Build Fee Delegation Example
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. How fee delegation works
- 2.1 Transaction signing by the sender
- 2.2 Transaction signing by the fee payer
- 3. Simple server and client for fee delegation
- 3.1 Environment setup
- 3.2 Sender's client
- 3.2 Fee payer's server
- 4. Run example
- 4.1 Run
feepayer_server.js - 4.2 Run
sender_client.js - 4.3 Check
feepayer_server.js - 4.4 View on Kaiascan
- 4.1 Run
1. Introduction
This tutorial guides you through creating a simple server-client example using the Kaia SDK (ethers-ext) to demonstrate how fee-delegated value transfer transactions work on Kaia. The tutorial and example code are tested on the Kairos testnet.
2. How fee delegation works
Let's skim through how fee delegation works.
2.1 Transaction signing by the sender
Sender always should sign the transaction before sending a transaction.
To sign a transaction, use signTransaction which signs a transaction with given private key.
const senderAddress = "SENDER_ADDRESS";const senderPrivateKey ="SENDER_PRIVATE_KEY";const recieverAddr = "RECEIVER_ADDRESS";// Create a new transactionlet tx = { type: TxType.FeeDelegatedValueTransfer, to: recieverAddr, value: parseKaia("0.01"), from: senderAddress,}; // Sign the transactiontx = await senderWallet.populateTransaction(tx);console.log(tx);const senderTxHashRLP = await senderWallet.signTransaction(tx);console.log("senderTxHashRLP", senderTxHashRLP);
If there are no errors, then senderTxHashRLP will have a signed transaction which is signed by the senderPrivateKey.
Now, you need to send the senderTxHashRLP to the fee payer. There are various ways to implement this. In this tutorial, we will provide you a simple server-client code as an example of sending a senderTxHashRLP to the fee payer.
2.2 Transaction signing by the fee payer
When fee payer receives the senderTxHashRLP, fee payer signs the senderTxHashRLP again with their private key and sends the transaction to Kaia. The below code snippet illustrates the process.
sendTransactionAsFeePayer method signs the transaction with the given fee payer private key before sending the transaction. Before running the code, kindly replace "FEEPAYER_ADDRESS" and "PRIVATE_KEY" with the actual values.
Note that when the fee payer submits the transaction to Kaia on behalf of the sender, the senderTxHashRLP type must be a FeeDelegatedValueTransfer type of transaction.
const feePayerAddress = "FEEPAYER_ADDRESS";const feePayerPrivateKey = "FEEPAYER_PRIVATE_KEY"const sentTx = await feePayerWallet.sendTransactionAsFeePayer(senderTxHashRLP);console.log("sentTx", sentTx);const rc = await sentTx.wait();console.log("receipt", rc);
3. Simple server and client for fee delegation
Let's write a simple server and client using above fee delegation code.
3.1 Environment setup
We will use npm init -y to setup our Node.js project, and install ethers-ext
mkdir feedelegation_servercd feedelegation_servernpm init -ynpm install - -save @kaiachain/ethers-ext@^1.2.0 ethers@6
@kaiachain/ethers-ext@^1.2.0 recommends node 22 or later
3.2 Sender's client
First, we are going to write a sender_client.js as below.
In the example, kindly replace "SENDER_ADDRESS", "SENDER_PRIVATEKEY" and "RECEIVER_ADDRESS" with the actual values.
const { Socket } = require("net");const client = new Socket();const { Wallet, TxType, parseKaia } = require("@kaiachain/ethers-ext").v6;const ethers = require("ethers");const senderAddress = "SENDER_ADDRESS";const senderPrivateKey = "SENDER_PRIVATE_KEY";const recieverAddr = "RECEIVER_ADDRESS";const sendFeeDelegateTx = async () => { try { const provider = new ethers.JsonRpcProvider("https://public-en-kairos.node.kaia.io"); const senderWallet = new Wallet(senderPrivateKey, provider); // Create a new transaction let tx = { type: TxType.FeeDelegatedValueTransfer, to: recieverAddr, value: parseKaia("0.01"), from: senderAddress, }; // Sign the transaction tx = await senderWallet.populateTransaction(tx); console.log(tx); const senderTxHashRLP = await senderWallet.signTransaction(tx); console.log("senderTxHashRLP", senderTxHashRLP); if (!senderTxHashRLP) { throw new Error("Failed to generate raw transaction"); } // Send signed raw transaction to fee payer's server client.connect(1337, "127.0.0.1", () => { console.log("Connected to fee delegated service"); client.write(senderTxHashRLP); }); client.on("data", (data) => { console.log("Received data from server:", data.toString()); }); client.on("error", (error) => { console.error("Connection error:", error); s; }); client.on("close", () => { console.log("Connection closed"); }); } catch (error) { console.error("Transaction error:", error); client.end(); process.exit(1); } }; sendFeeDelegateTx();
The above code signs a fee delegated value transfer transaction with senderPrivateKey and sends the signed senderTxHashRLP to the fee payer's server which is running on port 1337 on 127.0.0.1, i.e. localhost.
3.3 Fee payer's server
Now let's write the fee payer's server, feepayer_server.js, which signs the received senderTxHashRLP with feePayerPrivateKey and sends it to Kairos testnet.
In the below example, kindly replace "FEEPAYER_ADDRESS" and "FEEPAYER_PRIVATEKEY" with actual values.
const { createServer } = require("net");const { Wallet, JsonRpcProvider } = require("@kaiachain/ethers-ext").v6;const feePayerAddress = "FEEPAYER_ADDRESS";const feePayerPrivateKey = "FEEPAYER_PRIVATE_KEY";const provider = new JsonRpcProvider("https://public-en-kairos.node.kaia.io");const feePayerWallet = new Wallet(feePayerPrivateKey, provider);const feePayerSign = async (senderTxHashRLP, socket) => { try { // Send the transaction const sentTx = await feePayerWallet.sendTransactionAsFeePayer(senderTxHashRLP); console.log("sentTx", sentTx); const rc = await sentTx.wait(); console.log("receipt", rc); if (rc.transactionHash) { socket.write(`Tx hash: ${rc.transactionHash}\n`); socket.write(`Sender Tx hash: ${rc.senderTxHash || ""}\n`); } } catch (error) { console.error("Error in feePayerSign:", error); socket.write(`Error: ${error.message}\n`); }};const server = createServer(function (socket) { console.log("Client is connected ..."); socket.write("This is fee delegating service"); socket.write("Fee payer is " + feePayerAddress); socket.on("data", function (data) { console.log("Received data from client:", data.toString()); feePayerSign(data.toString(), socket); }); socket.on("error", (error) => { console.error("Socket error:", error); }); socket.on("end", () => { console.log("Client disconnected"); });});server.listen(1337, "127.0.0.1");console.log("Fee delegate service started ...");
The server listens on port 1337.
When there is incoming data, it signs the data with feePayerPrivateKey and sends it to the Kaia blockchain. It assumes that the data is senderTxHashRLP from the sender_client.js.
4. Run example
Prepare two terminals, one for sender_client.js and another for feepayer_server.js.
4.1 Run feepayer_server.js
Run the command below to start the fee payer's server:
node feepayer_server.js// outputFee delegate service started ...
The server starts and is now listening on port 1337.
4.2 Run sender_client.js
Let's run sender_client.js to send a fee delegated transaction.
$ node sender_client.js// output{ type: 9, to: '0x3a388d3fD71A0d9722c525E17007DdCcc41e1C47', value: 10000000000000000n, from: '0x7D3C7202582299470F2aD3DDCB8EF2F45407F871', nonce: 202, gasLimit: 52500, gasPrice: '27500000000', chainId: '1001'}senderTxHashRLP 0x09f88681ca85066720b30082cd14943a388d3fd71a0d9722c525e17007ddccc41e1c47872386f26fc10000947d3c7202582299470f2ad3ddcb8ef2f45407f871f847f8458207f6a0820d11029771f2fa368ce11da01f1c9e7f4de6d48915074d149e132692f9d63ea0131c62470a6799dfc5d7e3a7ac8d0a4f3b8fb8b59110ca5dabb26a9ee409f274Connected to fee delegated serviceReceived data from server: This is fee delegating, serviceFee payer is 0x88311cD55B656D2502b50f62E83F8279c1641e70
It will sign a transaction with the sender private key and send the signed transaction to the fee delegated service (i.e., fee payer's server). Then it will receive the response from the fee delegate service including the Fee payer address, Tx hash. Tx hash is hash of a transaction submitted to the Kaia network.
4.3 Check feepayer_server.js
On the server's console, you will see below outputs. It prints the transaction receipt from the Kaia.
$ node feepayer_server.jsFee delegate service started ...Client is connected ...Received data from client: 0x09f88681ca85066720b30082cd14943a388d3fd71a0d9722c525e17007ddccc41e1c47872386f26fc10000947d3c7202582299470f2ad3ddcb8ef2f45407f871f847f8458207f6a0820d11029771f2fa368ce11da01f1c9e7f4de6d48915074d149e132692f9d63ea0131c62470a6799dfc5d7e3a7ac8d0a4f3b8fb8b59110ca5dabb26a9ee409f274sentTx TransactionResponse {… to: '0x3a388d3fD71A0d9722c525E17007DdCcc41e1C47', from: '0x7D3C7202582299470F2aD3DDCB8EF2F45407F871', contractAddress: null, hash: '0x7cb1e8d20b4db7d9db1abc094781e1af83a9391153aab8cc935510639a548222', index: 0, blockHash: '0x50d3d7e143579e17dbc17b761c8e04331c6d4d950fe7563ac9a79d42a649de0a', blockNumber: 177078710, logsBloom: '0x00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000', gasUsed: 31000n, blobGasUsed: null, cumulativeGasUsed: 31000n, gasPrice: 27500000000n, blobGasPrice: null, type: 0, status: 1, root: undefined}
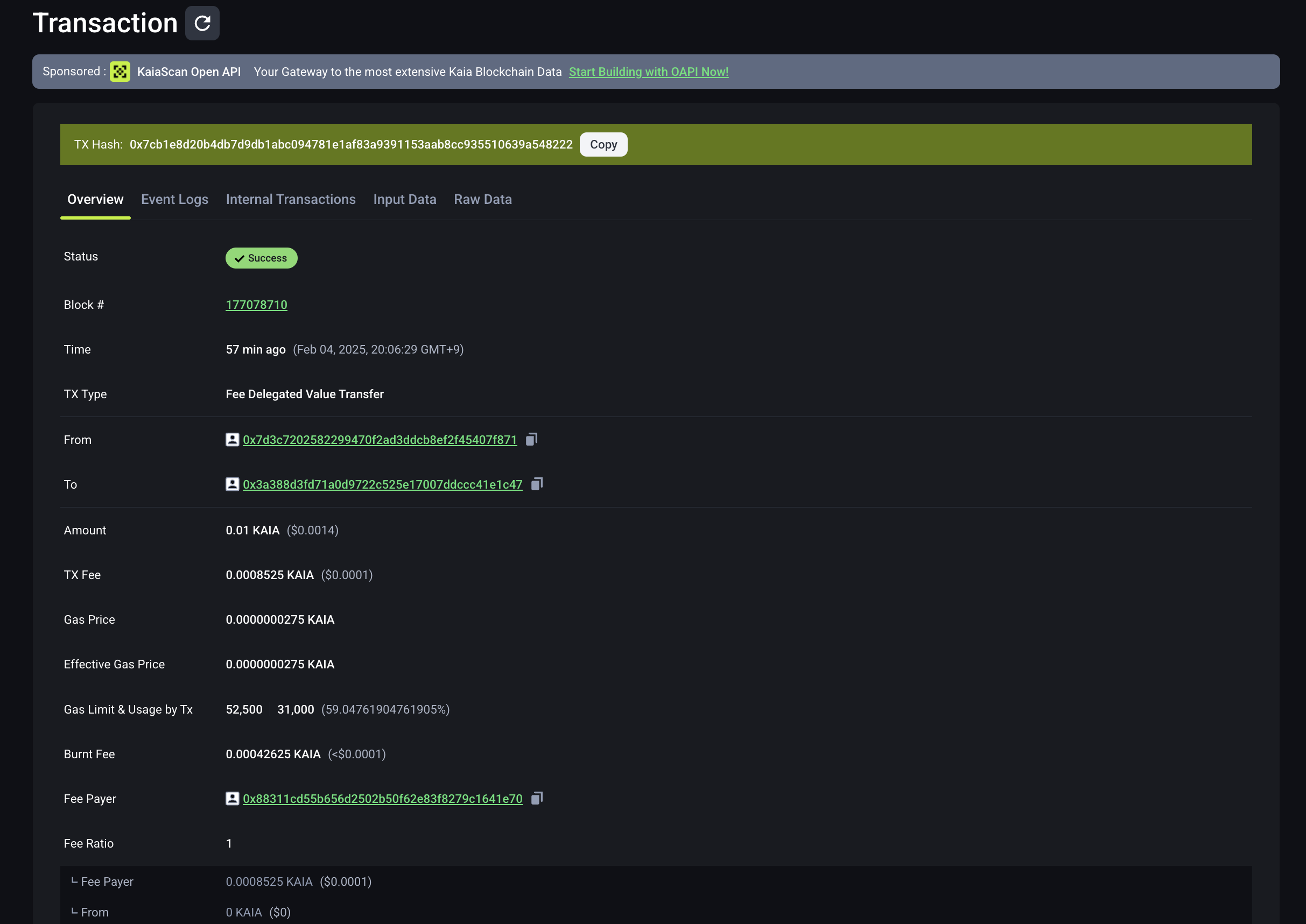
4.4 View on Kaiascan
You can also find the above transaction on Kaiascan.
It shows that the transaction is TxTypeFeeDelegatedValueTransfer and Fee payer is 0x88311cd55b656d2502b50f62e83f8279c1641e70 or feepayerAddress that you entered, while From is a different address which should be the senderAddress in above example.