Kaia Governance
This document describes the overall governance framework of Kaia, including its components, operational structure and process, participation criteria, reward mechanisms, and onboarding/offboarding procedures.
Overview
Kaia Governance consists of three key components:
- Kaia Community: The community members including KAIA token holders have the right to participate in on-chain governance and major decision-making processes. It also includes developers, service providers, and users who contribute to the overall ecosystem, playing a vital role not only in governance but also in the continuous development of the ecosystem.
- Kaia Governance Council (GC): The GC represents the community and participates in governance decisions through both directly held tokens and delegated voting power from community members.
- Kaia Foundation: The Foundation supports the GC's decision-making by leveraging its expertise in blockchain and Web3 technologies and executes the decisions made by the GC.
Kaia GC serves as the primary body for strategic decision-making within the Kaia ecosystem. It comprises a diverse set of entities, including traditional companies, DAOs, protocol teams, and community builders.
The GC's structure is decentralized to ensure stakeholder-centric governance. Voting power within the GC is determined by the amount of staked and delegated KAIA, with an upper limit to prevent monopolization by a single entity. This design ensures transparent and efficient operations while representing the broad interests of the community.
Key responsibilities of the GC include:
- Technical Policy: Introduction of new technologies, addition of new features, and improvement of blockchain infrastructure.
- Economic Policy: Issuance and distribution of KAIA, adjustment of transaction fees, and ecosystem budgeting.
- Operational Rules: Establishment and amendment of governance and voting processes, and definition of governance participants' rights and responsibilities.
Governance proposals are submitted through the Kaia Governance Forum, where they undergo public discussion before proceeding to on-chain voting. The GC model is designed to enable all KAIA holders to contribute and influence on Kaia ecosystem. As the ecosystem evolves, the GC continues to adapt its structure and operations accordingly.
On-Chain Governance
On-chain governance automates and transparently executes decision-making among stakeholders through smart contracts. This approach offers several advantages:
- Transparency: All governance activities are recorded on the blockchain and are verifiable by anyone.
- Integrity: Votes are processed by smart contracts, making them tamper-proof.
- Non-repudiation: Signed votes are permanently recorded on-chain and cannot be denied.
- Enforceability: Results are automatically executed, ensuring that decisions cannot be ignored.
The Kaia blockchain implements an on-chain governance system with these properties. Voting power is proportional to the amount of staked KAIA, with upper limits set to prevent excessive concentration. KAIA holders may also delegate their voting rights to GC members.
Voting Power Calculation
- The GC's voting power is proportional to the amount of staked KAIA (1 vote per 5M KAIA).
- Through a public delegation mechanism, KAIA holders who are not GC members may delegate their voting power to GC members.
- Delegated tokens are aggregated with the GC's own holdings, and voting power is calculated using the same standard (1 vote per 5M KAIA).
- A cap is set to prevent any single entity from dominating the voting power.
- Maximum votes: Total valid GC members - 1 (e.g., if there are 40 valid members, the cap is 39 votes).
Kaia Governance Process
- Discussion: Anyone may submit proposals via the governance forum.
- On-chain Registration & Voting: Once a proposal receives at least one positive feedback from a GC member on the governance forum, it is registered and opened for voting.
- Execution: Approved proposals are executed.
Proposals registered on-chain progress through several statuses until voting concludes:
- Pending: After registration, awaiting the start of voting.
- Active: Voting is in progress.
- Passed: Approved by quorum and majority vote.
- Failed: Did not receive sufficient approval.
- Queued: Approved but pending execution.
- Executed: Proposal has been completely executed.
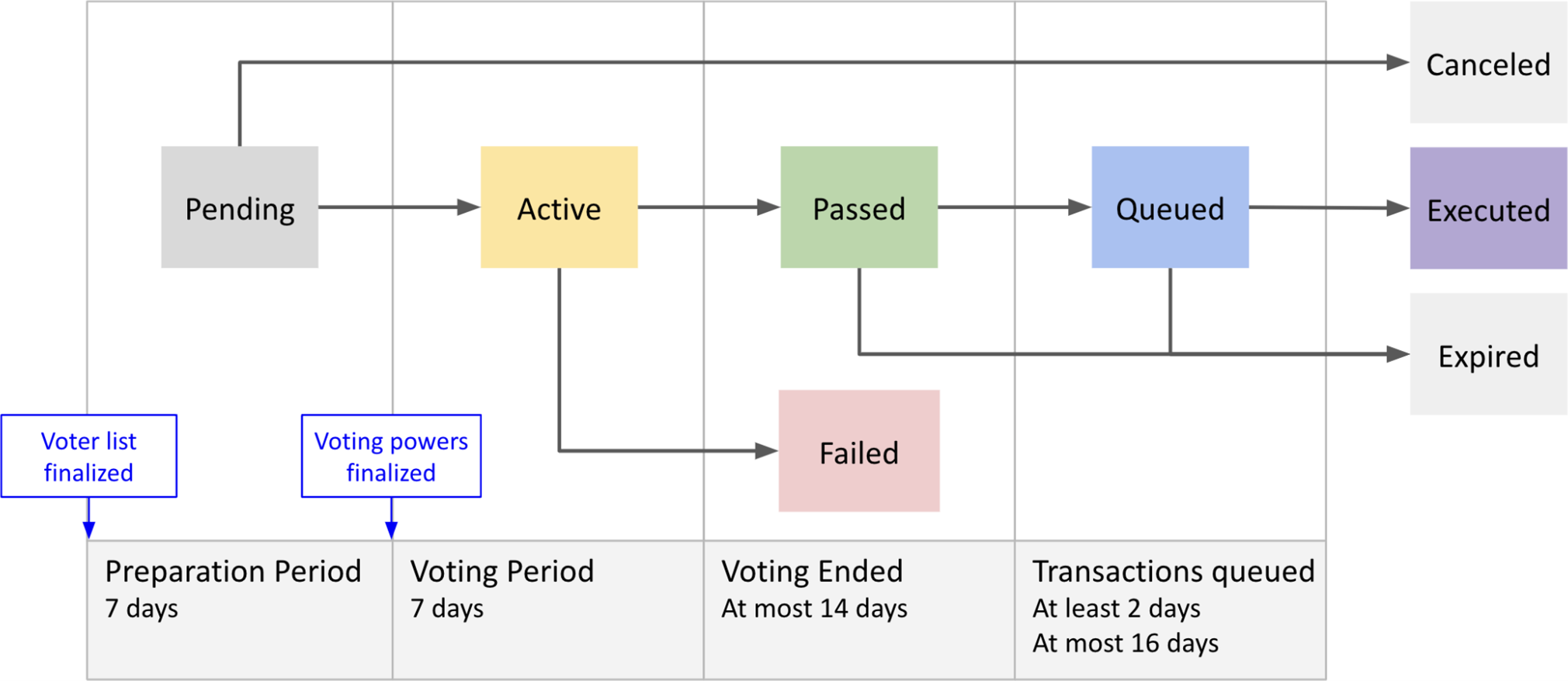
The standard voting period is seven days, though some proposals may require additional steps.
For example, text-only proposals (example) conclude after voting ends. However, parameter-change proposals (example) require not only approval but also execution of a related transaction after a 2-16 day delay.
For more details on parameter changes, refer to KIP-81: Introduction of On-chain Governance Voting. In urgent cases, this timeline may be shortened.
Quorum and Approval Criteria
- Minimum quorum: Either Count Quorum (participation by at least one-third of GC members) or Power Quorum (voted by at least one-third of total voting power).
- Approval: Majority of participating votes must approve.
- Abstain: counted as voting participation, but excluded from the calculation of yes and no votes.
Absence Penalty
The absence penalty policy was introduced and approved under KGP-31: Governance Policy to Encourage GC Voting Participation. A member who fails to participate in three consecutive votes will be excluded from block rewards for seven days.
GC Qualifications, Responsibilities, and Rewards
Qualifications
- Minimum 5,000,000 KAIA staked
- Operate Kaia node (refer to system requirements)
- Active participation in governance
- Participation in discussions and voting
- Attendance at regular and special meetings
Responsibilities
Node operation for the network security and stability
- Node Operation
Maintain continuous and secure node operation to support network consensus with high availability and minimal downtime. - Monitoring & Alerts
Monitor network threats or failures and respond promptly to ensure ecosystem stability.
Governance Participation and KEF Oversight
- GC members review and decide on proposals from the GC or the broader community. While the GC agenda does not include detailed technical details or implementation methods, it does include direction, policy decisions, and tokenomics. GCs must actively participate in the on-chain governance voting process, including submitting proposals, discussing them, and implementing voting results.
- GC meetings are held on the third Wednesday of each month and may be skipped if there are no agenda items.
- Special meetings may be convened for urgent matters.
- Kaia Ecosystem Fund (KEF) supports ecosystem sustainability through infrastructure enhancement, developer support, and indirect investment. The GC is responsible for approving KEF budgets and overseeing fund execution.
Community Engagement & Transparency
- Represent the interests of diverse stakeholders, uphold integrity, prevent conflicts of interest, and act in the best interest of the Kaia ecosystem.
- Maintain transparent and timely communication channels and disclose meeting summaries and decisions clearly.
- Encourage active participation of KAIA token holders through delegation.
Rewards
The current reward structure was proposed and approved under KIP-82. It consists of Proposer Rewards and Staking Rewards.
- Proposer Rewards:
All GC members stake at least 5M KAIA, operate CN/PN nodes, and equally participate in block production. Each GC member receives 0.96 KAIA per block proposed. - Staking Rewards:
GC members staking more than 5M KAIA receive proportional rewards on their excess stake. From 3.84 KAIA distributed per block, rewards are allocated based on each member's share of the total excess staked KAIA.
Onboarding Process
The onboarding process follows these stages:
- Expression of Interest:
Candidates express interest in joining to GC via the Governance Forum and request an invitation to the Kaia communication platform. - Pre-Onboarding Survey and Tool Distribution:
Candidates complete a pre-onboarding survey to assess governance activity experience and operational capacity. The Foundation provides Klaytool and related guides for node management and public delegation. - Private network/Testnet/Mainnet Onboarding:
Onboarding begins with private network and testnet environments before progressing to the mainnet. The process typically takes around three weeks, with the detailed schedule adjusted as needed. - Final Confirmation and Announcement:
Upon completion, the candidate officially becomes a GC member. Onboarding status can be verified on Kaia Square, and membership is announced via governance channels, with voting rights activated.
Offboarding Process
The offboarding process ensures network stability, integrity, and transparency to the community. It applies when a member voluntarily resigns, is dismissed for misconduct, or fails to meet participation requirements. If the node is not operating properly, it may lead to penalties or forced offboarding.
Offboarding Procedure:
- Notification of Resignation or Dismissal:
When a GC member notifies the Foundation of resignation, the Foundation posts it on the Governance Forum and initiates the official offboarding process. - Processing via Kaia Square:
An admin of Kaia Square designates the resignation date, deactivating the member's GC slot. - Validator, Address Book, and BLS Removal:
- Foundation node operators remove the member from the Validator list.
- The Finance team deletes the GC's record from the Address Book via the Token Manager (TM).
- The Core team removes the GC's BLS key.
- Node Shutdown and Public Announcement:
After the above steps, the member's node may be safely shut down. The offboarding is publicly announced via the Governance Forum and official communication channels.