체인링크 CCIP

소개
체인링크 크로스체인 상호운용성 프로토콜(CCIP)은 개발자와 탈중앙화 애플리케이션(dApp)이 블록체인 전반에서 안전하고 효율적으로 상호 작용할 수 있는 방법을 제공합니다. CCIP를 사용하면 토큰과 임의의 메시지를 전송하여 대상 컨트랙트에서 NFT 발행, 인덱스 재조정 또는 사용자 지정 함수 호출과 같은 작업을 트리거할 수 있습니다.
이 튜토리얼에서는 체인링크 CCIP를 사용해 카이아 스마트 콘트랙트에서 다른 체인의 콘트랙트로 메시지와 토큰을 전송하는 방법과 이를 다시 받는 방법을 배우게 됩니다.
전제 조건.
- 파운드리 설치
- curl -L https://foundry.paradigm.xyz | bash
로 설치한 다음foundryup`을 실행합니다. - forge --version,'
cast --version,anvil --version으로 확인합니다.
- curl -L https://foundry.paradigm.xyz | bash
- 메타마스크 지갑
- 개발자 지갑 설정
- 메타마스크에 카이아 카이로스 테스트넷과 이더리움 세폴리아 네트워크를 추가하세요.
- 수도꼭지에서 토큰 테스트
- 카이아: 카이아에서 배포 및 전송하기 위한 가스입니다.
- LINK (테스트넷): LINK로 결제할 때 CCIP 수수료입니다.
- 대상 체인의 네이티브 토큰(예: Sepolia ETH: 배포용 및 선택한 경우 네이티브로 CCIP 수수료 지불용).
시작하기
이 가이드에서는 체인링크 CCIP를 사용해 카이아(카이로스 테스트넷)와 이더리움 세폴리아 간에 크로스체인 메시지를 주고받게 됩니다.
결국에는 알게 될 것입니다:
- 카이로스 및 세폴리아에 대해 구성된 파운드리 프로젝트 초기화하기
- 종속성으로 체인링크 CCIP 컨트랙트 및 인터페이스 추가하기
- 체인 간에 메시지를 주고받는 메신저 컨트랙트 구현하기
- 양쪽 네트워크에 배포하고 왕복 메시지 확인
프로젝트 만들기
이 섹션에서는 파운드리를 사용하여 개발 환경을 설정합니다. 새 파운드리 프로젝트를 만들려면 먼저 새 디렉터리를 만듭니다:
mkdir kaia-foundry-ccip-example
그런 다음 실행합니다:
cd kaia-foundry-ccip-exampleforge init
그러면 다음과 같은 기본 레이아웃의 파운드리 프로젝트가 생성됩니다:
├── foundry.toml├── script├── src└── test
체인링크 스마트 컨트랙트 설치
파운드리 프로젝트 내에서 체인링크 CCIP를 사용하려면, 포지 인스톨을 사용하여 프로젝트 종속성으로 체인링크 CCIP 스마트 컨트랙트를 설치해야 합니다.
체인링크 CCIP 스마트 컨트랙트를 설치하려면 실행합니다:
forge install smartcontractkit/chainlink-ccip@2114b90f39c82c052e05af7c33d42c1ae98f4180forge install smartcontractkit/chainlink-evm@ff814eb0a01f89d9a215f825d243bf421e6434a9
설치가 완료되면 remapping.txt 파일을 생성합니다:
forge remappings > remappings.txt
그런 다음 새로 만든 파일에 다음을 붙여넣습니다:
@chainlink/contracts/=lib/chainlink-evm/contracts/@chainlink/contracts-ccip/=lib/chainlink-ccip/chains/evm/contracts/
스마트 컨트랙트 작성
이 섹션에서는 아래 코드를 사용하여 체인 간에 메시지를 주고받는 방법을 설명합니다.
프로젝트의 src 디렉토리에 'Messenger.sol'이라는 이름의 새 파일을 만들고 아래 코드를 파일에 복사합니다:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MITpragma solidity ^0.8.0;import { IRouterClient } from "@chainlink/contracts-ccip/interfaces/IRouterClient.sol";import {OwnerIsCreator} from "@chainlink/contracts/src/v0.8/shared/access/OwnerIsCreator.sol";import { Client } from "@chainlink/contracts-ccip/libraries/Client.sol";import { CCIPReceiver } from "@chainlink/contracts-ccip/applications/CCIPReceiver.sol";import {IERC20} from "@chainlink/contracts/src/v0.8/vendor/openzeppelin-solidity/v4.8.3/contracts/token/ERC20/IERC20.sol";import {SafeERC20} from "@chainlink/contracts/src/v0.8/vendor/openzeppelin-solidity/v4.8.3/contracts/token/ERC20/utils/SafeERC20.sol";/** * THIS IS AN EXAMPLE CONTRACT THAT USES HARDCODED VALUES FOR CLARITY. * THIS IS AN EXAMPLE CONTRACT THAT USES UN-AUDITED CODE. * DO NOT USE THIS CODE IN PRODUCTION. *//// @title - A simple messenger contract for sending/receiving string data across chains.contract Messenger is CCIPReceiver, OwnerIsCreator { using SafeERC20 for IERC20; // Custom errors to provide more descriptive revert messages. error NotEnoughBalance(uint256 currentBalance, uint256 calculatedFees); // Used to make sure contract has enough balance. error NothingToWithdraw(); // Used when trying to withdraw Ether but there's nothing to withdraw. error FailedToWithdrawEth(address owner, address target, uint256 value); // Used when the withdrawal of Ether fails. error DestinationChainNotAllowlisted(uint64 destinationChainSelector); // Used when the destination chain has not been allowlisted by the contract owner. error SourceChainNotAllowlisted(uint64 sourceChainSelector); // Used when the source chain has not been allowlisted by the contract owner. error SenderNotAllowlisted(address sender); // Used when the sender has not been allowlisted by the contract owner. error InvalidReceiverAddress(); // Used when the receiver address is 0. // Event emitted when a message is sent to another chain. event MessageSent( bytes32 indexed messageId, // The unique ID of the CCIP message. uint64 indexed destinationChainSelector, // The chain selector of the destination chain. address receiver, // The address of the receiver on the destination chain. string text, // The text being sent. address feeToken, // the token address used to pay CCIP fees. uint256 fees // The fees paid for sending the CCIP message. ); // Event emitted when a message is received from another chain. event MessageReceived( bytes32 indexed messageId, // The unique ID of the CCIP message. uint64 indexed sourceChainSelector, // The chain selector of the source chain. address sender, // The address of the sender from the source chain. string text // The text that was received. ); bytes32 private s_lastReceivedMessageId; // Store the last received messageId. string private s_lastReceivedText; // Store the last received text. // Mapping to keep track of allowlisted destination chains. mapping(uint64 => bool) public allowlistedDestinationChains; // Mapping to keep track of allowlisted source chains. mapping(uint64 => bool) public allowlistedSourceChains; // Mapping to keep track of allowlisted senders. mapping(address => bool) public allowlistedSenders; IERC20 private s_linkToken; /// @notice Constructor initializes the contract with the router address. /// @param _router The address of the router contract. /// @param _link The address of the link contract. constructor(address _router, address _link) CCIPReceiver(_router) { s_linkToken = IERC20(_link); } /// @dev Modifier that checks if the chain with the given destinationChainSelector is allowlisted. /// @param _destinationChainSelector The selector of the destination chain. modifier onlyAllowlistedDestinationChain(uint64 _destinationChainSelector) { if (!allowlistedDestinationChains[_destinationChainSelector]) revert DestinationChainNotAllowlisted(_destinationChainSelector); _; } /// @dev Modifier that checks if the chain with the given sourceChainSelector is allowlisted and if the sender is allowlisted. /// @param _sourceChainSelector The selector of the destination chain. /// @param _sender The address of the sender. modifier onlyAllowlisted(uint64 _sourceChainSelector, address _sender) { if (!allowlistedSourceChains[_sourceChainSelector]) revert SourceChainNotAllowlisted(_sourceChainSelector); if (!allowlistedSenders[_sender]) revert SenderNotAllowlisted(_sender); _; } /// @dev Modifier that checks the receiver address is not 0. /// @param _receiver The receiver address. modifier validateReceiver(address _receiver) { if (_receiver == address(0)) revert InvalidReceiverAddress(); _; } /// @dev Updates the allowlist status of a destination chain for transactions. function allowlistDestinationChain( uint64 _destinationChainSelector, bool allowed ) external onlyOwner { allowlistedDestinationChains[_destinationChainSelector] = allowed; } /// @dev Updates the allowlist status of a source chain for transactions. function allowlistSourceChain( uint64 _sourceChainSelector, bool allowed ) external onlyOwner { allowlistedSourceChains[_sourceChainSelector] = allowed; } /// @dev Updates the allowlist status of a sender for transactions. function allowlistSender(address _sender, bool allowed) external onlyOwner { allowlistedSenders[_sender] = allowed; } /// @notice Sends data to receiver on the destination chain. /// @notice Pay for fees in LINK. /// @dev Assumes your contract has sufficient LINK. /// @param _destinationChainSelector The identifier (aka selector) for the destination blockchain. /// @param _receiver The address of the recipient on the destination blockchain. /// @param _text The text to be sent. /// @return messageId The ID of the CCIP message that was sent. function sendMessagePayLINK( uint64 _destinationChainSelector, address _receiver, string calldata _text ) external onlyOwner onlyAllowlistedDestinationChain(_destinationChainSelector) validateReceiver(_receiver) returns (bytes32 messageId) { // Create an EVM2AnyMessage struct in memory with necessary information for sending a cross-chain message Client.EVM2AnyMessage memory evm2AnyMessage = _buildCCIPMessage( _receiver, _text, address(s_linkToken) ); // Initialize a router client instance to interact with cross-chain router IRouterClient router = IRouterClient(this.getRouter()); // Get the fee required to send the CCIP message uint256 fees = router.getFee(_destinationChainSelector, evm2AnyMessage); if (fees > s_linkToken.balanceOf(address(this))) revert NotEnoughBalance(s_linkToken.balanceOf(address(this)), fees); // Approve the Router to transfer LINK tokens on contract's behalf. It will spend the fees in LINK s_linkToken.approve(address(router), fees); // Send the CCIP message through the router and store the returned CCIP message ID messageId = router.ccipSend(_destinationChainSelector, evm2AnyMessage); // Emit an event with message details emit MessageSent( messageId, _destinationChainSelector, _receiver, _text, address(s_linkToken), fees ); // Return the CCIP message ID return messageId; } /// @notice Sends data to receiver on the destination chain. /// @notice Pay for fees in native gas. /// @dev Assumes your contract has sufficient native gas tokens. /// @param _destinationChainSelector The identifier (aka selector) for the destination blockchain. /// @param _receiver The address of the recipient on the destination blockchain. /// @param _text The text to be sent. /// @return messageId The ID of the CCIP message that was sent. function sendMessagePayNative( uint64 _destinationChainSelector, address _receiver, string calldata _text ) external onlyOwner onlyAllowlistedDestinationChain(_destinationChainSelector) validateReceiver(_receiver) returns (bytes32 messageId) { // Create an EVM2AnyMessage struct in memory with necessary information for sending a cross-chain message Client.EVM2AnyMessage memory evm2AnyMessage = _buildCCIPMessage( _receiver, _text, address(0) ); // Initialize a router client instance to interact with cross-chain router IRouterClient router = IRouterClient(this.getRouter()); // Get the fee required to send the CCIP message uint256 fees = router.getFee(_destinationChainSelector, evm2AnyMessage); if (fees > address(this).balance) revert NotEnoughBalance(address(this).balance, fees); // Send the CCIP message through the router and store the returned CCIP message ID messageId = router.ccipSend{value: fees}( _destinationChainSelector, evm2AnyMessage ); // Emit an event with message details emit MessageSent( messageId, _destinationChainSelector, _receiver, _text, address(0), fees ); // Return the CCIP message ID return messageId; } /// handle a received message function _ccipReceive( Client.Any2EVMMessage memory any2EvmMessage ) internal override onlyAllowlisted( any2EvmMessage.sourceChainSelector, abi.decode(any2EvmMessage.sender, (address)) ) // Make sure source chain and sender are allowlisted { s_lastReceivedMessageId = any2EvmMessage.messageId; // fetch the messageId s_lastReceivedText = abi.decode(any2EvmMessage.data, (string)); // abi-decoding of the sent text emit MessageReceived( any2EvmMessage.messageId, any2EvmMessage.sourceChainSelector, // fetch the source chain identifier (aka selector) abi.decode(any2EvmMessage.sender, (address)), // abi-decoding of the sender address, abi.decode(any2EvmMessage.data, (string)) ); } /// @notice Construct a CCIP message. /// @dev This function will create an EVM2AnyMessage struct with all the necessary information for sending a text. /// @param _receiver The address of the receiver. /// @param _text The string data to be sent. /// @param _feeTokenAddress The address of the token used for fees. Set address(0) for native gas. /// @return Client.EVM2AnyMessage Returns an EVM2AnyMessage struct which contains information for sending a CCIP message. function _buildCCIPMessage( address _receiver, string calldata _text, address _feeTokenAddress ) private pure returns (Client.EVM2AnyMessage memory) { // Create an EVM2AnyMessage struct in memory with necessary information for sending a cross-chain message return Client.EVM2AnyMessage({ receiver: abi.encode(_receiver), // ABI-encoded receiver address data: abi.encode(_text), // ABI-encoded string tokenAmounts: new Client.EVMTokenAmount[](0), // Empty array as no tokens are transferred extraArgs: Client._argsToBytes( // Additional arguments, setting gas limit and allowing out-of-order execution. // Best Practice: For simplicity, the values are hardcoded. It is advisable to use a more dynamic approach // where you set the extra arguments off-chain. This allows adaptation depending on the lanes, messages, // and ensures compatibility with future CCIP upgrades. Read more about it here: https://docs.chain.link/ccip/concepts/best-practices/evm#using-extraargs Client.GenericExtraArgsV2({ gasLimit: 200_000, // Gas limit for the callback on the destination chain allowOutOfOrderExecution: true // Allows the message to be executed out of order relative to other messages from the same sender }) ), // Set the feeToken to a feeTokenAddress, indicating specific asset will be used for fees feeToken: _feeTokenAddress }); } /// @notice Fetches the details of the last received message. /// @return messageId The ID of the last received message. /// @return text The last received text. function getLastReceivedMessageDetails() external view returns (bytes32 messageId, string memory text) { return (s_lastReceivedMessageId, s_lastReceivedText); } /// @notice Fallback function to allow the contract to receive Ether. /// @dev This function has no function body, making it a default function for receiving Ether. /// It is automatically called when Ether is sent to the contract without any data. receive() external payable {} /// @notice Allows the contract owner to withdraw the entire balance of Ether from the contract. /// @dev This function reverts if there are no funds to withdraw or if the transfer fails. /// It should only be callable by the owner of the contract. /// @param _beneficiary The address to which the Ether should be sent. function withdraw(address _beneficiary) public onlyOwner { // Retrieve the balance of this contract uint256 amount = address(this).balance; // Revert if there is nothing to withdraw if (amount == 0) revert NothingToWithdraw(); // Attempt to send the funds, capturing the success status and discarding any return data (bool sent, ) = _beneficiary.call{value: amount}(""); // Revert if the send failed, with information about the attempted transfer if (!sent) revert FailedToWithdrawEth(msg.sender, _beneficiary, amount); } /// @notice Allows the owner of the contract to withdraw all tokens of a specific ERC20 token. /// @dev This function reverts with a 'NothingToWithdraw' error if there are no tokens to withdraw. /// @param _beneficiary The address to which the tokens will be sent. /// @param _token The contract address of the ERC20 token to be withdrawn. function withdrawToken( address _beneficiary, address _token ) public onlyOwner { // Retrieve the balance of this contract uint256 amount = IERC20(_token).balanceOf(address(this)); // Revert if there is nothing to withdraw if (amount == 0) revert NothingToWithdraw(); IERC20(_token).safeTransfer(_beneficiary, amount); }}
위의 코드는 허용된 체인에서 문자열 메시지를 주고받는 양방향 CCIP 컨트랙트로, 소유자 게이트 제어, LINK 또는 기본 수수료 지불이 가능합니다. 이 계약에서 사용할 주요 기능을 살펴보겠습니다:
1. 허용 목록
- 허용목록소스체인(선택자, 허용): 이 컨트랙트에 메시지를 전달할 수 있는 소스체인을 제어합니다.
- 허용목록대상체인(선택자, 허용): 이 컨트랙트를 전송할 수 있는 대상 체인을 제어합니다.
- 허용목록발신자[주소](허용목록발신자(addr, 허용됨) 경유): 메시지가 도착할 때 소스 체인에서 어떤 발신자 주소를 신뢰할지 제한합니다.
테스트하기 전에 양쪽 끝에 설정하세요. 발신자는 발신자와 체인을 신뢰해야 합니다. 대상도 전송을 허용 목록에 추가해야 합니다.
2. 메시지 보내기
sendMessagePayLINK(선택자, 수신자, 텍스트): 메시지를 보내고 LINK로 CCIP 수수료를 결제합니다. 그러면 메시지가 작성되고, 요금이 견적되고, LINK 잔액이 확인되고, 라우터가 승인한 다음 ccipSend가 실행됩니다. 완료되면 전송된 메시지와 연결된 고유 ID를 반환합니다.
sendMessagePayNative(선택자, 수신자, 텍스트): 메시지를 전송하고 네이티브 토큰으로 CCIP 수수료를 지불합니다. 이렇게 하면 메시지를 작성하고, 수수료를 인용하고, 기본 잔액을 확인한 다음 ccipSend(value: 수수료)를 실행합니다. 완료되면 전송된 메시지와 연결된 고유 ID를 반환합니다.
3. 메시지 작성
_buildCCIPMessage(수신자, 텍스트, 수수료토큰주소) -> EVM2AnyMessage
- 수신기 및 텍스트 인코딩
- 토큰을 보내지 않음(토큰 금액이 비어 있음)
- 구성 가능한 gasLimit과 함께 GenericExtraArgsV2를 사용하여 extraArgs를 패키징합니다.
- 수수료 토큰을 LINK 또는 네이티브의 경우 주소(0)로 설정합니다.
4. 메시지 수신
CCIP 호출 _ccipReceive(...) 대상 체인에 있습니다. 계약서:
- 허용 목록에 대해 소스 체인과 발신자의 유효성을 검사합니다.
- 문자열을 디코딩합니다.
- 마지막으로 수신한 페이로드로 저장
- 메시지 수신됨
- 다음과 같이 마지막 인바운드 페이로드를 읽어옵니다: getLastReceivedMessageDetails() -> (messageId, text).
스마트 컨트랙트 컴파일하기
스마트 컨트랙트를 컴파일하려면 실행하세요:
forge build
스마트 컨트랙트 배포
지갑을 배포자로 설정하기
스마트 컨트랙트를 네트워크에 배포하려면 먼저 배포자로 사용할 지갑을 설정해야 합니다. 이렇게 하려면 cast wallet import 명령을 사용하여 지갑의 개인키를 Foundry의 안전하게 암호화된 키 저장소로 가져오면 됩니다:
cast wallet import deployer --interactive
위의 명령을 실행하면 거래 서명을 위한 비밀번호와 개인 키를 입력하라는 메시지가 표시됩니다.
지갑이 Foundry 프로젝트에서 배포자 계정으로 가져왔는지 확인하려면 다음을 실행합니다:
cast wallet list
환경 변수 설정
환경을 설정하려면 프로젝트의 홈 디렉토리에 .env 파일을 생성하고, 카이로스 테스트넷과 이더리움 세폴리아 모두에 대한 CCIP 체인 선택기, CCIP 라우터 주소, LINK 토큰 주소를 추가합니다:
KAIROS_RPC_URL="https://public-en-kairos.node.kaia.io"ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL="https://ethereum-sepolia-rpc.publicnode.com"KAIROS_CHAIN_SELECTOR=2624132734533621656ETH_SEPOLIA_CHAIN_SELECTOR=16015286601757825753KAIROS_ROUTER_ADDRESS="0x41477416677843fCE577748D2e762B6638492755"ETH_SEPOLIA_ROUTER_ADDRESS="0x0BF3dE8c5D3e8A2B34D2BEeB17ABfCeBaf363A59"KAIROS_LINK_ADDRESS="0xAF3243f975afe2269Da8Ffa835CA3A8F8B6A5A36"ETH_SEPOLIA_LINK_ADDRESS="0x779877A7B0D9E8603169DdbD7836e478b4624789"
.env` 파일이 생성되면 다음 명령을 실행하여 현재 명령줄 세션에서 환경 변수를 로드합니다:
source .env
컨트랙트가 컴파일되고 환경이 설정되면 스마트 컨트랙트를 배포할 준비가 된 것입니다.
파운드리를 사용하여 스마트 컨트랙트를 배포하려면 forge create 명령을 사용하면 됩니다. 이 명령은 배포할 스마트 컨트랙트, 배포할 네트워크의 RPC URL, 배포할 계정을 지정해야 합니다.
카이로스 테스트넷에 발신자 컨트랙트 배포하기
카이아 카이로스 테스트넷에 발신자 스마트 컨트랙트를 배포하려면 다음 명령을 실행하세요:
forge create --rpc-url $KAIROS_RPC_URL --account deployer --broadcast src/Messenger.sol:Messenger --constructor-args $KAIROS_ROUTER_ADDRESS $KAIROS_LINK_ADDRESS
메시지가 표시되면 앞서 지갑의 개인키를 가져올 때 설정한 비밀번호를 입력합니다.
위의 명령을 실행하면 컨트랙트가 카이로스 테스트 네트워크에 배포됩니다. 카이아스캔 블록 탐색기](https://kairos.kaiascan.io)를 통해 배포 상태와 컨트랙트를 확인할 수 있습니다.
컨트랙트가 이더리움 세폴리아의 컨트랙트 수신자에게 CCIP 메시지를 보낼 수 있도록 설정하세요.
먼저 트랜잭션에 대한 대상 체인의 허용 목록 상태를 업데이트해야 합니다. 이렇게 하려면 다음 명령을 실행합니다:
cast send `SENDER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $KAIROS_RPC_URL "allowlistDestinationChain(uint64, bool)" $ETH_SEPOLIA_CHAIN_SELECTOR true --account deployer
위 코드는 *allowlistDestinationChain()*을 호출하여 발신자 컨트랙트에서 허용할 대상 체인 선택기를 설정합니다. 각 체인 선택기는 CCIP 디렉토리에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
이더리움 세폴리아에 수신자 컨트랙트 배포하기
수신자 스마트 컨트랙트를 이더리움 세폴리아에 배포하려면 다음 명�령을 실행하세요:
forge create --rpc-url $ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL --account deployer --broadcast src/Messenger.sol:Messenger --constructor-args $ETH_SEPOLIA_ROUTER_ADDRESS $ETH_SEPOLIA_LINK_ADDRESS
메시지가 표시되면 앞서 지갑의 개인키를 가져올 때 설정한 비밀번호를 입력합니다.
위의 명령을 실행하면 컨트랙트가 이더리움 세폴리아에 배포됩니다. 이더 세폴리아 블록 탐색기](https://sepolia.etherscan.io/)를 사용하여 배포 상태와 컨트랙트를 확인할 수 있습니다.
카이로스 테스트넷의 발신자 컨트랙트로부터 CCIP 메시지를 수신하도록 컨트랙트를 활성화합니다.
먼저 트랜잭션에 대한 소스 체인의 허용 목록 상태를 업데이트해야 합니다. 이렇게 하려면 다음 명령을 실행합니다:
cast send `RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL "allowlistSourceChain(uint64, bool)" $KAIROS_CHAIN_SELECTOR true --account deployer
위의 코드는 수신자 컨트랙트에서 허용할 소스 체인 선택기를 설정하기 위해 *allowlistSourceChain()*을 호출합니다. 각 체인 선택기는 CCIP 디렉토리에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
카이로스 테스트넷의 발신자 컨트랙트로부터 CCIP 메시지를 수신하도록 컨트랙트를 활성화합니다.
트랜잭션에 대한 발신자의 허용 목록 상태를 업데이트하려면 다음 명령을 실행합니다:
cast send `RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL "allowlistSender(address, bool)" 0x12798F1E2013A110E3C8B23aC1f36c00B8DFD4d9 true --account deployer
이 시점에서 카이로스 테스트넷에는 하나의 발신자 컨트랙트가 있고, 이더리움 세폴리아에는 하나의 수신자 컨트랙트가 있습니다. 보안 조치로 발신자 컨트랙트가 이더리움 세폴리아에 CCIP 메시지를 보내고, 수신자 컨트랙트가 발신자와 카이로스 테스트넷으로부터 CCIP 메시지를 받도록 활성화했습니다.
스마트 컨트랙트 자금 조달
메시지 전송과 관련된 수수료를 지불하기 위해 발신자 계약은 데이터를 전송하고 네이티브 토큰으로 결제하는 경우 LINK 토큰, ETH 및 KAIA의 잔액을 보유해야 합니다.
LINK
지갑에서 직접 또는 다음 캐스트 명령을 실행하여 컨트랙트에 자금을 입금할 수 있습니다:
cast send $KAIROS_LINK_ADDRESS --rpc-url $KAIROS_RPC_URL "transfer(address,uint256)" `SENDER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` 5000000000000000000 --account deployer
위의 명령은 카이로스 테스트넷에서 5개의 LINK 토큰을 발신자 컨트랙트로 전송합니다.
제공된 캐스트 명령을 실행하기 전에 배포된 Sender 컨트랙트의 컨트랙트 주소로 SENDER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS를 바꾸세요.
스마트 컨트랙트와 상호작용하기
이 섹션에서는 배포된 스마트 컨트랙트와 상호 작용하고 Foundry 캐스트 명령줄 도구를 사용하여 해당 함수를 호출합니다.
LINK로 데�이터 전송 및 결제
이 단계에서는 CCIP를 사용하여 문자를 보내게 되며, CCIP 사용에 대한 CCIP 수수료는 LINK로 결제됩니다.
이를 위해 캐스트 명령을 사용하여 카이로스 테스트넷에 배포된 발신자 컨트랙트에서 sendMessagePayLINK(uint64, 주소, 문자열) 함수를 호출하여 이더리움 세폴리아의 수신자 컨트랙트로 메시지 데이터를 전송합니다.
발신자 스마트 컨트랙트의 sendMessagePayLINK(uint64, 주소, 문자열) 함수를 호출하려면, 실행합니다:
cast send `SENDER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $KAIROS_RPC_URL "sendMessagePayLINK(uint64, address, string)" $ETH_SEPOLIA_CHAIN_SELECTOR `RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` "gKaia builders" --account deployer
위의 명령은 *sendMessagePayLINK(uint64, 주소, 문자열)*를 호출하여 메시지를 전송합니다. 메서드에 전달되는 파라미터는 다음과 같습니다: 대상 체인에 대한 체인 선택기(이더리움 세폴리아), 수신자 컨트랙트 주소, 메시지에 포함할 텍스트 데이터(헬로 빌더).
명령을 실행하면 고유한 messageId가 반환되어야 합니다.
트랜잭션이 완료되면 CCIP가 이더리움 세폴리아에 데이터를 전달하고 수신자 컨트랙트의 ccipReceive 함수를 호출하는 데 몇 분 정도 걸립니다. 크로스체인 거래를 확인하려면 CCIP 탐색기를 열고 거래 해시를 사용해 검색하세요.
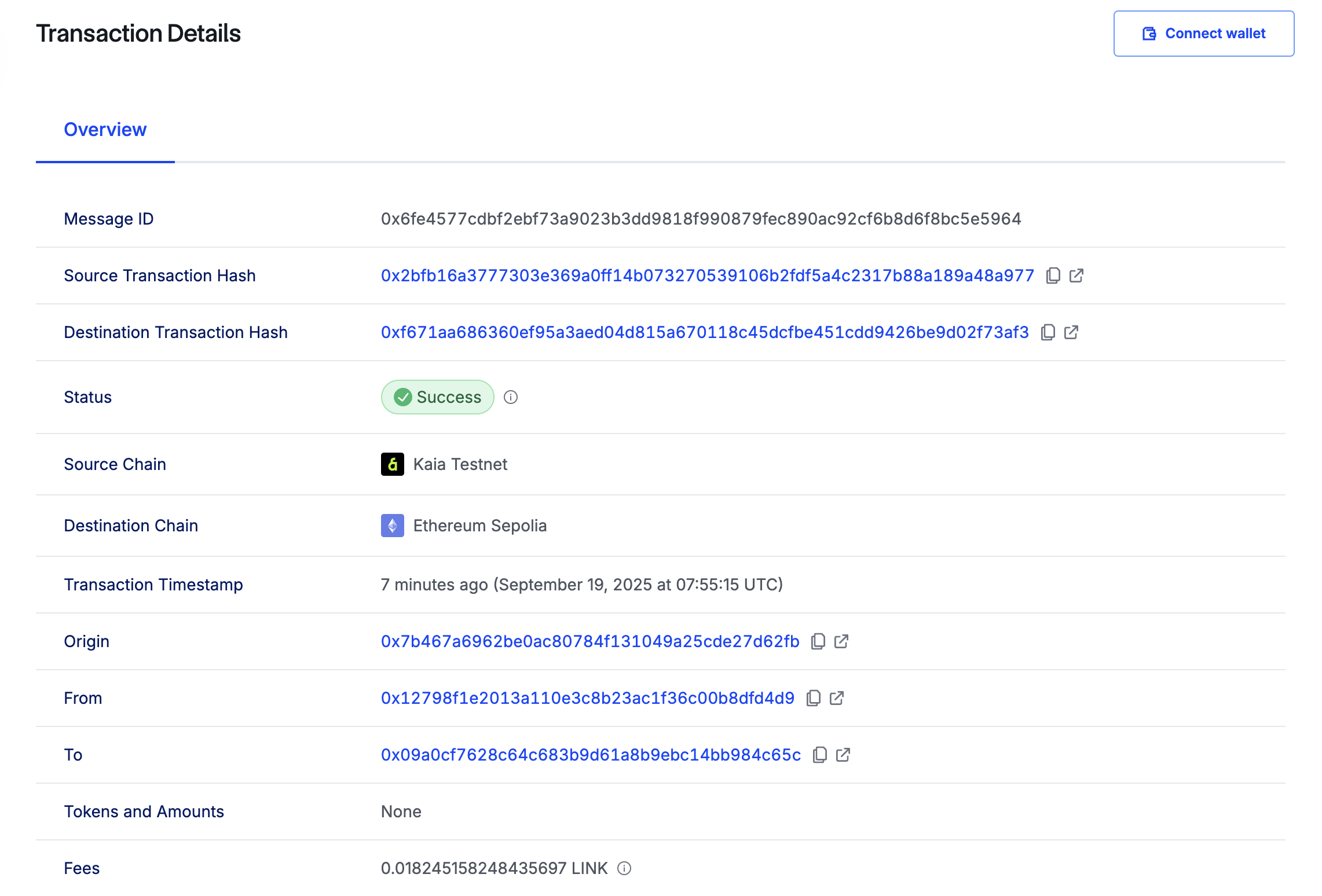
다음으로 할 일은 대상 체인에서 수신자 컨트랙트를 확인하는 것입니다. 이를 위해 아래 명령을 실행하여 *getLastReceivedMessageDetails()*를 호출합니다:
cast call `RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL "getLastReceivedMessageDetails()"
제공된 캐스트 명령을 실행하기 전에 배포된 수신자 컨트랙트의 컨트랙트 주소로 RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS를 바꾸세요.
수신된 문자 및 메시지 ID가 다음과 같이 16진수 데이터로 반환되는 것을 볼 수 있습니다:
0x6fe4577cdbf2ebf73a9023b3dd9818f990879fec890ac92cf6b8d6f8bc5e59640000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000040000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000e48656c6c6f206275696c64657273000000000000000000000000000000000000
특히 수신된 텍스트에 대해 16진수 데이터를 문자열로 변환하려면 아래 명령을 실행하세요:
cast to-utf8 e48656c6c6f206275696c64657273000000000000000000000000000000000000
이제 크로스 체인 작업이 성공했음을 의미하는 안녕 빌더가 표시되어야 합니다.
이 예시 계약은 양방향으로 작동하도록 설계되었습니다. 이를 사용하여 카이로스 테스트넷에서 이더리움 세폴리아로, 이더리움 세폴리아에서 다시 카이로스 테스트넷으로 데이터를 전�송할 수 있습니다.
네이티브로 데이터 전송 및 결제
이 섹션에서는 CCIP가 포함된 문자 메시지를 전송하고 네이티브 토큰으로 수수료를 결제합니다. 이더리움 세폴리아에서 카이아(카이로스 테스트넷)로 전송합니다. 이는 이전 방향과 반대되는 것으로, 세폴리아 컨트랙트는 발신자 역할을 하고 카이로스 컨트랙트는 수신자 역할을 합니다.
먼저 이더리움 세폴리아에서 ETH로 발신자 계약에 자금을 조달해야 합니다. 이렇게 하려면 다음 캐스트 명령을 실행합니다:
cast send --rpc-url $ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL `SENDER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --value 300000000000000000 --account deployer
이렇게 하면 이더리움 세폴리아에서 0.3 ETH가 발신자 컨트랙트로 전송됩니다.
발신자 계약 주소를 발신자 계약 주소로 바꿉니다.
다음은 이더리움 세폴리아의 발신자 컨트랙트에서 목적지 체인을 허용하는 것입니다. 이렇게 하려면 아래 명령을 실행하세요:
cast send `SENDER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL "allowlistDestinationChain(uint64, bool)" $KAIROS_CHAIN_SELECTOR true --account deployer
다음은 카이로스 테스트넷의 리시버 컨트랙트에서 소스 체인을 허용하는 것입니다. 이렇게 하려면 아래 명령을 실행하세요:
cast send `RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $KAIROS_RPC_URL "allowlistSourceChain(uint64, bool)" $ETH_SEPOLIA_CHAIN_SELECTOR true --account deployer
그런 다음 아래 명령을 실행하여 카이로스 테스트넷에서 수신자 컨트랙트에 허용리스트발신자를 실행합니다:
cast send `RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $KAIROS_RPC_URL "allowlistSender(address, bool)" 0x09a0CF7628c64c683B9d61a8B9EBc14BB984c65c true --account deployer
컨트랙트를 함께 연결한 후 이 명령을 실행하여 수신자 컨트랙트로 데이터를 전송할 수 있습니다:
cast send `SENDER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL "sendMessagePayNative(uint64, address, string)" $KAIROS_CHAIN_SELECTOR 0x12798F1E2013A110E3C8B23aC1f36c00B8DFD4d9 "gKaia Builders" --account deployer
위의 명령은 *sendMessagePayNative(uint64, 주소, 문자열)*를 호출하여 메시지를 전송합니다. 메서드에 전달되는 파라미터는 다음과 같습니다: 대상 체인에 대한 체인 선택기(카이로스 테스트넷), 수신자 컨트랙트 주소, 메시지에 포함될 텍스트 데이터(gKaia 빌더).
명령을 실행하면 고유한 messageId가 반환되어야 합니다.
트랜잭션이 완료되면 CCIP가 데이터를 카이로스 테스트넷에 전달하고 수신자 컨트랙트에서 ccipReceive 함수를 호출하는 데 몇 분 정도 걸립니다. 크로스체인 거래를 확인하려면 CCIP 탐색기를 열고 거래 해시를 사용해 검색하세요.
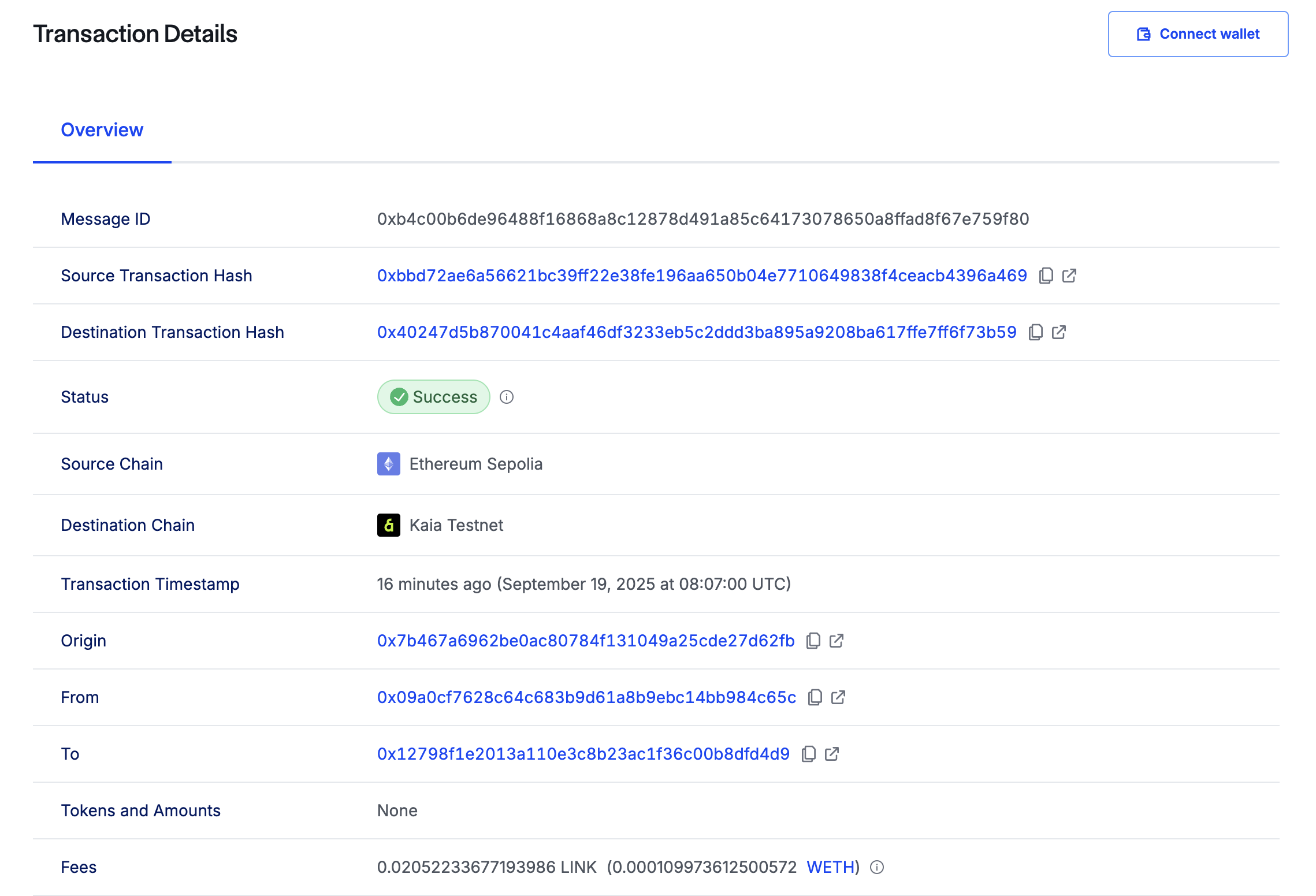
다음으로 할 일은 대상 체인에서 수신자 컨트랙트를 확인하는 것입니다. 이를 위해 아래 명령을 실행하여 *getLastReceivedMessageDetails()*를 호출합니다:
cast call `RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $KAIROS_RPC_URL "getLastReceivedMessageDetails()"
수신자 계약의 계약 주소를 수신자_배치된_주소로 바꿉니다.
수신된 문자 및 메시지 ID가 다음과 같이 16진수 데이터로 반환되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다:
0xb4c00b6de96488f16868a8c12878d491a85c64173078650a8ffad8f67e759f800000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000040000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000e674b616961206275696c64657273000000000000000000000000000000000000
특히 수신된 텍스트에 대해 16진수 데이터를 문자열로 변환하려면 아래 명령을 실행하세요:
cast to-utf8 674b616961206275696c64657273000000000000000000000000000000000000
이제 크로스 체인 작업이 성공했음을 의미하는 gKaia 빌더가 표시되어야 합니다.
결론
이 튜토리얼에서는 체인링크 CCIP를 사용하여 카이아 카이로스 테스트넷에서 다른 체인 이더리움 세폴리아로 또는 그 반대로 메시지를 전송하는 방법을 배웠습니다. 체인링크 CCIP와 작동 방식에 대한 자세한 가이드는 체인링크 CCIP 문서를 참조하시기 바랍니다.