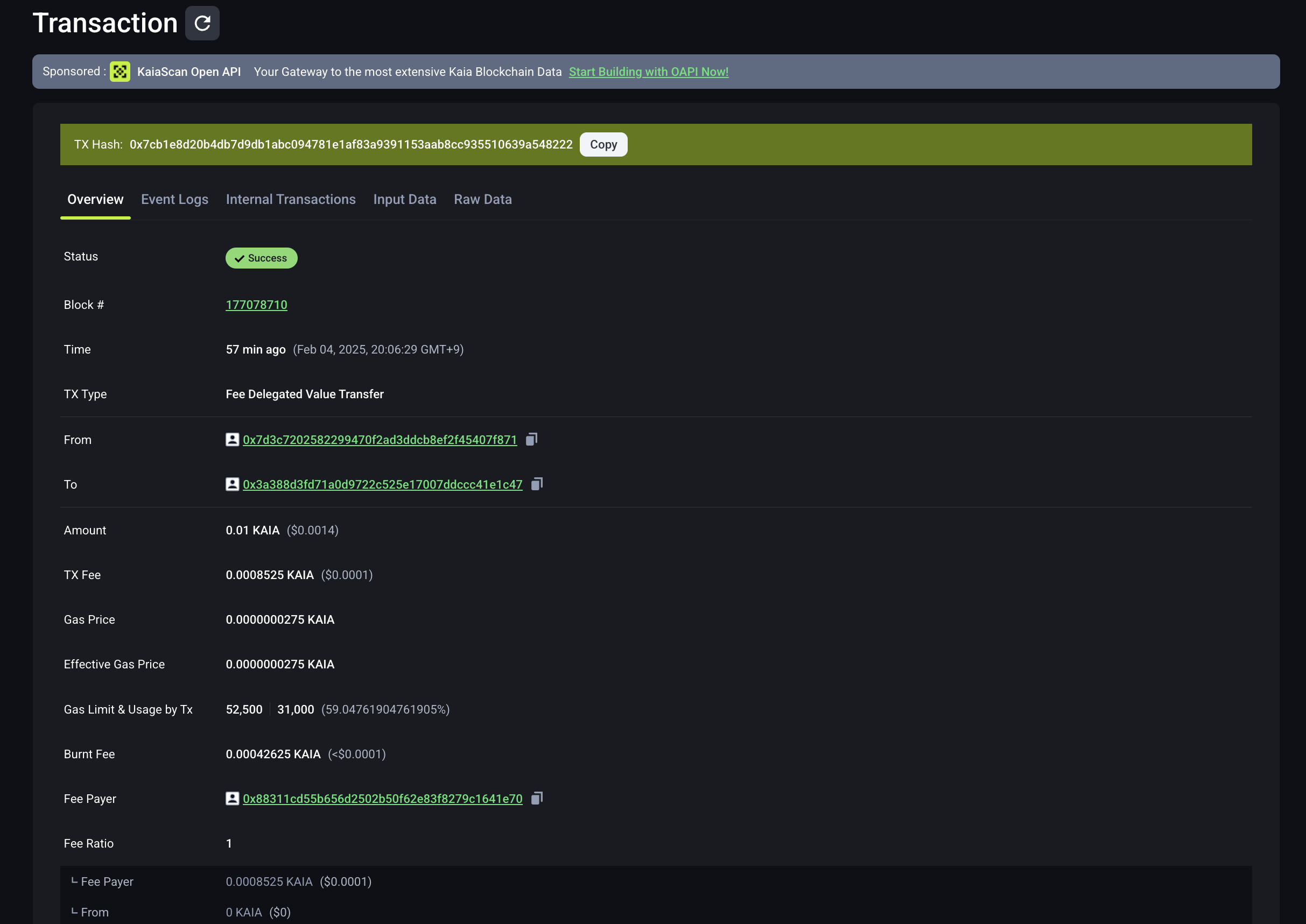
4.4 Xem trên Kaiascan
Bạn cũng có thể tìm thấy giao dịch trên tại Kaiascan.
Nó cho thấy giao dịch có loại TxTypeFeeDelegatedValueTransfer và Fee payer là 0x88311cd55b656d2502b50f62e83f8279c1641e70 hoặc feepayerAddress mà bạn đã nhập, trong khi From là một địa chỉ khác, đây nên là senderAddress trong ví dụ trên.