Kaia Overview
Kaia is a highly optimized, BFT-based public blockchain designed to meet enterprise-grade reliability and performance standards. This overview details Kaia's architecture, features, and ecosystem.
Key Design Goals
Kaia blockchain aims to:
- Achieve immediate finality for transactions.
- Provide high transaction processing speed for real-world use cases.
- Lower the cost of running blockchain applications.
- Reduce barriers to entry for end-users.
- Facilitate easy technology adoption for various industries.
Core Specifications
Kaia blockchain offers:
- 1-second block generation and confirmation time.
- Processing capability of 4,000 transactions per second.
- Low gas price, approximately 1/10 of Ethereum.
- EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) compatibility, supporting Solidity contracts.
- Governance by reputable corporations worldwide forming Kaia Governance Council.
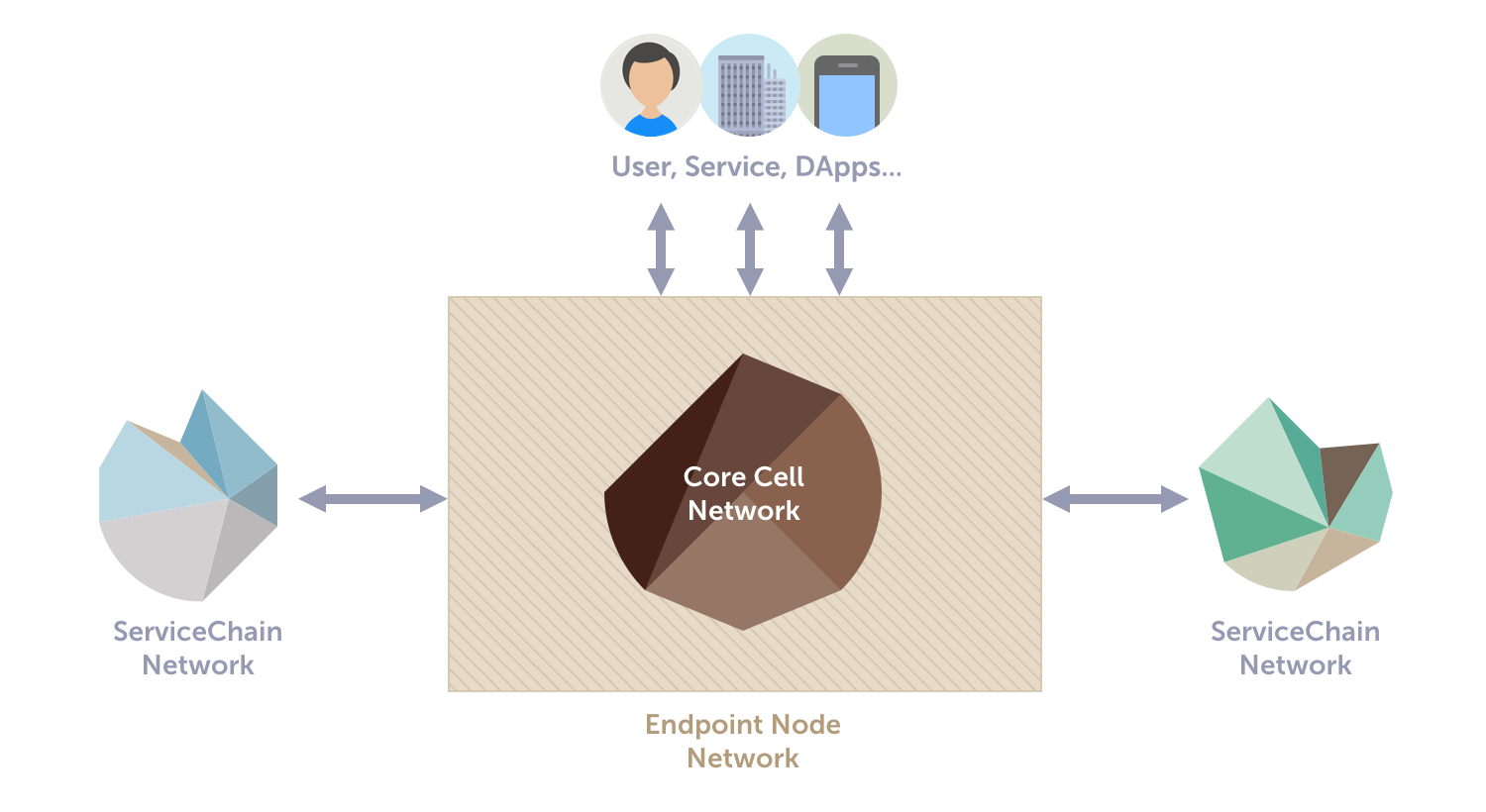
Network Architecture
Kaia's network is structured into three logical subnetworks:
-
Core Cell Network (CCN): Consists of Core Cells (CCs) responsible for transaction verification, execution, and block creation.
-
Endpoint Node Network (ENN): Composed of Endpoint Nodes (ENs) that handle RPC API requests and process data for service chains.
-
Service Chain Network (SCN): Auxiliary blockchains independently operated by dApps, connected to the main chain via ENs.
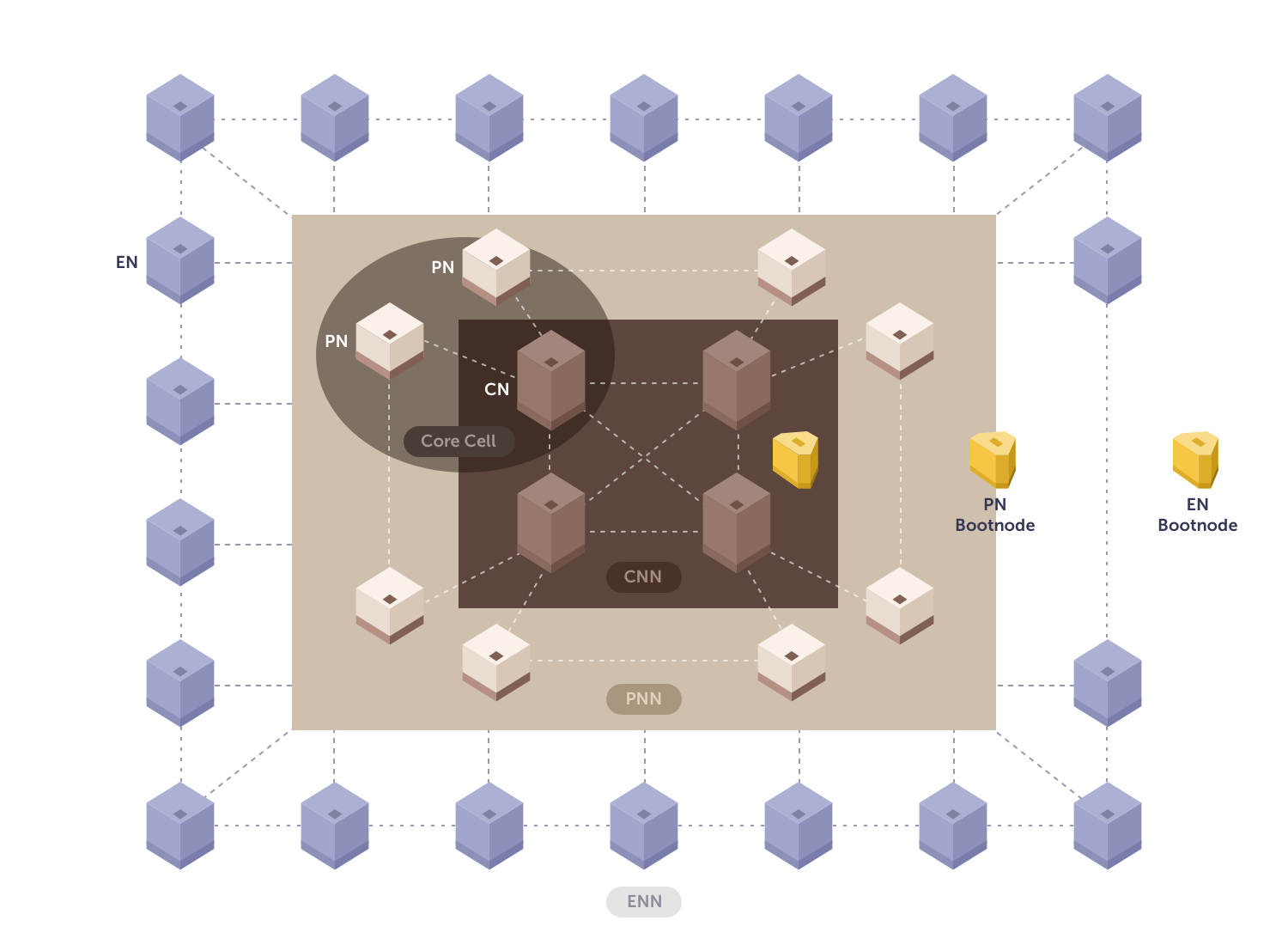
Node Types
-
Core Cell (CC): Composed of one Consensus Node (CN) and two Proxy Nodes (PNs).
- Consensus Node (CN): Participates in block generation.
- Proxy Node (PN): Provides network interface, transmits transaction requests, and propagates blocks.
-
Endpoint Node (EN): Serves as network endpoints, handling API requests and data processing.
-
Bootnode: Special nodes operated by Kaia to help new nodes join the network.
Consensus Algorithm
Kaia uses an optimized version of Istanbul BFT, implementing Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) with blockchain-specific modifications. The consensus process involves:
- Election of a committee (proposer and validator) using Verifiable Random Function (VRF).
- Block generation by the elected proposer.
- Block verification and signing by the committee.
This consensus mechanism enables Kaia to achieve high performance, processing 4,000 transactions per second with instant transaction finality.
Block Generation and Propagation
- Blocks are generated in rounds, targeting a 1-second interval.
- Proposer and committee selection is random but deterministic.
- Blocks require signatures from more than two-thirds of committee members.
- Separate propagation channels for blocks and transactions (multichannel approach) manage network congestion.
Kaia Virtual Machine (KVM)
The Kaia Virtual Machine (KVM) provides a robust environment for smart contract execution:
- Based on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
- Supports all EVM opcodes and additional Kaia-specific precompiled contracts.
- Compatible with Solidity and Ethereum development tools (e.g. Remix, Hardhat, Foundry).
- Allows developers to port Ethereum smart contracts to Kaia with minimal modifications.
Security Measures
Kaia implements several security measures:
- VRF for random selection of block proposers, adding unpredictability to the process.
- Separation of validator keys and reward keys to protect validators from potential key theft.
- Transparent block verification process, with all committee members verifying signatures on proposed blocks.
Interoperability
Kaia is designed for seamless interaction with other blockchain networks:
- EVM-compatible, allowing easy deployment of Ethereum smart contracts.
- Designed to interoperate with other EVM-SDK based chains.
- Supports cross-platform transactions and smart contract execution.
Token Economy
Kaia's native token, KAIA, plays a central role in the blockchain's economy:
- KAIA tokens are issued automatically with each new block.
- Initial annual inflation rate: 5.2%.
- Block rewards are distributed as follows:
- CCO and Community: 50% (20% Block Creator rewards, 80% Staking rewards)
- KEF (Kaia Ecosystem Fund): 25%
- KIF (Kaia Infrastructure Fund): 25%
This distribution model incentivizes network participation while supporting the growth and development of the Kaia ecosystem.
Governance
Kaia implements an on-chain governance system designed to be fair and inclusive:
- Voting rights are proportional to the amount of KAIA tokens staked.
- A cap on voting rights prevents suppression of minority opinions.
- Delegation of voting power is allowed.
- All governance proposals are recorded on-chain, ensuring transparency.
Auditability and Transparency
Kaia prioritizes transparency and auditability:
- All transactions provide an immutable and verifiable history of state changes.
- Two primary tools for blockchain exploration:
- Kaiascan: The official block explorer for Kaia, providing insights into blocks, transactions, addresses, tokens, and smart contracts.
- OKX Kaia Explorer: An alternative block explorer offering similar functionalities.
- The "Square" voting platform discloses all expenses and quarterly known transactions.
Network Monitoring
To ensure optimal performance and reliability, Kaia implements:
- A multi-channel approach to manage network congestion.
- Dedicated network monitoring for all validators.