チェーンリンク CCIP

はじめに
Chainlink Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol(CCIP)は、開発者と分散型アプリケーション(dApps)に、ブロックチェーン間で相互作用する安全で効率的な方法を提供する。 CCIPを使用すると、トークンや任意のメッセージを送信して、NFTの鋳造、インデックスのリバランス、カスタム関数の呼び出しなど、宛先コントラクトのアクションをトリガーすることができます。
このチュートリアルでは、Chainlink CCIPを使用して、Kaiaスマートコントラクトから別のチェーンのコントラクトにメッセージとトークンを送信し、それらを受信する方法を学びます。
前提条件
- ファウンドリ・インストール
- curl -L https://foundry.paradigm.xyz | bash
でインストールし、foundryup`を実行する。 - forge --version
、cast --version、anvil --version`で検証する。
- curl -L https://foundry.paradigm.xyz | bash
- メタマスク ウォレット
- デベロッパーウォレットの設定
- MetaMaskにKaia KairosテストネットとEthereum Sepoliaネットワークを追加。
- 蛇口からのテスト・トークン
- KAIA: カイアからのデプロイと送信のためのガス。
- LINK (testnet): LINKで支払う場合のCCIP料金。
- デスティネーションチェーン上のネイティブトークン(例えば、Sepolia ETH:デプロイ用で、選択された場合はネイティブでCCIP手数料を支払う)。
はじめに
このガイドでは、Chainlink CCIPを使用してKaia(Kairos Testnet)とEthereum Sepoliaの間でクロスチェーンメッセージを送受信します。
最後には
- KairosとSepolia用に設定されたFoundryプロジェクトを初期化する。
- Chainlink CCIPコントラクトとインタフェースを依存関係として追加する
- チェーンをまたいでメッセージを送受信するMessengerコントラクトを実装する
- 両方のネットワークに展開し、ラウンドトリップ・メッセージを検証する。
プロジェクトの作成
このセクションで��は、Foundryを使用して開発環境をセットアップします。 新しいFoundryプロジェクトを作成するには、まず新しいディレクトリを作成します:
mkdir kaia-foundry-ccip-example
それから走れ:
cd kaia-foundry-ccip-exampleforge init
これにより、以下のような基本レイアウトのFoundryプロジェクトが作成される:
├── foundry.toml├── script├── src└── test
Chainlinkスマートコントラクトのインストール
FoundryプロジェクトでChainlink CCIPを使用するには、forge installを使ってプロジェクトの依存関係としてChainlink CCIPスマートコントラクトをインストールする必要があります。
Chainlink CCIPスマート・コントラクトをインストールするには、以下を実行する:
forge install smartcontractkit/chainlink-ccip@2114b90f39c82c052e05af7c33d42c1ae98f4180forge install smartcontractkit/chainlink-evm@ff814eb0a01f89d9a215f825d243bf421e6434a9
インストールしたら、remapping.txtファイルを作成する:
forge remappings > remappings.txt
そして、新しく作成したファイルに以下を貼り付ける:
@chainlink/contracts/=lib/chainlink-evm/contracts/@chainlink/contracts-ccip/=lib/chainlink-ccip/chains/evm/contracts/
スマート・コントラクトの作成
このセクションでは、以下のコードを使用して、チェーン間でメッセージを送受信します。
プロジェクトのsrcディレクトリの下にMessenger.solという名前で新しいファイルを作成し、以下のコードをコピーしてください:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MITpragma solidity ^0.8.0;import { IRouterClient } from "@chainlink/contracts-ccip/interfaces/IRouterClient.sol";import {OwnerIsCreator} from "@chainlink/contracts/src/v0.8/shared/access/OwnerIsCreator.sol";import { Client } from "@chainlink/contracts-ccip/libraries/Client.sol";import { CCIPReceiver } from "@chainlink/contracts-ccip/applications/CCIPReceiver.sol";import {IERC20} from "@chainlink/contracts/src/v0.8/vendor/openzeppelin-solidity/v4.8.3/contracts/token/ERC20/IERC20.sol";import {SafeERC20} from "@chainlink/contracts/src/v0.8/vendor/openzeppelin-solidity/v4.8.3/contracts/token/ERC20/utils/SafeERC20.sol";/** * THIS IS AN EXAMPLE CONTRACT THAT USES HARDCODED VALUES FOR CLARITY. * THIS IS AN EXAMPLE CONTRACT THAT USES UN-AUDITED CODE. * DO NOT USE THIS CODE IN PRODUCTION. *//// @title - A simple messenger contract for sending/receiving string data across chains.contract Messenger is CCIPReceiver, OwnerIsCreator { using SafeERC20 for IERC20; // Custom errors to provide more descriptive revert messages. error NotEnoughBalance(uint256 currentBalance, uint256 calculatedFees); // Used to make sure contract has enough balance. error NothingToWithdraw(); // Used when trying to withdraw Ether but there's nothing to withdraw. error FailedToWithdrawEth(address owner, address target, uint256 value); // Used when the withdrawal of Ether fails. error DestinationChainNotAllowlisted(uint64 destinationChainSelector); // Used when the destination chain has not been allowlisted by the contract owner. error SourceChainNotAllowlisted(uint64 sourceChainSelector); // Used when the source chain has not been allowlisted by the contract owner. error SenderNotAllowlisted(address sender); // Used when the sender has not been allowlisted by the contract owner. error InvalidReceiverAddress(); // Used when the receiver address is 0. // Event emitted when a message is sent to another chain. event MessageSent( bytes32 indexed messageId, // The unique ID of the CCIP message. uint64 indexed destinationChainSelector, // The chain selector of the destination chain. address receiver, // The address of the receiver on the destination chain. string text, // The text being sent. address feeToken, // the token address used to pay CCIP fees. uint256 fees // The fees paid for sending the CCIP message. ); // Event emitted when a message is received from another chain. event MessageReceived( bytes32 indexed messageId, // The unique ID of the CCIP message. uint64 indexed sourceChainSelector, // The chain selector of the source chain. address sender, // The address of the sender from the source chain. string text // The text that was received. ); bytes32 private s_lastReceivedMessageId; // Store the last received messageId. string private s_lastReceivedText; // Store the last received text. // Mapping to keep track of allowlisted destination chains. mapping(uint64 => bool) public allowlistedDestinationChains; // Mapping to keep track of allowlisted source chains. mapping(uint64 => bool) public allowlistedSourceChains; // Mapping to keep track of allowlisted senders. mapping(address => bool) public allowlistedSenders; IERC20 private s_linkToken; /// @notice Constructor initializes the contract with the router address. /// @param _router The address of the router contract. /// @param _link The address of the link contract. constructor(address _router, address _link) CCIPReceiver(_router) { s_linkToken = IERC20(_link); } /// @dev Modifier that checks if the chain with the given destinationChainSelector is allowlisted. /// @param _destinationChainSelector The selector of the destination chain. modifier onlyAllowlistedDestinationChain(uint64 _destinationChainSelector) { if (!allowlistedDestinationChains[_destinationChainSelector]) revert DestinationChainNotAllowlisted(_destinationChainSelector); _; } /// @dev Modifier that checks if the chain with the given sourceChainSelector is allowlisted and if the sender is allowlisted. /// @param _sourceChainSelector The selector of the destination chain. /// @param _sender The address of the sender. modifier onlyAllowlisted(uint64 _sourceChainSelector, address _sender) { if (!allowlistedSourceChains[_sourceChainSelector]) revert SourceChainNotAllowlisted(_sourceChainSelector); if (!allowlistedSenders[_sender]) revert SenderNotAllowlisted(_sender); _; } /// @dev Modifier that checks the receiver address is not 0. /// @param _receiver The receiver address. modifier validateReceiver(address _receiver) { if (_receiver == address(0)) revert InvalidReceiverAddress(); _; } /// @dev Updates the allowlist status of a destination chain for transactions. function allowlistDestinationChain( uint64 _destinationChainSelector, bool allowed ) external onlyOwner { allowlistedDestinationChains[_destinationChainSelector] = allowed; } /// @dev Updates the allowlist status of a source chain for transactions. function allowlistSourceChain( uint64 _sourceChainSelector, bool allowed ) external onlyOwner { allowlistedSourceChains[_sourceChainSelector] = allowed; } /// @dev Updates the allowlist status of a sender for transactions. function allowlistSender(address _sender, bool allowed) external onlyOwner { allowlistedSenders[_sender] = allowed; } /// @notice Sends data to receiver on the destination chain. /// @notice Pay for fees in LINK. /// @dev Assumes your contract has sufficient LINK. /// @param _destinationChainSelector The identifier (aka selector) for the destination blockchain. /// @param _receiver The address of the recipient on the destination blockchain. /// @param _text The text to be sent. /// @return messageId The ID of the CCIP message that was sent. function sendMessagePayLINK( uint64 _destinationChainSelector, address _receiver, string calldata _text ) external onlyOwner onlyAllowlistedDestinationChain(_destinationChainSelector) validateReceiver(_receiver) returns (bytes32 messageId) { // Create an EVM2AnyMessage struct in memory with necessary information for sending a cross-chain message Client.EVM2AnyMessage memory evm2AnyMessage = _buildCCIPMessage( _receiver, _text, address(s_linkToken) ); // Initialize a router client instance to interact with cross-chain router IRouterClient router = IRouterClient(this.getRouter()); // Get the fee required to send the CCIP message uint256 fees = router.getFee(_destinationChainSelector, evm2AnyMessage); if (fees > s_linkToken.balanceOf(address(this))) revert NotEnoughBalance(s_linkToken.balanceOf(address(this)), fees); // Approve the Router to transfer LINK tokens on contract's behalf. It will spend the fees in LINK s_linkToken.approve(address(router), fees); // Send the CCIP message through the router and store the returned CCIP message ID messageId = router.ccipSend(_destinationChainSelector, evm2AnyMessage); // Emit an event with message details emit MessageSent( messageId, _destinationChainSelector, _receiver, _text, address(s_linkToken), fees ); // Return the CCIP message ID return messageId; } /// @notice Sends data to receiver on the destination chain. /// @notice Pay for fees in native gas. /// @dev Assumes your contract has sufficient native gas tokens. /// @param _destinationChainSelector The identifier (aka selector) for the destination blockchain. /// @param _receiver The address of the recipient on the destination blockchain. /// @param _text The text to be sent. /// @return messageId The ID of the CCIP message that was sent. function sendMessagePayNative( uint64 _destinationChainSelector, address _receiver, string calldata _text ) external onlyOwner onlyAllowlistedDestinationChain(_destinationChainSelector) validateReceiver(_receiver) returns (bytes32 messageId) { // Create an EVM2AnyMessage struct in memory with necessary information for sending a cross-chain message Client.EVM2AnyMessage memory evm2AnyMessage = _buildCCIPMessage( _receiver, _text, address(0) ); // Initialize a router client instance to interact with cross-chain router IRouterClient router = IRouterClient(this.getRouter()); // Get the fee required to send the CCIP message uint256 fees = router.getFee(_destinationChainSelector, evm2AnyMessage); if (fees > address(this).balance) revert NotEnoughBalance(address(this).balance, fees); // Send the CCIP message through the router and store the returned CCIP message ID messageId = router.ccipSend{value: fees}( _destinationChainSelector, evm2AnyMessage ); // Emit an event with message details emit MessageSent( messageId, _destinationChainSelector, _receiver, _text, address(0), fees ); // Return the CCIP message ID return messageId; } /// handle a received message function _ccipReceive( Client.Any2EVMMessage memory any2EvmMessage ) internal override onlyAllowlisted( any2EvmMessage.sourceChainSelector, abi.decode(any2EvmMessage.sender, (address)) ) // Make sure source chain and sender are allowlisted { s_lastReceivedMessageId = any2EvmMessage.messageId; // fetch the messageId s_lastReceivedText = abi.decode(any2EvmMessage.data, (string)); // abi-decoding of the sent text emit MessageReceived( any2EvmMessage.messageId, any2EvmMessage.sourceChainSelector, // fetch the source chain identifier (aka selector) abi.decode(any2EvmMessage.sender, (address)), // abi-decoding of the sender address, abi.decode(any2EvmMessage.data, (string)) ); } /// @notice Construct a CCIP message. /// @dev This function will create an EVM2AnyMessage struct with all the necessary information for sending a text. /// @param _receiver The address of the receiver. /// @param _text The string data to be sent. /// @param _feeTokenAddress The address of the token used for fees. Set address(0) for native gas. /// @return Client.EVM2AnyMessage Returns an EVM2AnyMessage struct which contains information for sending a CCIP message. function _buildCCIPMessage( address _receiver, string calldata _text, address _feeTokenAddress ) private pure returns (Client.EVM2AnyMessage memory) { // Create an EVM2AnyMessage struct in memory with necessary information for sending a cross-chain message return Client.EVM2AnyMessage({ receiver: abi.encode(_receiver), // ABI-encoded receiver address data: abi.encode(_text), // ABI-encoded string tokenAmounts: new Client.EVMTokenAmount[](0), // Empty array as no tokens are transferred extraArgs: Client._argsToBytes( // Additional arguments, setting gas limit and allowing out-of-order execution. // Best Practice: For simplicity, the values are hardcoded. It is advisable to use a more dynamic approach // where you set the extra arguments off-chain. This allows adaptation depending on the lanes, messages, // and ensures compatibility with future CCIP upgrades. Read more about it here: https://docs.chain.link/ccip/concepts/best-practices/evm#using-extraargs Client.GenericExtraArgsV2({ gasLimit: 200_000, // Gas limit for the callback on the destination chain allowOutOfOrderExecution: true // Allows the message to be executed out of order relative to other messages from the same sender }) ), // Set the feeToken to a feeTokenAddress, indicating specific asset will be used for fees feeToken: _feeTokenAddress }); } /// @notice Fetches the details of the last received message. /// @return messageId The ID of the last received message. /// @return text The last received text. function getLastReceivedMessageDetails() external view returns (bytes32 messageId, string memory text) { return (s_lastReceivedMessageId, s_lastReceivedText); } /// @notice Fallback function to allow the contract to receive Ether. /// @dev This function has no function body, making it a default function for receiving Ether. /// It is automatically called when Ether is sent to the contract without any data. receive() external payable {} /// @notice Allows the contract owner to withdraw the entire balance of Ether from the contract. /// @dev This function reverts if there are no funds to withdraw or if the transfer fails. /// It should only be callable by the owner of the contract. /// @param _beneficiary The address to which the Ether should be sent. function withdraw(address _beneficiary) public onlyOwner { // Retrieve the balance of this contract uint256 amount = address(this).balance; // Revert if there is nothing to withdraw if (amount == 0) revert NothingToWithdraw(); // Attempt to send the funds, capturing the success status and discarding any return data (bool sent, ) = _beneficiary.call{value: amount}(""); // Revert if the send failed, with information about the attempted transfer if (!sent) revert FailedToWithdrawEth(msg.sender, _beneficiary, amount); } /// @notice Allows the owner of the contract to withdraw all tokens of a specific ERC20 token. /// @dev This function reverts with a 'NothingToWithdraw' error if there are no tokens to withdraw. /// @param _beneficiary The address to which the tokens will be sent. /// @param _token The contract address of the ERC20 token to be withdrawn. function withdrawToken( address _beneficiary, address _token ) public onlyOwner { // Retrieve the balance of this contract uint256 amount = IERC20(_token).balanceOf(address(this)); // Revert if there is nothing to withdraw if (amount == 0) revert NothingToWithdraw(); IERC20(_token).safeTransfer(_beneficiary, amount); }}
上のコードは、オーナー・ゲート・コントロール、LINK、またはネイティブな料金支払いで、許可リストに登録されたチェーン間で文字列メッセージを送受信する双方向��のCCIPコントラクトである。 この契約で使う主な関数を見てみよう:
**1. アロリスト
- allowlistSourceChain(セレクタ, allowed):このコントラクトへのメッセージ配信を許可するソースチェーンを制御します。
- allowlistDestinationChain(selector, allowed):このコントラクトがどの宛先チェーンへの送信を許可するかを制御します。
- allowlistedSenders[address](allowlistSender(addr,allowed)を経由する):メッセージが到着したときに、送信元チェーン上のどの送信者アドレスが信頼されるかを制限する。
テストの前に、両端にこれをセットする。 送信元は送信者とチェーンを信頼しなければならない。 送信先もallowlistedでなければならない。
**2. メッセージの送信
sendMessagePayLINK(selector, receiver, text):メッセージを送信し、CCIP料金をLINKで支払う。 これはメッセージを作成し、料金を提示し、LINK残高をチェックし、ルータを承認し、そしてccipSendを実行��する。 完了すると、送信されたメッセージに関連する一意のIDが返される。
sendMessagePayNative(selector, receiver, text):メッセージを送信し、ネイティブ・トークンでCCIP料金を支払う。 これはメッセージを作成し、料金を提示し、ネイティブの残高をチェックし、そしてccipSend(value: fees)を実行する。 完了すると、送信されたメッセージに関連する一意のIDが返される。
**3. メッセージの構築
_buildCCIPMessage(receiver, text, feeTokenAddress) -> EVM2AnyMessage
- レシーバーとテキストをエンコードする
- トークンを送信しない(tokenAmountsが空)。
- GenericExtraArgsV2を使用し、設定可能なgasLimitを持つextraArgsをパッケージ化。
- feeTokenをLINKまたはネイティブのaddress(0)に設定する。
**4. メッセージの受信
CCIPは_ccipReceive(...)を呼び出す。 をデスティネーションチェーンに追加する。 契約だ:
- 送信元チェーンと送信者を許可リストに照らして検証する。
- 文字列をデコードする
- 最後に受信したペイロードとして保存
- MessageReceivedを発する
- 最後の受信ペイロードを以下のようにして読み返す: getLastReceivedMessageDetails() -> (messageId, text)
スマート・コントラクトのコンパイル
スマート・コントラクトをコンパイルするには、以下を実行する:
forge build
スマートコントラクトの導入
デプロイヤーとしてウォレットを設定する
スマートコントラクトをネットワークにデプロイする前に、デプロイ先となるウォレットをセットアップする必要がある。 そのためには、cast wallet import コマンドを使って、ウォレットの秘密鍵をFoundryの安全に暗号化されたキーストアにインポートします:
cast wallet import deployer --interactive
上記のコマンドを実行すると、秘密鍵とトランザクション署名用のパスワードの入力を求められる。
ウォレットがFoundryプロ�ジェクトのデプロイアカウントとしてインポートされたことを確認するには、以下を実行します:
cast wallet list
環境変数の設定
環境をセットアップするには、プロジェクトのホームディレクトリに.envファイルを作成し、Kairos TestnetとEthereum Sepoliaの両方のRPC URL、CCIP chain selectors、CCIP router addresses、LINK token addressesを追加します:
KAIROS_RPC_URL="https://public-en-kairos.node.kaia.io"ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL="https://ethereum-sepolia-rpc.publicnode.com"KAIROS_CHAIN_SELECTOR=2624132734533621656ETH_SEPOLIA_CHAIN_SELECTOR=16015286601757825753KAIROS_ROUTER_ADDRESS="0x41477416677843fCE577748D2e762B6638492755"ETH_SEPOLIA_ROUTER_ADDRESS="0x0BF3dE8c5D3e8A2B34D2BEeB17ABfCeBaf363A59"KAIROS_LINK_ADDRESS="0xAF3243f975afe2269Da8Ffa835CA3A8F8B6A5A36"ETH_SEPOLIA_LINK_ADDRESS="0x779877A7B0D9E8603169DdbD7836e478b4624789"
.env`ファイルを作成したら、以下のコマンドを実行して、現在のコマンドラインセッションの環境変数をロードする:
source .env
コントラクトがコンパイルされ、環境がセットアップされれば、スマート・コントラクトをデプロイする準備は完了だ。
Foundryを使用してスマート・コントラクトをデプロイするには、forge createコマンドを使用します。 このコマンドでは、デプロイしたいスマート・コントラクト、デプロイ先のネットワークのRPC URL、デプロイするアカウントを指定する必要がある。
Kairos TestnetへのSender契約の展開
SenderスマートコントラクトをKaia Kairos Testnetにデプロイするには��、以下のコマンドを実行する:
forge create --rpc-url $KAIROS_RPC_URL --account deployer --broadcast src/Messenger.sol:Messenger --constructor-args $KAIROS_ROUTER_ADDRESS $KAIROS_LINK_ADDRESS
プロンプトが表示されたら、ウォレットの秘密鍵をインポートしたときに設定したパスワードを入力します。
上記のコマンドを実行すると、契約はKairosテストネットワーク上に展開されます。 Kaiascan ブロックエクスプローラー](https://kairos.kaiascan.io)を使用することで、デプロイ状況や契約を確認することができます。
イーサリアム・セポリア上のレシーバー・コントラクトにCCIPメッセージを送信するコントラクトを有効にする
まず、取引先チェーンの許可リストステータスを更新する必要がある。 そのためには、以下のコマンドを実行する:
cast send `SENDER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $KAIROS_RPC_URL "allowlistDestinationChain(uint64, bool)" $ETH_SEPOLIA_CHAIN_SELECTOR true --account deployer
上記のコードでは、*allowlistDestinationChain()*を呼び出して、Senderコントラクトで許可するデスティネーションチェーンセレクタを設定している。 各チェーンセレクターはCCIPディレクトリに掲載されている。
Ethereum SepoliaへのReceiverコントラクトのデプロイ
ReceiverスマートコントラクトをEthereum Sepoliaにデプロイするには、以下のコマンドを実行する:
forge create --rpc-url $ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL --account deployer --broadcast src/Messenger.sol:Messenger --constructor-args $ETH_SEPOLIA_ROUTER_ADDRESS $ETH_SEPOLIA_LINK_ADDRESS
プロンプトが表示されたら、ウォレットの秘密鍵をインポートしたときに設定したパスワードを入力します。
上記のコマンドを実行すると、コントラクトがEthereum Sepoliaにデプロイされる。 ETHセポリアブロックエクスプローラー](https://sepolia.etherscan.io/)を使用することで、デプロイ状況やコントラクトを確認することができます。
Kairos TestnetのSender ContractからCCIPメッセージを受信できるようにする。
まず、トランザクションのソース・チェーンの許可リスト・ステータスを更新する必要がある。 そのためには、以下のコマンドを実行する:
cast send `RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL "allowlistSourceChain(uint64, bool)" $KAIROS_CHAIN_SELECTOR true --account deployer
上記のコードでは、allowlistSourceChain() を呼び出して、Receiver 契約で許可されるソース・ チェーン・セレクタを設定します。 各チェーンセレクターはCCIPディレクトリに掲載されている。
Kairos TestnetのSender契約からCCIPメッセージを受信できるようにする。
トランザクションの送信者の許可リスト・ステータスを更新するには、以下のコマンドを実行する:
cast send `RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL "allowlistSender(address, bool)" 0x12798F1E2013A110E3C8B23aC1f36c00B8DFD4d9 true --account deployer
この時点で、あなたはKairos Testnet上の1つの送信者契約とEthereum Sepolia上の1つの受信者契約を持っています。 セキュリティ対策として、Ethereum SepoliaにCCIPメッセージを送信する送信者コントラクトと、送信者とKairos TestnetからCCIPメッセージを受信する受信者コントラクトを有効にしました。
スマートコントラクトの資金調達
メッセージ送信に関連する手数料を支払うために、Sender契約はLINKトークン、データを送信しネイティブトークンで支払う場合はETHとKAIAの残高を保持する必要があります。
**リンク
ウォレットから直接、または以下のキャストコマンドを実行することで、コントラクトに資金を供給します:
cast send $KAIROS_LINK_ADDRESS --rpc-url $KAIROS_RPC_URL "transfer(address,uint256)" `SENDER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` 5000000000000000000 --account deployer
上記のコマンドは、Kairos Testnet上の5 LINKトークンをSenderコントラクトに送信する。
提供されたキャストコマンドを実行する前に、SENDER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESSをデプロイされたSenderコントラクトのコントラクトアドレスに置き換えてください。
スマート・コントラクトとの対話
このセクションでは、デプロイされたスマートコントラクトと対話し、Foundry castコマンドラインツールを使用してその機能を呼び出します。
データを送信し、LINKで支払う
このステップでは、CCIPを使ってテキストを送信し、CCIPの使用料はLINKで支払う。
そのためには、Ethereum Sepolia上のReceiverコントラクトにメッセージデータを送信するために、Kairos TestnetにデプロイされたSenderコントラクト上で*sendMessagePayLINK(uint64, address, string)*関数を呼び出すためにcastコマンドを使用します。
Senderスマートコントラクトの*sendMessagePayLINK(uint64, address, string)*関数を呼び出すには、以下を実行する:
cast send `SENDER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $KAIROS_RPC_URL "sendMessagePayLINK(uint64, address, string)" $ETH_SEPOLIA_CHAIN_SELECTOR `RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` "gKaia builders" --account deployer
上のコマンドは、*sendMessagePayLINK(uint64, address, string)*を呼び出してメッセージを送信している。 メソッドに渡されるパラメータは以下の通り:送信先チェーンへのチェーンセレクタ(Ethereum Sepolia)、Receiverコントラクトアドレス、メッセージに含まれるテキストデータ(Hello Builders)。
コマンドを実行すると、一意な messageId が返されるはずである。
トランザクションが確定すると、CCIPがEthereum Sepoliaにデータを配信し、ReceiverコントラクトのccipReceive関数を呼び出すのに数分かかる。 クロスチェーン取引を確認するには、CCIPエクスプローラーを開き、取引ハッシュを使って検索します。
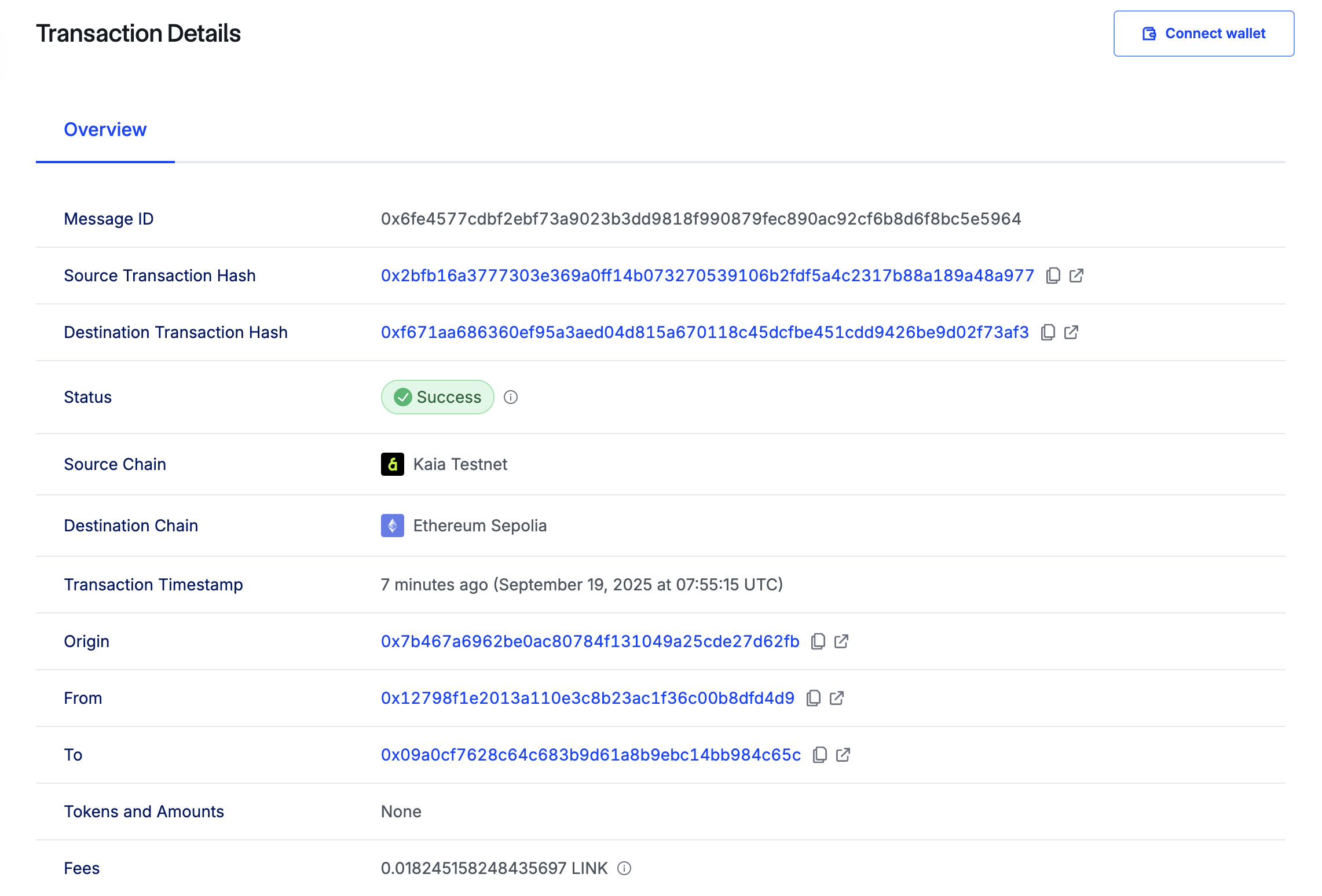
次にすべきことは、デスティネーションチェーンのレシーバー契約をチェックすることだ。 そのためには、以下のコマンドを実行して getLastReceivedMessageDetails() を呼び出す:
cast call `RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL "getLastReceivedMessageDetails()"
提供されたキャストコマンドを実行する前に、RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESSをデプロイ済みのReceiverコントラクトのコントラクトアドレスに置き換えてください。
このように、受信したテキストとメッセージIDが16進数データとして返されるはずだ:
0x6fe4577cdbf2ebf73a9023b3dd9818f990879fec890ac92cf6b8d6f8bc5e59640000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000040000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000e48656c6c6f206275696c64657273000000000000000000000000000000000000
受信した16進数データを文字列に変換するには、以下のコマンドを実行する:
cast to-utf8 e48656c6c6f206275696c64657273000000000000000000000000000000000000
これで、Hello builders と表示されるはずです。これは、クロス・チェーン・アクションが成功したことを意味します。
これらの契約例は双方向に機能するように設計されている。 Kairos TestnetからEthereum Sepoliaへ、Ethereum SepoliaからKairos Testnetへデータを送信するために使用できます。
データを送信し、ネイティブで支払う
このセクションでは、CCIPでテキストメッセージを送信し、ネイティブトークンで料金を支払います。 イーサリアム・セポリアからKaia(Kairos Testnet)に送金します。 つまり、セポリアの契約は送り手として機能し、カイロスの契約は受け手として機能する。
まず、イーサリアム・セポリア上のETHで送信者コントラクトに資金を供給する必要がある。 そのためには、以下のキャスト・コマンドを実行する:
cast send --rpc-url $ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL `SENDER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --value 300000000000000000 --account deployer
これは、イーサリアムのセポリアで0.3 ETHをあなたの送信者コントラクトに送信します。
SENDER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESSを送信者の契約アドレスに置き換える。
次に、イーサリアム・セポリア上の送信者コントラクトから送信先チェーンを許可する。 そのためには、以下のコマンドを実行する:
cast send `SENDER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL "allowlistDestinationChain(uint64, bool)" $KAIROS_CHAIN_SELECTOR true --account deployer
次に、Kairos Testnetのレシーバー契約からソースチェーンを許可する。 そのためには、以下のコマンドを実行する:
cast send `RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $KAIROS_RPC_URL "allowlistSourceChain(uint64, bool)" $ETH_SEPOLIA_CHAIN_SELECTOR true --account deployer
次に、Kairos Testnetのreceiverコントラクトで以下のコマンドを実行して、allowlistSenderを実行します:
cast send `RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $KAIROS_RPC_URL "allowlistSender(address, bool)" 0x09a0CF7628c64c683B9d61a8B9EBc14BB984c65c true --account deployer
コントラクトの配線が完了したら、このコマンドを実行してデータをレシーバーコントラクトに送信することができる:
cast send `SENDER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $ETH_SEPOLIA_RPC_URL "sendMessagePayNative(uint64, address, string)" $KAIROS_CHAIN_SELECTOR 0x12798F1E2013A110E3C8B23aC1f36c00B8DFD4d9 "gKaia Builders" --account deployer
上のコマンドは、*sendMessagePayNative(uint64, address, string)*を呼び出してメッセージを送信している。 メソッドに渡されるパラメータは以下の通り:送信先のチェーンセレクタ(Kairos Testnet)、受信契約アドレス、メッセージに含まれるテキストデータ(gKaia Builders)。
コマンドを実行すると、一意な messageId が返されるはずである。
トランザクションが確定すると、CCIPがKairos Testnetにデータを配信し、ReceiverコントラクトのccipReceive関数を呼び出すのに数分かかります。 クロスチェーン取引を確認するには、CCIPエクスプローラーを開き、取引ハッシュを使って検索します。
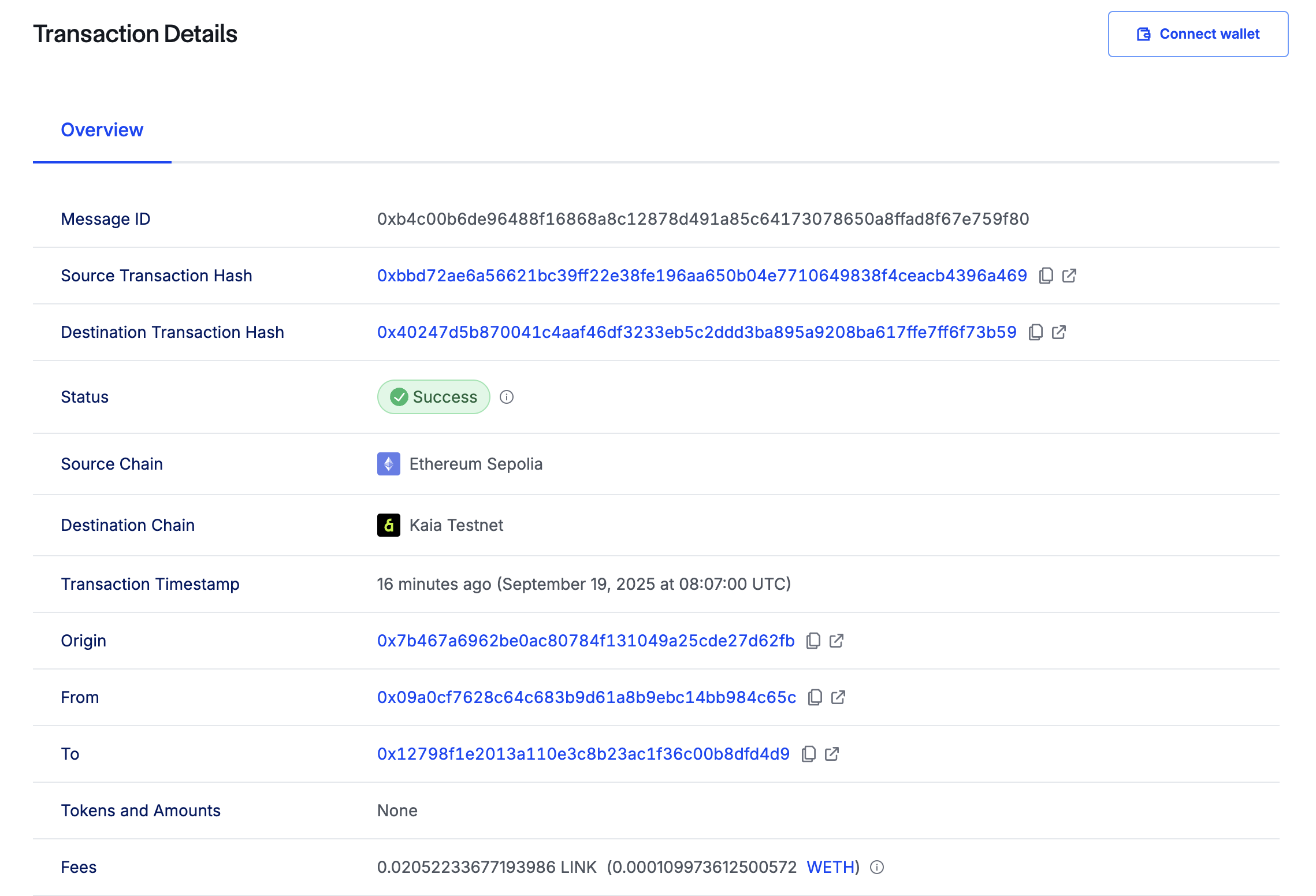
次にすべきことは、デスティネーションチェーンのレ��シーバー契約をチェックすることだ。 そのためには、以下のコマンドを実行して getLastReceivedMessageDetails() を呼び出す:
cast call `RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESS` --rpc-url $KAIROS_RPC_URL "getLastReceivedMessageDetails()"
RECEIVER_DEPLOYED_ADDRESSを受信契約の契約アドレスに置き換える。
このように、受信したテキストとメッセージIDが16進数データとして返されるはずだ:
0xb4c00b6de96488f16868a8c12878d491a85c64173078650a8ffad8f67e759f800000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000040000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000e674b616961206275696c64657273000000000000000000000000000000000000
受信した16進数データを特に文字列に変換するには、以下のコマンドを実行する:
cast to-utf8 674b616961206275696c64657273000000000000000000000000000000000000
これで、gKaiaビルダーと表示されるはずだ。
結論
このチュートリアルでは、Chainlink CCIPを使ってKaia Kairos Testnetから別のチェーンEthereum Sepoliaにメッセージを送信する方法と、その逆の方法を学びました。 Chainlink CCIPとその仕組みについてのより詳細なガイドについては、Chainlink CCIP Documentationを参照してください。